What is the method used to maintain a constant voltage in a voltage source?
Methods for Maintaining Constant Voltage in a Voltage SourceMaintaining a constant voltage in a voltage source is achieved through the use of voltage regulators. Voltage regulators ensure that the output voltage remains stable despite variations in load, input voltage fluctuations, or environmental conditions. Below are several common methods for maintaining a constant voltage and their working principles:1. Linear RegulatorWorking Principle: A linear regulator adjusts its internal transistor's
Encyclopedia
11/30/2024
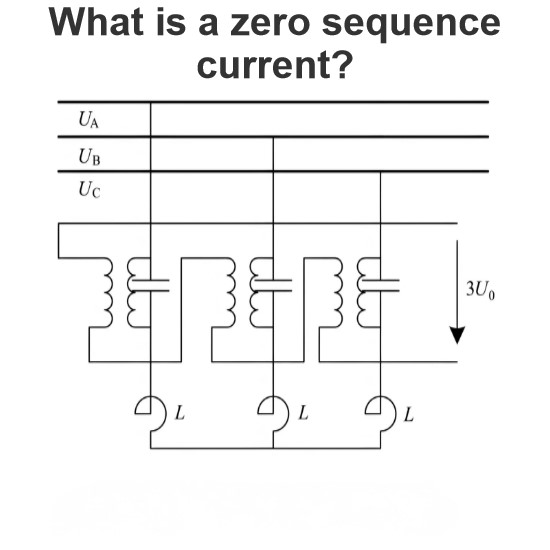
What is a zero sequence current?
Zero sequence current (Zero Sequence Current) is a special current component in a three-phase power system. It is one of the symmetrical components along with positive sequence current (Positive Sequence Current) and negative sequence current (Negative Sequence Current). The presence of zero sequence current indicates an imbalance or fault condition in the system. Below is a detailed explanation of the concept of zero sequence current and its characteristics:Definition of Zero Sequence CurrentIn
Encyclopedia
11/28/2024
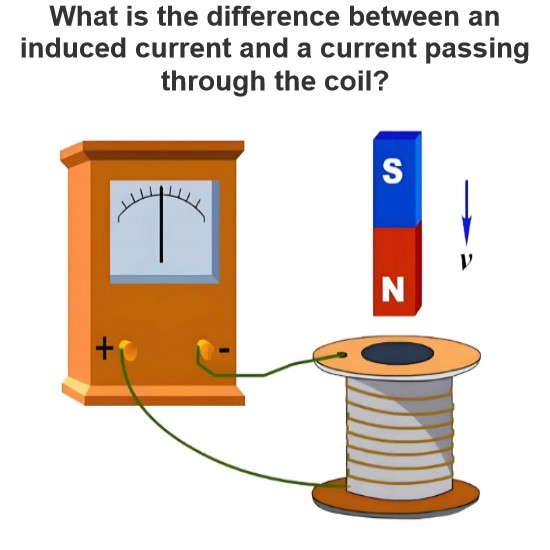
What is the difference between an induced current and a current passing through the coil?
Induced current and current through a coil are two different concepts, each with distinct physical principles and applications. Below is a detailed explanation of the differences between these two types of currents:1. Induced CurrentDefinition:Induced current is the current generated in a conductor due to the electromagnetic induction effect caused by a changing magnetic field. According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, when the magnetic flux through a closed loop changes, an elect
Encyclopedia
11/28/2024

What is the difference between a lightning impulse current and an impulse discharge current?
Lightning surge current and impulse discharge current are two different electrical phenomena, each with distinct characteristics, sources, and applications. Below is a detailed explanation of the differences between these two types of currents:Lightning Surge CurrentDefinition:Lightning surge current refers to the instantaneous large current caused by lightning. When lightning strikes the ground or a building, it generates a massive current pulse, which is the lightning surge current.Characteris
Encyclopedia
11/27/2024

How does a change in primary resistance affect an ideal transformer?
How Does the Change in Primary Resistance Affect an Ideal Transformer?The change in primary resistance has significant implications for the performance of an ideal transformer, especially in practical applications. While an ideal transformer assumes no losses, real-world transformers have some resistance in both the primary and secondary windings, which can affect performance. Below is a detailed explanation of how changes in primary resistance impact an ideal transformer:Assumptions of an Ideal
Encyclopedia
11/27/2024

What is gap power?
Air-gap power is an important concept in electromagnetic devices, particularly in the analysis and design of these devices. It refers to the electromagnetic power transmitted through the air gap. Below is a detailed explanation of the concept of air-gap power and its applications in different devices.Detailed ExplanationDefinition:Air-gap power is the electromagnetic power transmitted through the air gap, which is the energy transferred from the rotor (or primary side) to the stator (or secondar
Encyclopedia
11/27/2024
What is the difference between aluminum and silicon in terms of their use as semiconductors?
Differences Between Aluminum and Silicon in Semiconductor ApplicationsAluminum and silicon have different applications in semiconductor technology, primarily due to their distinct physical and chemical properties and their specific roles in device fabrication. Here are the main differences between aluminum and silicon in semiconductor applications:SiliconPhysical Properties: Crystal Structure: Silicon typically exists in a single-crystal form, with the most common crystal structure being the dia
Encyclopedia
11/27/2024
How does lack of frequency stability affect a microgrid?
Insufficient frequency stability can have multifaceted impacts on microgrids, including but not limited to the following aspects:1. Equipment Damage Motors and Generators: Frequency fluctuations can cause instability in the speed of motors and generators. Running these devices at non-rated frequencies for extended periods can accelerate wear and even lead to equipment failure. Electronic Devices: Many electronic devices are highly sensitive to frequency changes. Frequency instability can cause t
Encyclopedia
11/26/2024

What is the difference between energy forms that can be easily transformed and those that cannot?
Differences Between Easily Convertible and Hard-to-Convert Forms of EnergyThe ease of converting different forms of energy varies due to the nature of the physical and chemical processes involved, as well as the efficiency and reversibility of these processes. Below is a detailed explanation of the differences between easily convertible and hard-to-convert forms of energy, along with the reasons behind these differences.Easily Convertible Forms of Energy1. Electrical Energy and Mechanical Energy
Encyclopedia
11/25/2024

What causes batteries with the same charge to have different voltages?
Why Do Batteries with the Same Capacity Have Different Voltages?There are several reasons why batteries with the same capacity can have different voltages. These reasons can be explained from multiple perspectives:1. Different Chemical CompositionDifferent types of batteries use different chemical compositions, which determine their voltage. For example: Alkaline Batteries (such as AA and AAA) typically provide 1.5V. Lithium-ion Batteries (used in mobile phones and laptops) typically provide 3.7
Encyclopedia
11/22/2024









