| Brand | Wone |
| Model NO. | 25-36kW Three Phase 3 MPPTs C&I Grid-tied Inverters |
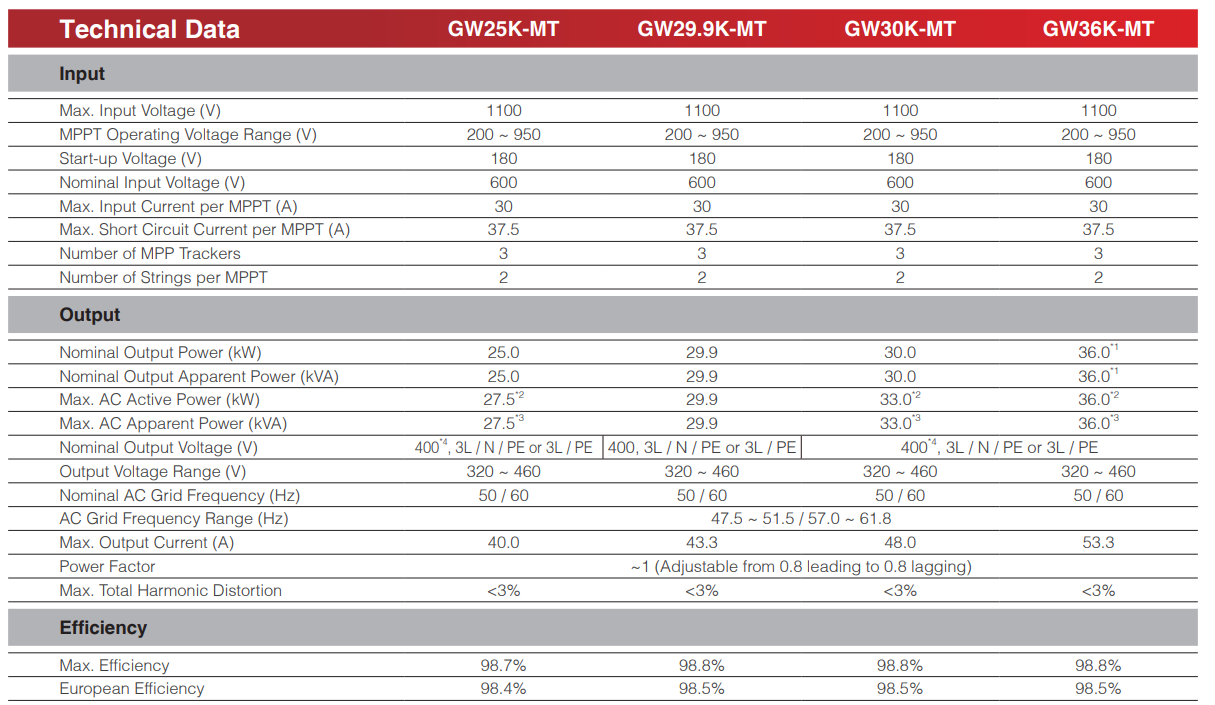
| Max.Input Voltage | 1100V |
| Max. Input Current per MPPT | 30A |
| Number of MPP trackers | 3 |
| Nominal Output Voltage | 400V |
| Max.Efficiency | 98.8% |
| Series | C&I Grid-tied Inverters |
Description:
The three-phase inverter is ideal for commercial rooftop system solutions. The SMT series achieves maximum efficiency of 98.8% and features unique design highlights, including solid capacitors, fuse-free design, and optional Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) function. These new features ensure a longer lifespan and a higher safety level of operation, allowing for an improved user experience. With a compact design and weight of just 40 kg, the SMT series is more convenient to install. With a maximum DC input voltage of 1100V, a wider MPPT range for complex rooftops, and a start-up voltage of 180V, the SMT series guarantees an earlier generation of power and a longer working time to maximize long-term returns and profitability in safe operating conditions.
Feature:
Smart Control & Monitoring
String level monitoring.
Dynamic power export limit.
Optimal Generation for Higher Return
98.8% Max. Efficiency.
Up to 130% DC input oversizing & 110%.
AC output overloading
Superb Safety & Reliability.
