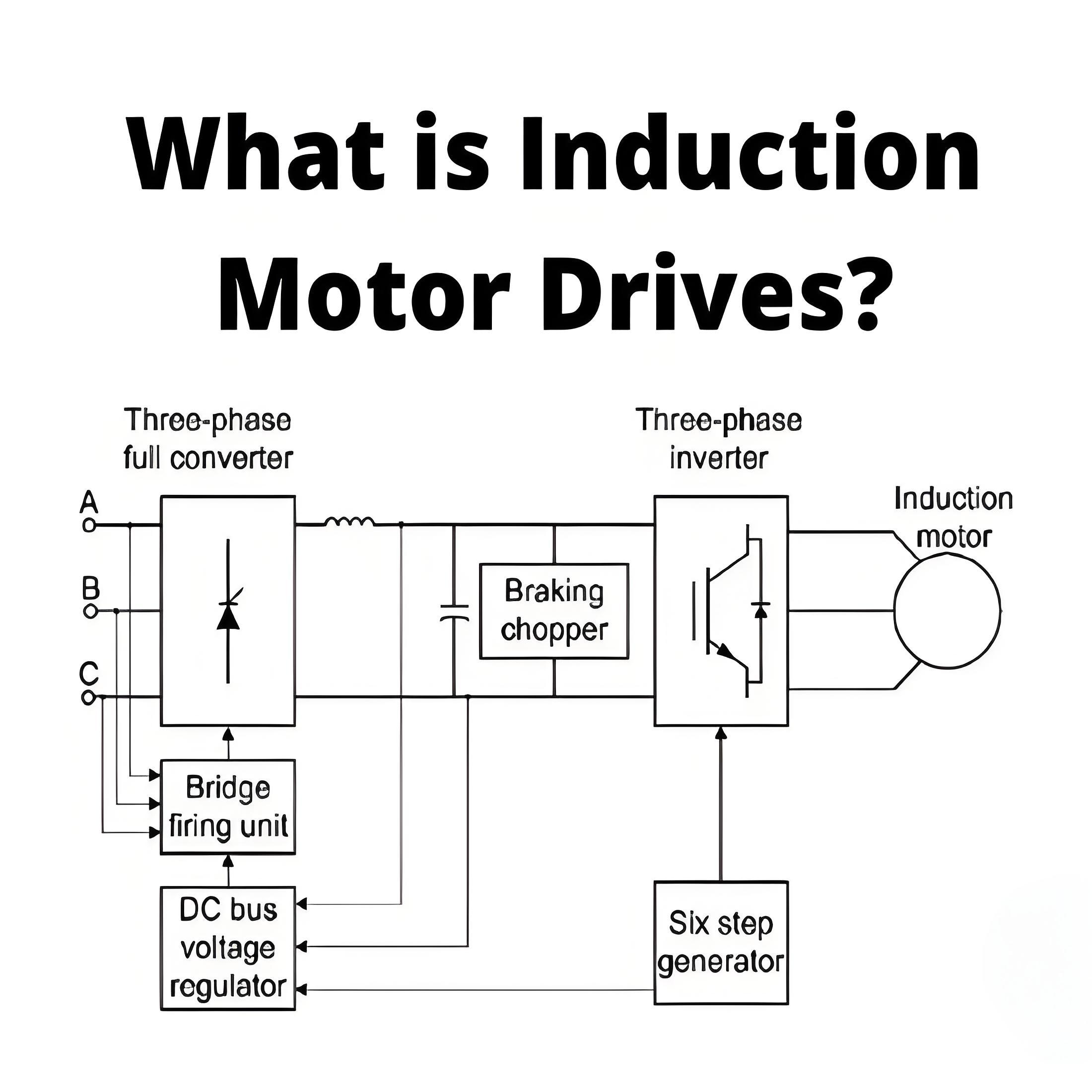
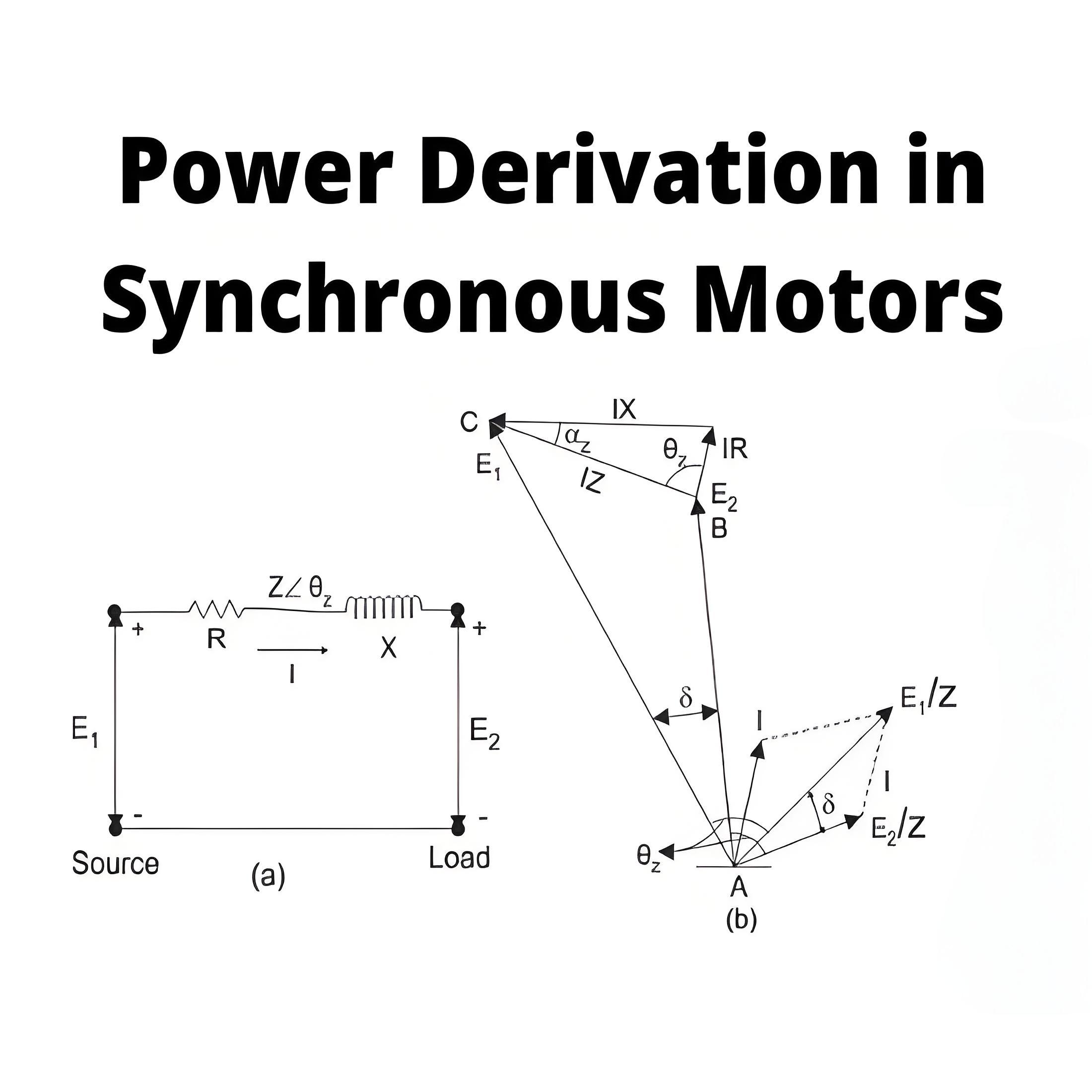
Torque Equation of Three Phase Induction Motor
Torque equation definition
The torque in the three-phase induction motor is calculated based on rotor current, magnetic flux and power factor.
Rotor current
The rotor current is critical for generating torque and is affected by the induced electromotive force and impedance of the rotor.
Starting torque
Starting torque is the torque generated when the induction motor is started. We know that at the beginning of the rotor speed, N is zero.
Therefore, just by placing the value of s=1 in the torque equation of the three-phase induction motor, it is easy to obtain the starting torque equation.
Starting torque is also called rest torque.
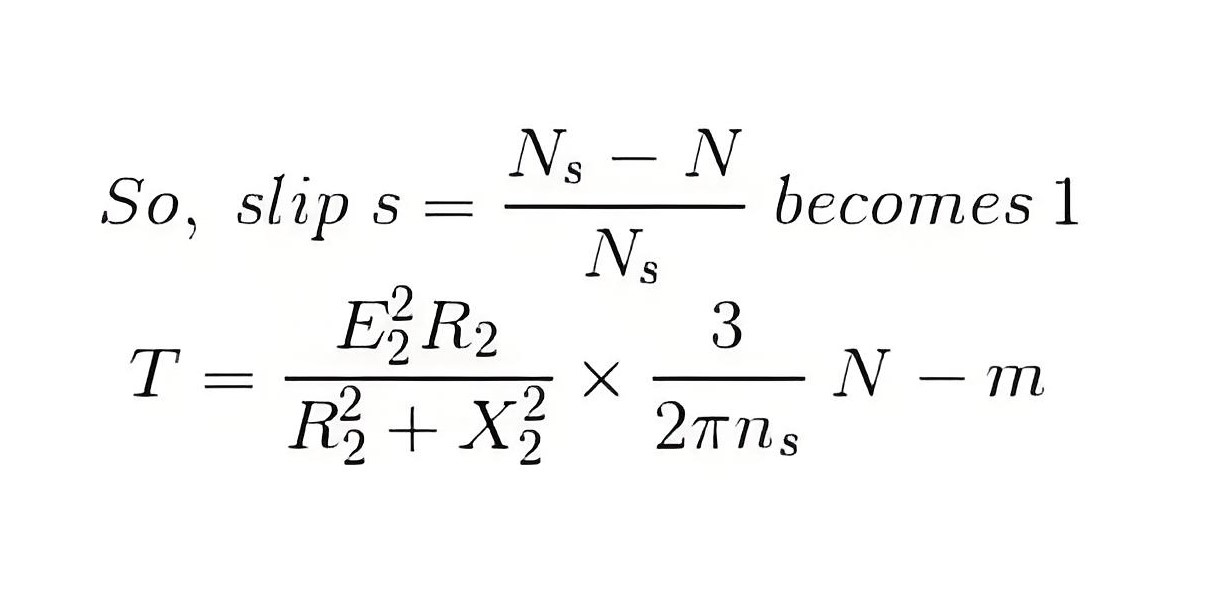
Maximum torque condition
When the slip is equal to the ratio of rotor resistance to rotor reactance, the maximum torque is reached, which highlights the importance of rotor design.
