| Brand | RW Energy |
| Model NO. | 435 W- 460 W High-efficiency N-type TOPCON modules |
| Max. System Voltage | 1500V (IEC) |
| Max. Series Fuse Rating | 20A |
| Module Fire Performance | CLASS C |
| Max. power of the module | 435W |
| Max. efficiency of Module | 21.8% |
| Series | N-type TOPCon Technology |
Features
Module power up to 460 W Module efficiency up to 23.0 %.
Excellent anti-LeTID & anti-PID performance. Low power degradation, high energy yield.
Lower temperature coefficient (Pmax): -0.29%/°C, increases energy yield in hot climate.
Lower LCOE & system cost.
Standard
Tested up to ice ball of 35 mm diameter according to IEC 61215 standard.
Minimizes micro-crack impacts.
Heavy snow load up to 6000 Pa, wind load up to 4000 Pa*.
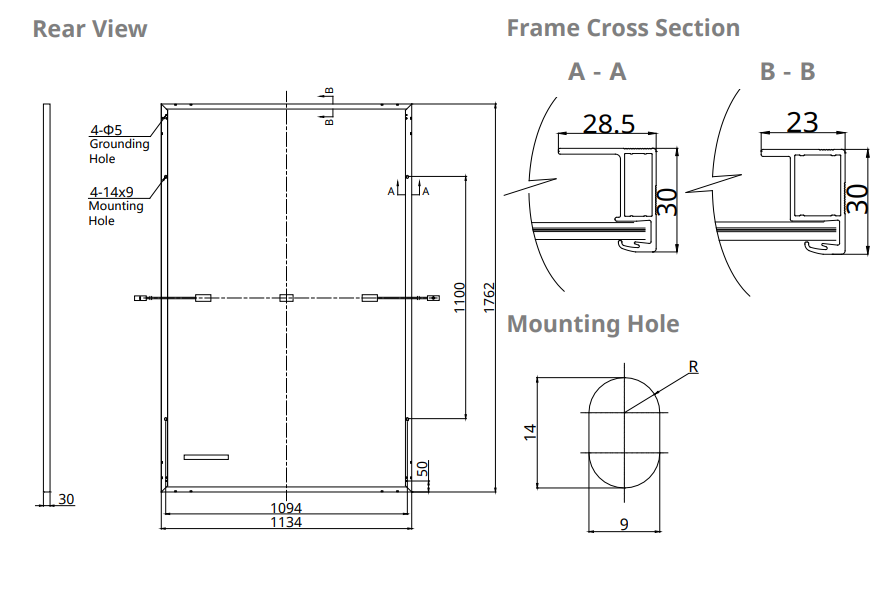
Engineering drawing(mm)
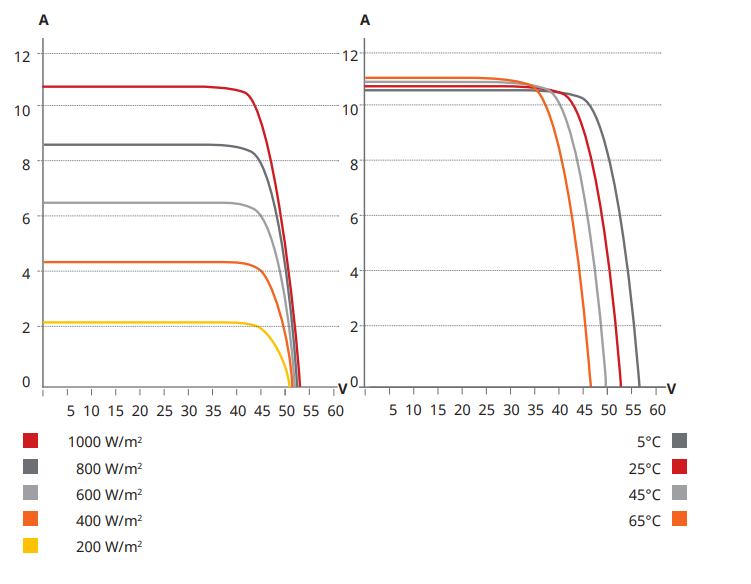
CS6.2-48TD-455/ I-V gurves
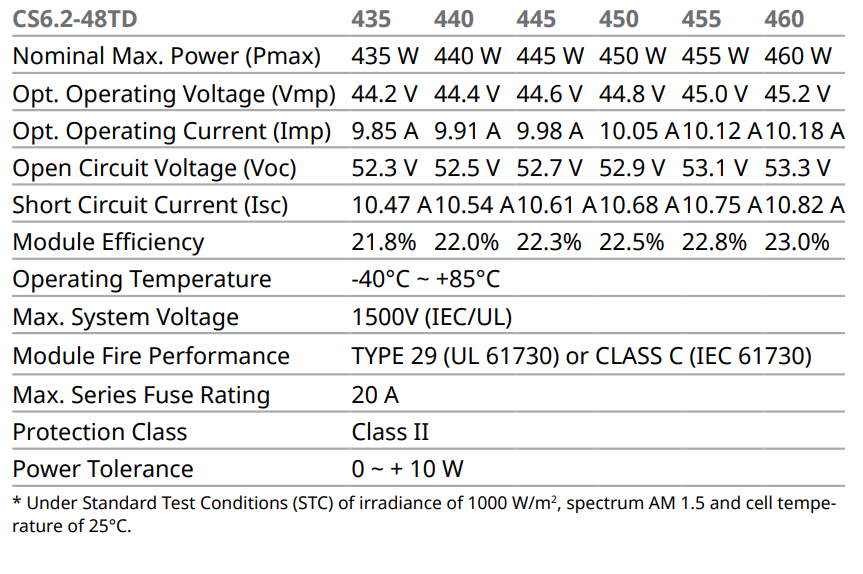
Electrical date/STC*
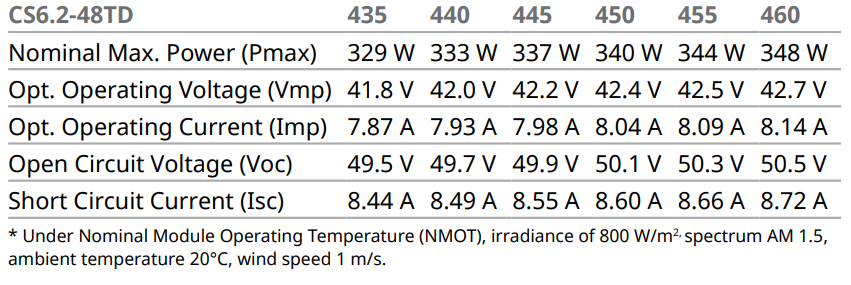
Electrical date/NMOT*
Mechanical charactheristics
