Description:
Medium Voltage single-phase circuit breaker with magnetic actuator, designed for railway power supply up to 27.5 kV, 2500 A, 31.5 kA
With a rated voltage of 31.5kV, it can effectively handle the electrical loads in railway applications. Equipped with brushless servomotors (one per phase) and double encoders, it enables precise control over switching operations. Each phase also has an electronic controller that communicates hierarchically, ensuring coordinated and reliable system operation. This breaker is designed to safeguard the railway electrical network from overloads and short - circuits, ensuring stable and safe power supply for trains and related facilities.
The GSR+ II range is the first commercially available single-phase vacuum circuit breaker for railway power supply applications to feature a vacuum interrupter, magnetic actuator and electronic controller. This solution is robust, reliable and essentially maintenance-free.
Feature:
- High Voltage Adaptability and Stable Insulation: With a rated voltage of 31.5kV, it is suitable for high-voltage environments in railway power systems. The three-pole structure encapsulated in epoxy resin, with built-in vacuum interrupters, offers excellent insulation performance and can withstand harsh environmental factors such as moisture and dust.
- Precision Control Operation: Each phase is equipped with a brushless servo motor and dual encoders to achieve high-precision control of switching operations. It can quickly and stably respond to the on/off demands of the power system, ensuring the timeliness of power supply.
- Intelligent Collaborative Operation: The electronic controllers of each phase have hierarchical communication functions, enabling mutual collaboration and linkage with the main control unit. This ensures that the circuit breaker can coordinate consistently and operate stably and reliably under complex working conditions.
- Efficient Fault Protection: It has the ability to quickly cut off overloads, short circuits, and other faults, effectively protecting the railway electrical network. This avoids the impact of power faults on train operation safety and ensures the stability of the railway power supply system.
- Compact Indoor Design: Optimized for indoor installation, its compact structure saves space, adapts to the limited installation environments in railway substations and control rooms, and facilitates integration and maintenance.
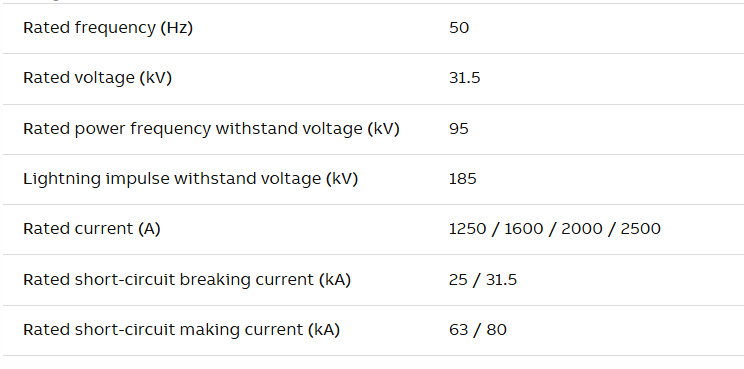
Technical Characteristics: