What is a zero sequence current?
Zero sequence current (Zero Sequence Current) is a special current component in a three-phase power system. It is one of the symmetrical components along with positive sequence current (Positive Sequence Current) and negative sequence current (Negative Sequence Current). The presence of zero sequence current indicates an imbalance or fault condition in the system. Below is a detailed explanation of the concept of zero sequence current and its characteristics:
Definition of Zero Sequence Current
In a three-phase power system, zero sequence current refers to the current component that exists when the vector sum of the three phase currents is not zero. Specifically, the zero sequence current is the average of the three phase currents, given by:
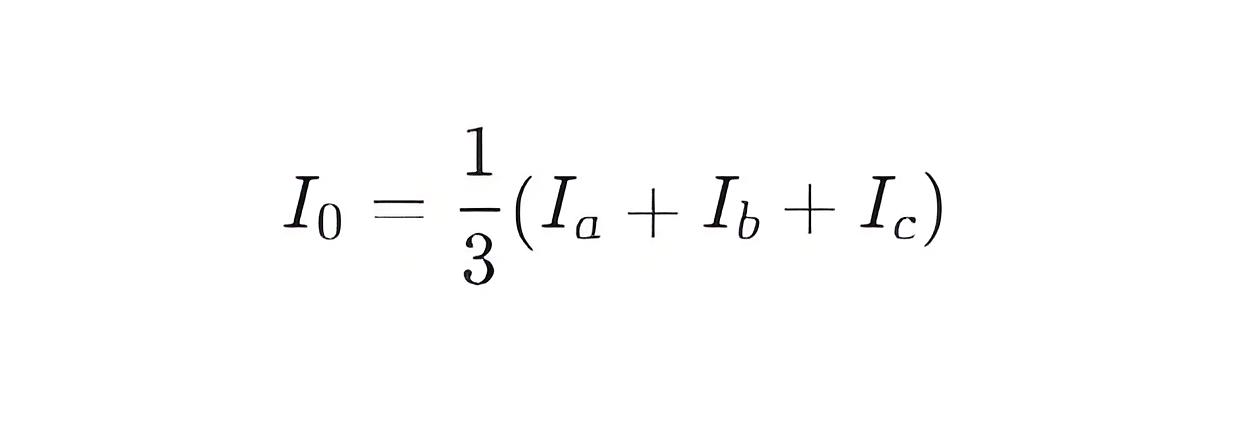
where Ia, Ib , and Ic are the currents in phases A, B, and C, respectively.
Characteristics of Zero Sequence Current
Symmetry:
Zero sequence current is symmetrical in a three-phase system, meaning the magnitudes of the zero sequence currents in the three phases are equal, and their phases are identical.
Phase Relationship:The phase relationship of zero sequence current is the same for all three phases, i.e., the phase difference between the zero sequence currents in the three phases is 0°.
Existence Conditions:Zero sequence current only appears when there is an imbalance or fault in the three-phase system. For example, it occurs in single-phase ground faults, unbalanced three-phase loads, etc.
Applications of Zero Sequence Current
Fault Detection:The presence of zero sequence current can be used to detect single-phase ground faults in a three-phase system. When a single-phase ground fault occurs, the zero sequence current significantly increases, allowing for quick fault location by monitoring the zero sequence current.
Protection Devices:Many relay protection devices are equipped with zero sequence current protection functions to detect and protect the system from single-phase ground faults. For example, zero sequence current transformers (ZSCT) are used to measure zero sequence current.
System Analysis:In power system analysis, zero sequence current is an important parameter for studying system imbalances and faults. By analyzing zero sequence current, the stability and safety of the system can be assessed.
Causes of Zero Sequence Current
Single-Phase Ground Fault:When a ground fault occurs in one phase of a three-phase system, the zero sequence current significantly increases.
Unbalanced Three-Phase Load:If the three-phase load distribution is uneven, it can also produce zero sequence current.
Neutral Line Disconnection:A disconnection in the neutral line can prevent the zero sequence current from returning, resulting in the formation of zero sequence current in the system.
Summary
Zero sequence current is a special current component in a three-phase power system that only appears when there is an imbalance or fault. It is characterized by symmetry and identical phase relationships, and is commonly used in fault detection and protection devices. Understanding the concept and characteristics of zero sequence current helps in better analyzing and maintaining the stability and safety of power systems.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