Slip and speed
Slip values are critical for determining the speed and efficiency of a motor, and lower slip values usually lead to higher efficiency.
The torque equation is
When slip s = R, torque will be maximum
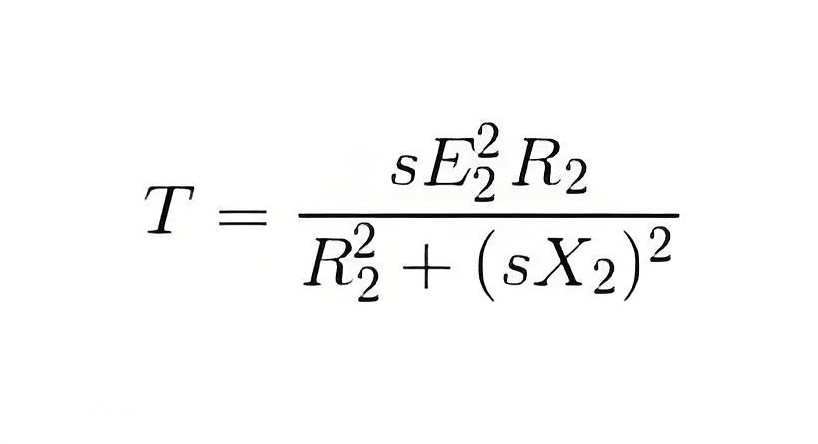
By plugging in this slip from the equation above, we get the maximum torque,
Because in order to increase the starting torque, additional resistance should be added to the rotor circuit at the time of starting and gradually cut off as the motor accelerates.
Conclusion
From the above equation, we can conclude that:
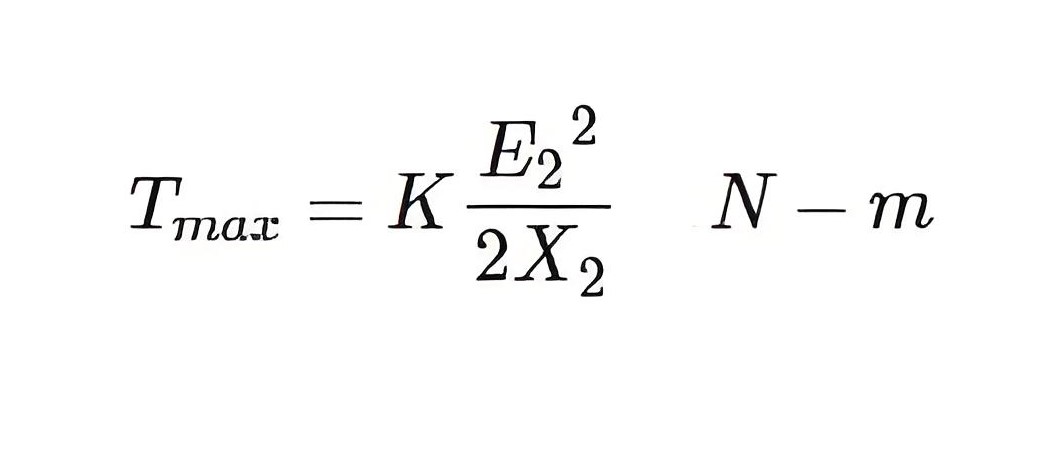
The maximum torque is proportional to the square of the rotor induced electromotive force at rest.
The maximum torque is inversely proportional to the rotor reactance.
It is worth noting that the maximum torque does not depend on the rotor resistance.
The slip where the maximum torque occurs depends on the rotor resistance R2. Therefore, by varying the rotor resistance, the maximum torque can be obtained with any desired slip.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.