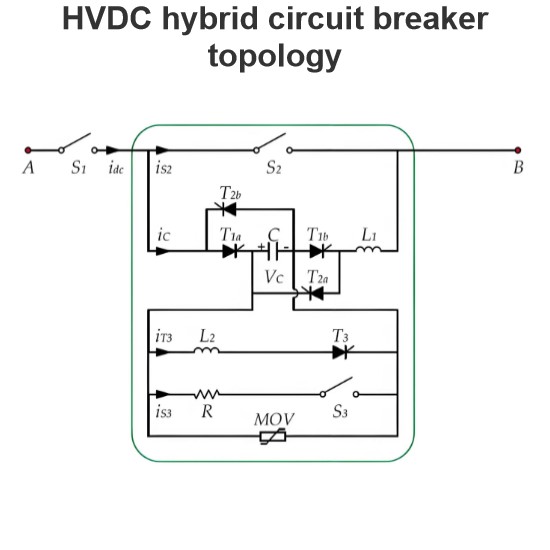
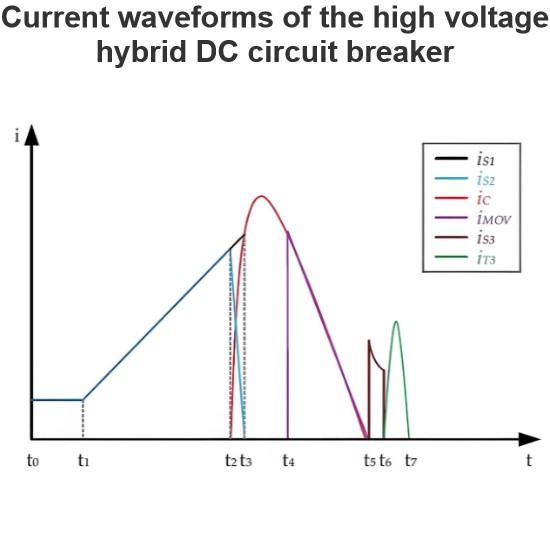
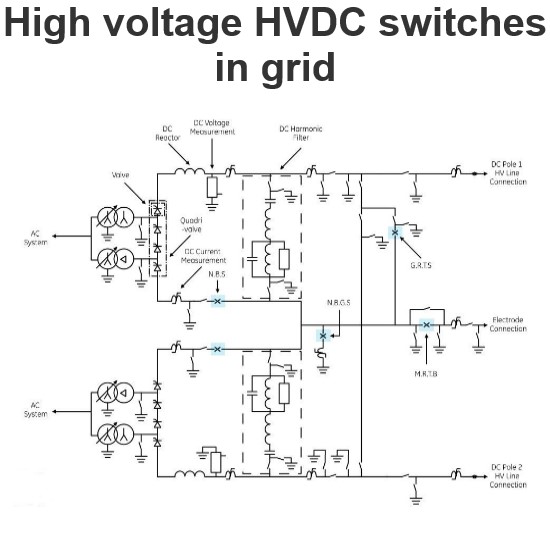
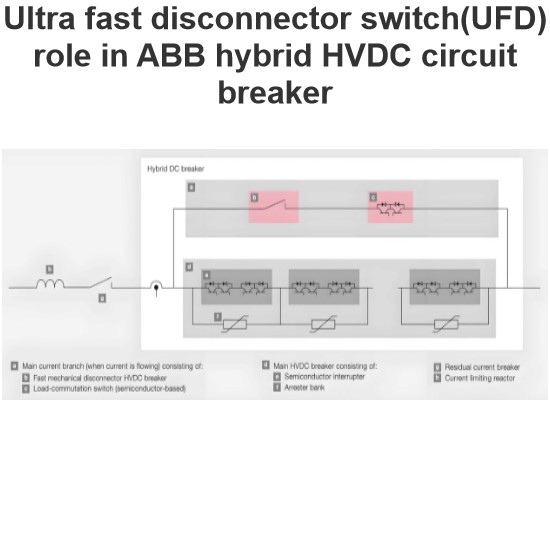
HVDC main challenges with protection and switching
DC Fault Current Has No Natural Zero Crossing
DC fault current does not have a natural zero crossing. This presents a problem because all mechanical DC circuit breakers rely on the natural zero crossing to interrupt the current arc.
Reduced Impedance in DC Lines
The impedance in DC lines is significantly lower. This means that the magnitude of fault currents during DC faults is much higher, and the voltage levels across the entire grid are lower.
Difficulty in Locating Faults
Due to the low impedance, it is more challenging to locate faults in a DC grid.
Semiconductor-Based Components in DC Grids
Semiconductor-based components in DC grids—such as Voltage Source Converters (VSCs), DC/DC converters, and DC circuit breakers—have very small thermal constants and very low rated overcurrent capacities.
High Cost of Semiconductor Components
Given the high cost of semiconductor components, there is a high requirement to clear DC faults within a very short time, making the rapid operation of protection systems crucial.
Voltage Drop and Converter Blocking
If the DC voltage drops to around 80-90% of its nominal value, the voltage source converter will be blocked.
Capacitive Impedance in DC Systems
Many DC systems involve cables with significant parallel capacitive impedance. Additionally, capacitors on the DC side of converters and DC filters introduce further capacitance.
Summary
The lack of a natural zero crossing in DC fault currents poses significant challenges for mechanical DC circuit breakers, which rely on this feature to interrupt arcs. The reduced impedance in DC lines leads to higher fault current magnitudes and lower grid voltage levels, making fault location more difficult. Semiconductor-based components in DC grids, such as VSCs, DC/DC converters, and DC circuit breakers, have limited thermal capacity and low overcurrent ratings, necessitating rapid fault clearance to avoid damage. Given the high cost of these components, it is essential for protection systems to operate quickly and efficiently. If the DC voltage drops to 80-90% of its nominal value, voltage source converters may be blocked. Furthermore, the presence of capacitive impedance in DC systems, including cables, converter capacitors, and DC filters, adds complexity to the system's behavior and fault management.