Types of Braking in a DC Motor
Braking of DC Motor Definition
Electrical braking stops a DC motor by controlling voltage and current instead of using mechanical friction.
Regenerative Braking
It is a form of braking in which the kinetic energy of the motor is returned to the power supply system. This type of braking is possible when the driven load forces the motor to run at a speed higher than its no-load speed with a constant excitation.
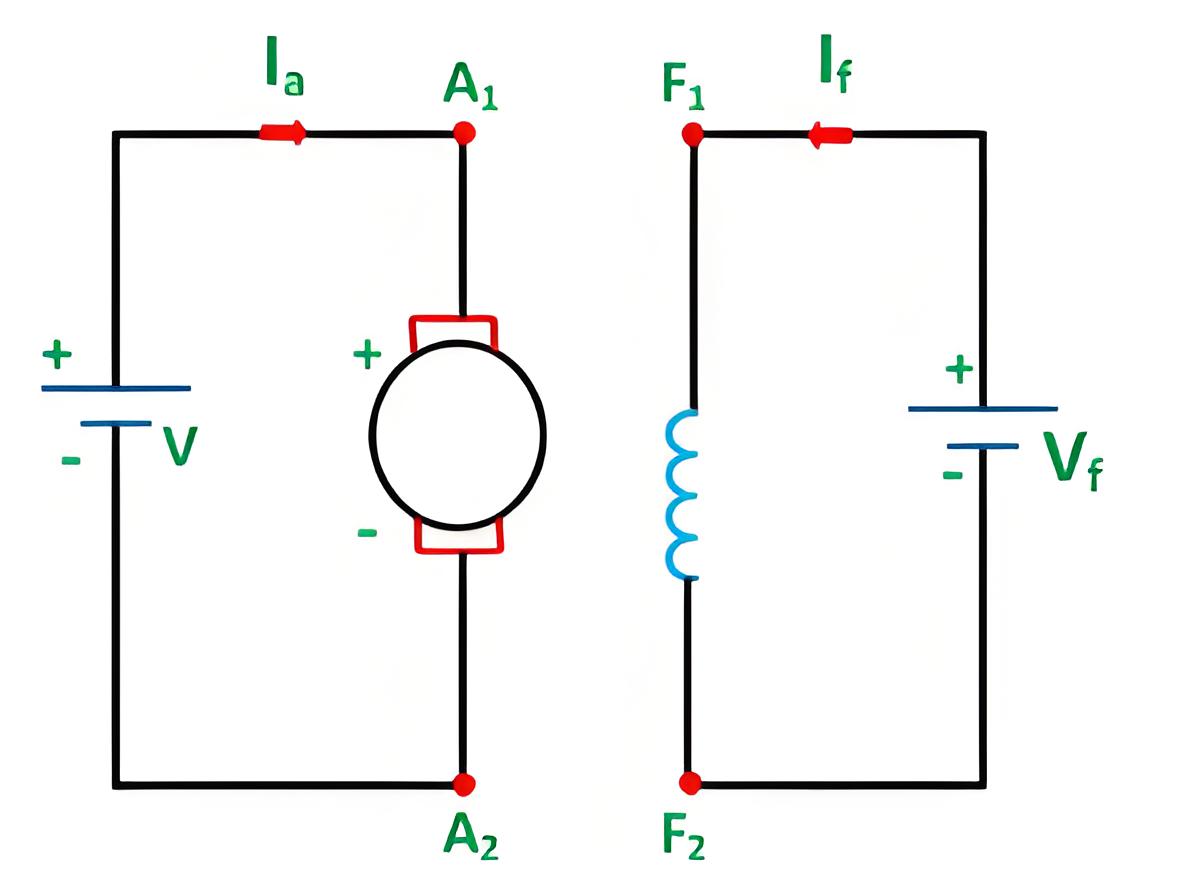
The motor back emf Eb is greater than the supply voltage V, which reverses the direction of the motor armature current. The motor begins to operate as an electric generator.
Interestingly, regenerative braking cannot stop a motor; it only controls its speed above the no-load speed when driving descending loads.
Dynamic Braking
It is also known as Rheostatic braking. In this type of braking, the DC motor is disconnected from the supply and a braking resistor Rb is immediately connected across the armature. The motor will now work as a generator and produces the braking torque.
During electric braking, the motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy of its rotating parts and connected load into electrical energy. This energy is then dissipated as heat in the braking resistor (Rb) and armature circuit resistance (Ra).
Dynamic Braking is an inefficient method of braking as all the generated energy is dissipated as heat in resistances.
Plugging
It is also known as reverse current braking. The armature terminals or supply polarity of a separately excited DC motor or shunt DC motor when running are reversed. Therefore, the supply voltage V and the induced voltage Eb i.e. back emf will act in the same direction. The effective voltage across the armature will be V + Eb which is almost twice the supply voltage.
Thus, the armature current is reversed and a high braking torque is produced. Plugging is very inefficient because it wastes both the power supplied by the load and the source in resistances.
It is used in elevators, printing press etc.These were the main three types of braking techniques preferred to stop a DC motor and used widely in industrial applications.
Industrial Applications
These braking techniques are used in industries like elevators and printing presses.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













