Current waveforms of the high voltage hybrid DC circuit breaker
Edwiin
11/28/2024
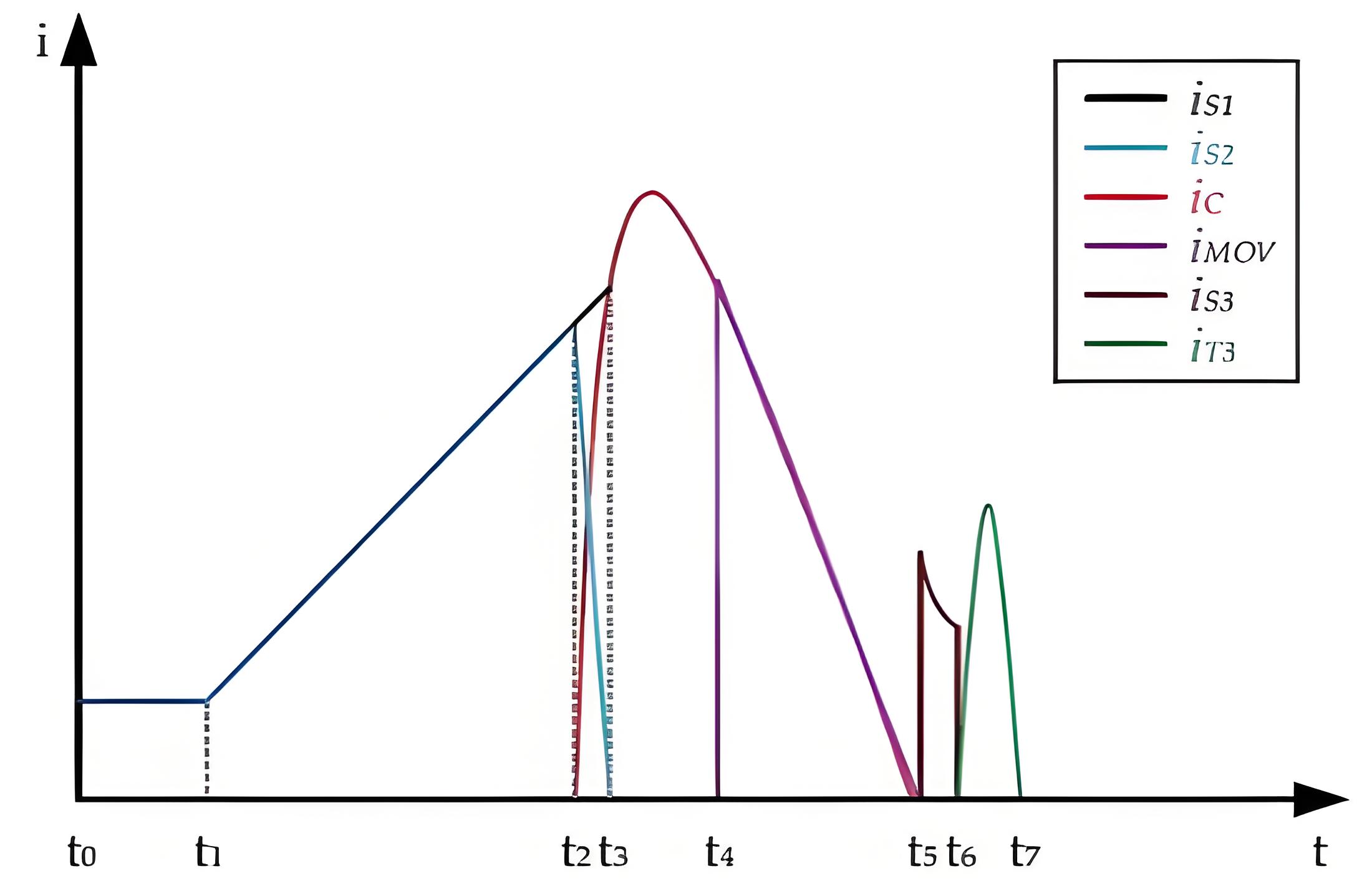
The operation of a hybrid circuit breaker is divided into eight intervals, corresponding to four operational modes. These intervals and modes are as follows:
- Normal Mode (t0~t2):During this interval, power is transmitted seamlessly between the two sides of the circuit breaker.
- Breaking Mode (t2~t5):This mode is used to interrupt fault currents. The circuit breaker rapidly disconnects the faulty section to prevent further damage.
- Discharge Mode (t5~t6):In this interval, the voltage across the capacitor is reduced to its rated value. This ensures that the capacitor is safely discharged and ready for the next operation.
- Reverse Mode (t6~t7):This mode is used to change the polarity of the capacitor. The polarity reversal prepares the capacitor for subsequent operations and ensures proper functionality.
Key Components and Their Functions
- IS1: Residual DC current breaker. This component is responsible for breaking any residual DC current that may remain after the main current has been interrupted.
- IS2, S3: Fast mechanical switches. These switches are designed to rapidly open and close the circuit, ensuring quick response times during fault conditions.
- IC: Auxiliary branch capacitor current. This current flows through the auxiliary branch capacitor, which helps in energy storage and release during the operation of the circuit breaker.
- I MOV: Metal oxide varistor (MOV) current. The MOV is used to protect the circuit from overvoltage conditions by clamping the voltage to a safe level.
- IT3: Thyristor current for reversing the polarity of the capacitor. This current flows through the thyristor to reverse the polarity of the capacitor during the reverse mode.
Topics
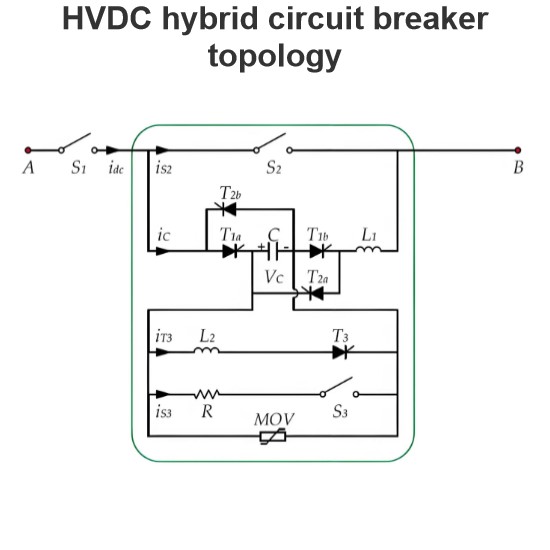
HVDC hybrid circuit breaker topology
A high-voltage DC hybrid circuit breaker is a sophisticated and efficient device designed to quickly and reliably interrupt fault currents in high-voltage DC circuits. The breaker primarily consists of three components: the main branch, the energy absorption branch, and the auxiliary branch.The main branch features a fast mechanical switch (S2), which rapidly disconnects the main circuit upon detection of a fault, preventing further flow of fault current. This rapid response capability is crucia
Edwiin
11/29/2024
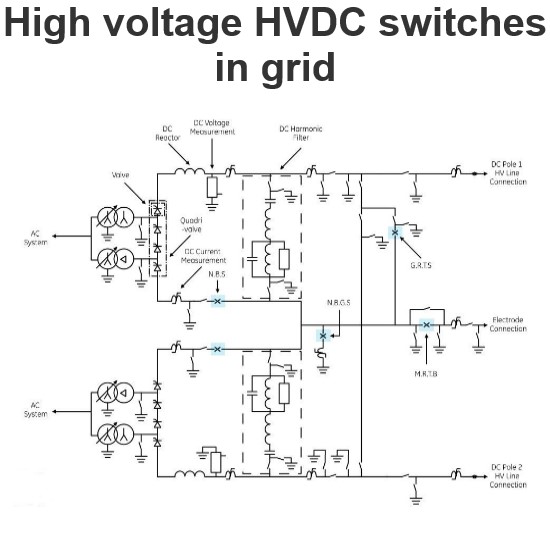
High voltage HVDC switches in grid
The Typical Single-Line Diagram of an HVDC Transmission Scheme Using DC Side SwitchgearThe typical single-line diagram shown in the figure illustrates an HVDC transmission scheme utilizing DC side switchgear. The following switches can be identified from the diagram:NBGS – Neutral Bus Grounding Switch:This switch is typically in the open position. When closed, it firmly connects the converter's neutral line to the station ground pad. If the converter can operate in bipolar mode with balanc
Edwiin
11/27/2024
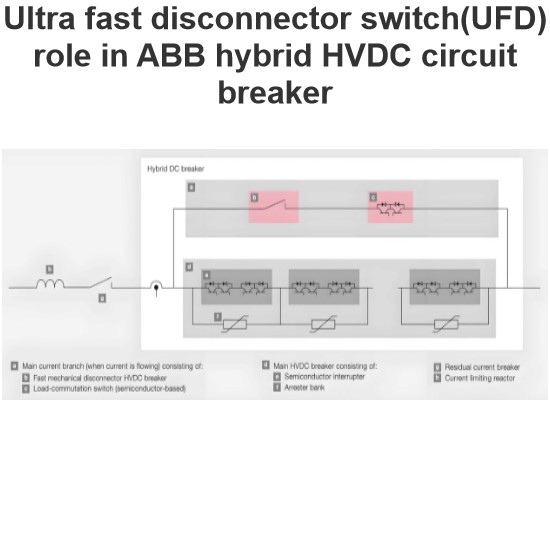
Ultra fast disconnector switch(UFD) role in ABB hybrid HVDC circuit breaker
Hybrid DC Circuit Breaker SolutionThe hybrid DC circuit breaker solution combines the excellent switching capabilities of power electronic devices (such as IGBTs) with the low-loss characteristics of mechanical switchgear. This design ensures that, unless interruption is needed, current does not flow through the semiconductors in the main circuit breaker. This is achieved through a mechanical bypass path, which consists of a super-fast disconnector (UFD) and an auxiliary commutation switch conne
Edwiin
11/26/2024

HVDC valve hall earthing switches
Valve Hall OverviewThe valve hall is a specialized building housing the valves of a High-Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) static inverter. These valves are typically composed of thyristors, and in older plants, they may consist of mercury-arc rectifiers. The valve hall is a crucial component of the HVDC system, ensuring its safe and efficient operation.Grounding SystemThe grounding of valve hall components is ensured by highly customized grounding switches. For this purpose, two different types of
Edwiin
11/25/2024









