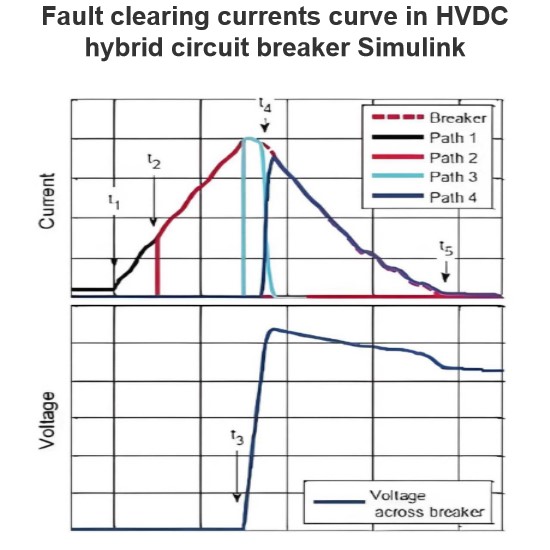
Synthetic current test for HVDC circuit breakers
Circuit Description
A 12-pulse rectifier is used as the current source to provide a DC test current, while a voltage oscillation circuit provides the recovery voltage after current switching. Auxiliary breakers and spark gaps are implemented in the circuit to connect these two sources to the test object at specific intervals. The specific implementation is as follows:
12-Pulse Rectifier: The rectifier is controlled to provide a DC test current to the test breaker (TB) through a smoothing reactor Ls and an auxiliary breaker (AB1) at a relatively low generator drive voltage.
Breaker Operation:
- Initial Stage: Both the auxiliary breaker AB1 and the test breaker TB are closed, allowing the DC test current to flow through AB1 and TB to the test object.
- Opening Stage: At a predetermined time, AB1 and TB are simultaneously opened, establishing a DC arc in the arc chutes of these breakers.
Spark Gap Triggering:
Spark Gap Action: The spark gap in the voltage circuit is ignited at the moment when the arc duration in TB reaches the expected value, providing the recovery voltage.
Current Bypass:
- Bypass Stage: The auxiliary breaker AB2 closes, bypassing the DC current, which switches from the AB1 – TB branch to the AB2 bypass branch.
- Clearing AB1: As the DC current switches from the AB1 – TB branch to the AB2 bypass branch, AB1 is cleared.
Recovery Voltage Application:
Injected Current: After AB1 is cleared, TB is only subjected to the injected current from the voltage circuit.
Clearing TB: When the injected current crosses zero, TB clears and is subjected to the transient recovery voltage and the subsequent DC voltage.
Rectifier Control:
Rectifier Blocking: The DC source rectifier is blocked upon receiving a stop signal, ceasing to provide the DC test current.
Diagram Explanation
- 12-Pulse Rectifier: Provides a DC test current to the test breaker (TB) through a smoothing reactor Ls and an auxiliary breaker AB1.
- Auxiliary Breaker AB1 and Test Breaker TB: Simultaneously open to establish a DC arc.
- Spark Gap: Ignites when the arc duration in TB reaches the expected value, providing the recovery voltage.
- Auxiliary Breaker AB2: Closes to bypass the DC current, clearing AB1.
- Test Breaker TB: Clears when the injected current crosses zero, and is subjected to the transient recovery voltage and the subsequent DC voltage.
- Rectifier: Is blocked upon receiving a stop signal, ceasing to provide the DC test current.
By following these steps, the circuit effectively tests the performance of the breaker under DC conditions, particularly during current switching and recovery voltage application.