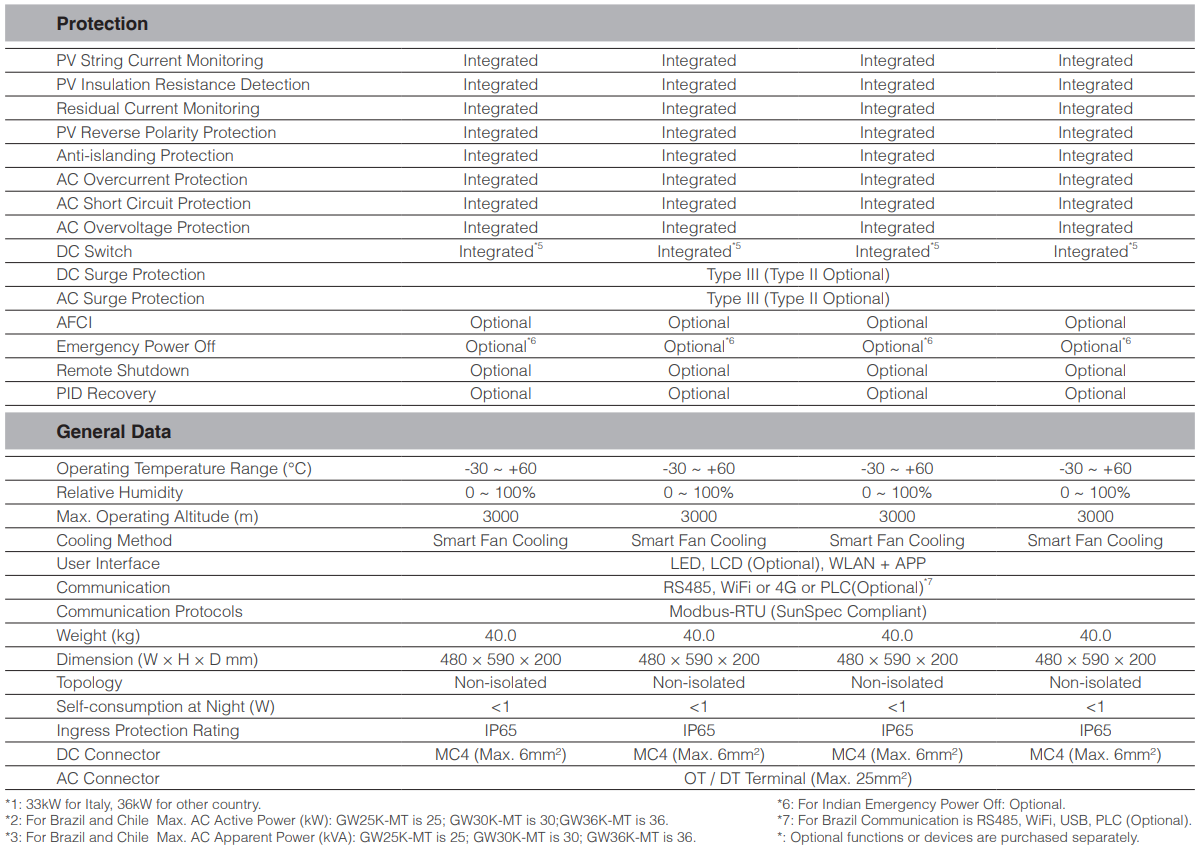
Optional Arc-fault circuit interrupter.
Optional Type II SPD on both DC and AC.
Friendly & Thoughtful Design
40kg compact design.
Power line communication optional.
System Parameters:
What is G&I grid-tied inverter?
Definition:
A grid-connected inverter is a device that converts direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) and ensures that the output AC matches the frequency, phase, and voltage amplitude of the power grid. In this way, the converted electrical energy can be directly integrated into the power grid for use by households, enterprises, and the power grid itself.
Working Principle:
Input Circuit: The grid-connected inverter receives direct current from solar photovoltaic panels, wind turbines, or other DC power sources.
DC/AC Conversion: Through internal power electronic converters (such as inverter bridges), the direct current is converted into alternating current.
Synchronization Control: Through advanced control algorithms (such as Phase-Locked Loop, PLL), it ensures that the output alternating current is synchronized with the frequency, phase, and voltage amplitude of the power grid.
Output Circuit: The converted alternating current is fed to the power grid, and it is ensured that the output of the inverter complies with the power quality of the power grid.






