What is Speed Regulation of DC Motor?
What is Speed Regulation of DC Motor?
Speed regulation definition
The speed regulation of a DC motor is a change in speed from no-load to full load, expressed as a fraction or percentage of full load speed.
Good speed regulation
A motor with good speed regulation has the smallest difference between no-load and full-load speeds.
Motor type
Permanent magnet dc motor
Dc shunt motor
Dc series motor
Compound dc motor
Velocity and electromotive force relation
The speed of a DC motor is proportional to the electromotive force (emf) and inversely proportional to the magnetic flux per pole.
Here,
N = speed of rotation in rpm.
P = number of poles.
A = number of parallel paths.
Z = total no. conductors in armature.
Therefore, the speed of a DC motor is directly proportional to the electromotive force (emf) and inversely proportional to the flux per pole (φ).
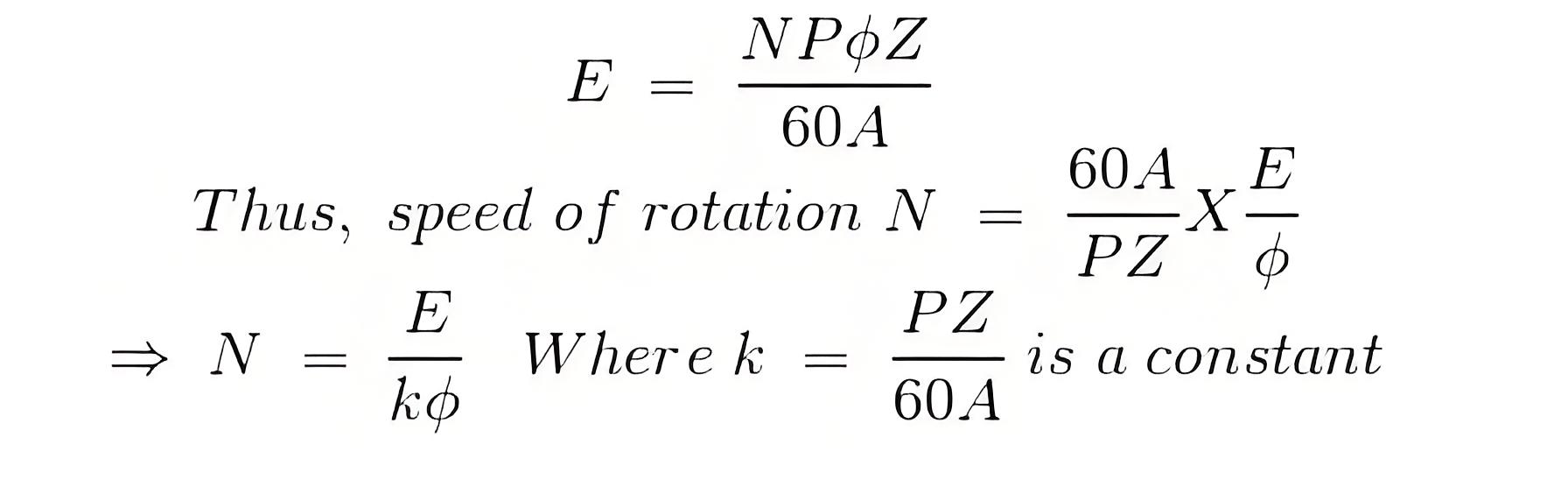
Speed regulation formula
Speed regulation is calculated using a specific formula that takes into account the no-load and full-load speeds.
Speed regulation is defined as the change in speed from no load to full load, expressed as a fraction or percentage of full-load speed.
Therefore, as per definition per unit (p.u) speed regulation of DC motor is given as,
Similarly, percentage (%) speed regulation is given as,
Where,
Therefore,
A motor that maintains nearly constant speed at all loads below full rated load has good speed regulation.
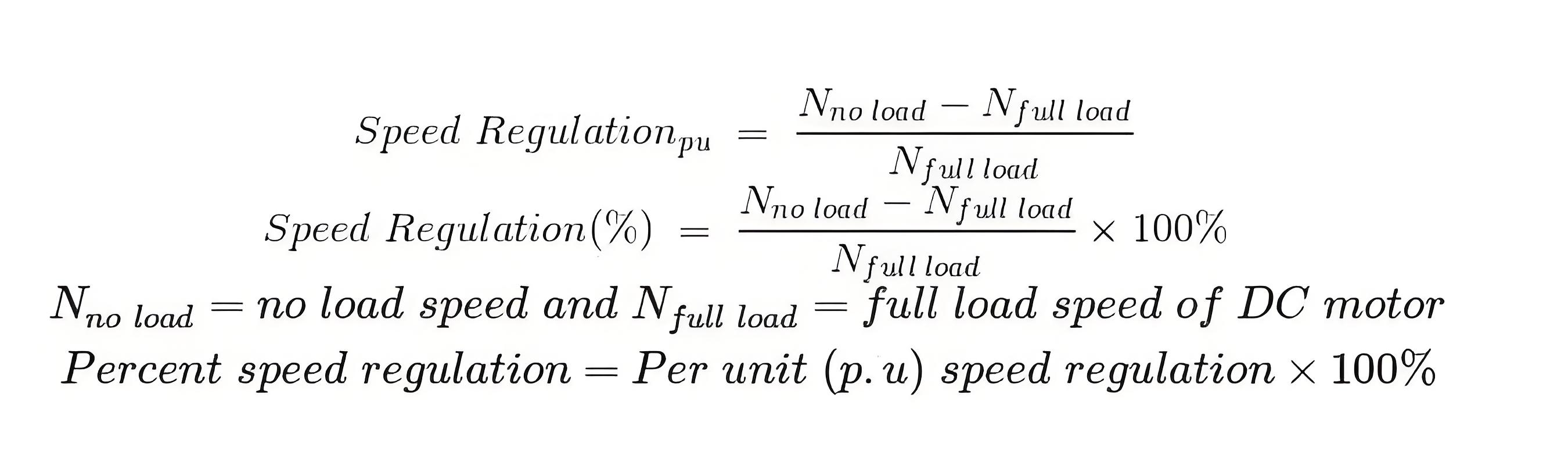
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.