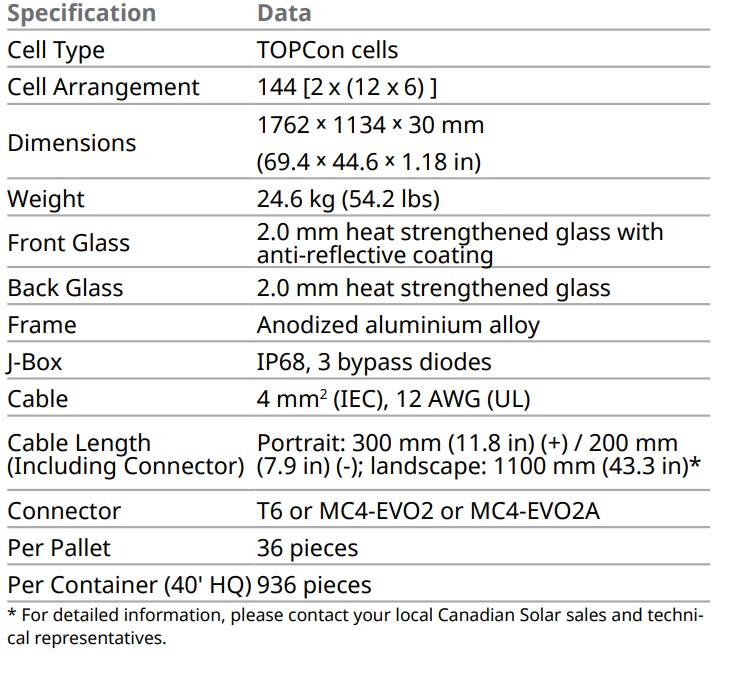
Temperature characteristics
What does PID mean in PV modules?
Definition of PID:
PID is a phenomenon of performance degradation caused by a high potential difference either inside or outside photovoltaic modules. When there is a high voltage difference between the positive and negative poles of the modules (usually due to improper installation or system configuration issues), and the surrounding environmental humidity is relatively high, this high voltage difference will lead to the migration of electrolytes, thereby causing a decline in battery performance.
Manifestations of PID:
PID will result in a reduction in the output power of photovoltaic modules, which is manifested as follows:
Decrease in Output Voltage: PID mainly affects the open-circuit voltage (Voc) of photovoltaic modules, causing it to decrease.
Decrease in Efficiency: Due to the decrease in the open-circuit voltage, the overall efficiency of the photovoltaic modules will also decline accordingly.






