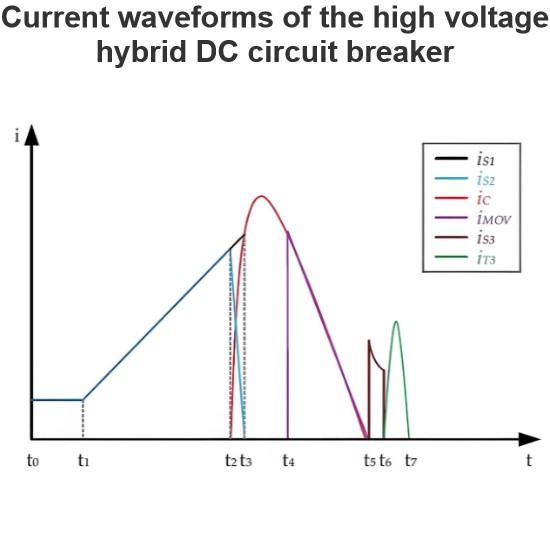
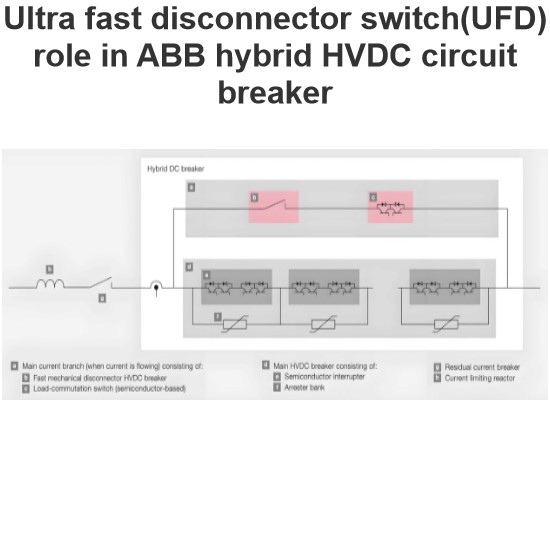
HVDC hybrid circuit breaker topology
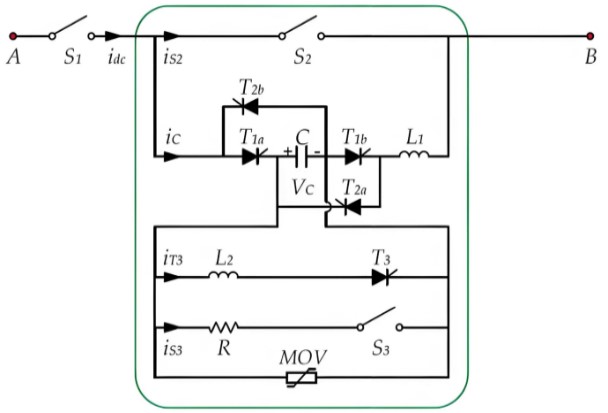
A high-voltage DC hybrid circuit breaker is a sophisticated and efficient device designed to quickly and reliably interrupt fault currents in high-voltage DC circuits. The breaker primarily consists of three components: the main branch, the energy absorption branch, and the auxiliary branch.
The main branch features a fast mechanical switch (S2), which rapidly disconnects the main circuit upon detection of a fault, preventing further flow of fault current. This rapid response capability is crucial for preventing system damage.
The auxiliary branch is more intricate, comprising a capacitor (C), a resistor (R), a fast mechanical switch (S3), and two inductors (L1 and L2). Additionally, it includes five thyristors (T1a, T1b, T2a, T2b, and T3) that play key roles in controlling the circuit. Thyristors T1a, T1b, T2a, and T2b are used to interrupt bidirectional fault currents, ensuring effective disconnection regardless of the direction of the current. Thyristor T3 is responsible for reversing the polarity of the capacitor voltage when necessary, providing essential conditions for subsequent operations.
The energy absorption branch consists of a series and parallel arrangement of metal oxide varistors (MOVs). These components effectively absorb and dissipate excess energy generated by fault currents, while also protecting the capacitor from overvoltage. This feature is particularly important for maintaining system stability and safety.
To achieve complete isolation of the entire DC circuit, a residual DC current circuit breaker (S1) is also included. When it is necessary to completely disconnect the circuit from the power source, this breaker comes into play, ensuring the safety of maintenance and repair work.
Notably, mechanical switches S1, S2, and S3 all utilize vacuum interrupter technology, which not only enhances the speed and efficiency of switching operations but also effectively extinguishes arcs, reducing electrical wear and extending the lifespan of the equipment. In summary, the high-voltage DC hybrid circuit breaker achieves safe and efficient management of high-voltage DC circuits through its meticulously designed multi-branch structure.