Dynamics of Electrical Drives
Dynamics of Electrical Drives Definition
The dynamics of electrical drives explain how motors and loads interact, especially when their speeds differ.
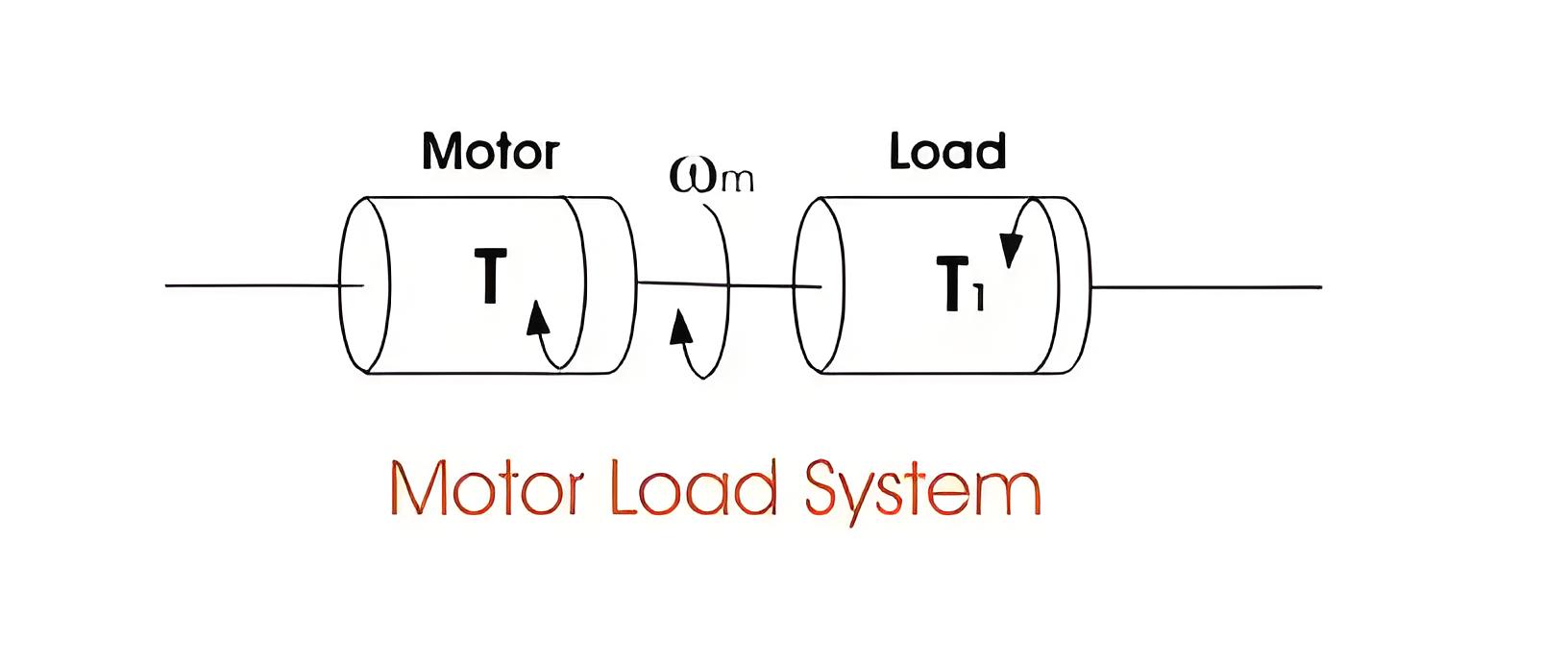
Key Components
Important components include the polar moment of inertia (J), angular velocity (Wm), motor torque (T), and load torque (T1).
Fundamental Torque Equation
This equation shows that motor torque balances load torque and dynamic torque, which is crucial during changes in motion.
J = Polar moment of inertia of motor load
Wm = Instantaneous angular velocity
T = Instantaneous value of developed motor torque
T1 = Instantaneous value of load torque referred to motor shaft
Now, from the fundamental torque equation –For drives with constant inertia,
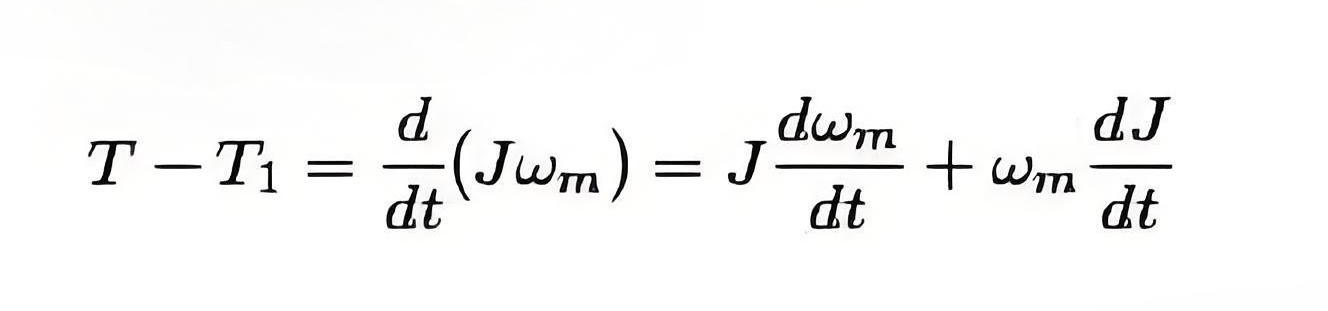
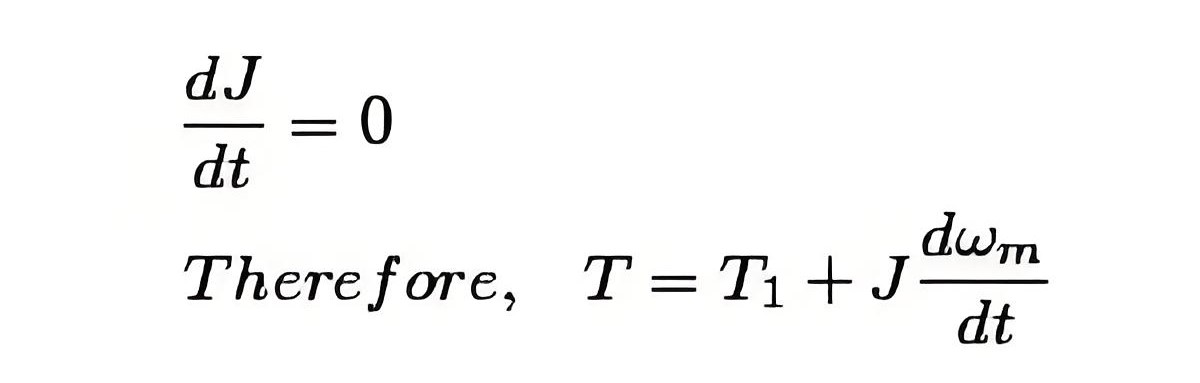
Dynamic Torque
Dynamic torque, J(dωm/dt), appears only during transient operations like starting or stopping, indicating acceleration or deceleration.
Impact on Motion
By analyzing dynamic torque, we can determine if the motor is accelerating or decelerating, which is essential for efficient drive operation.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













