Construction of Three Phase Induction Motor
Three phase induction motor definition
The three-phase induction motor is defined as a type of electric motor that is most widely used in industry due to its efficient power delivery and simple structure.
Main component
The motor consists of a stationary component called a stator and a rotating component called a rotor.
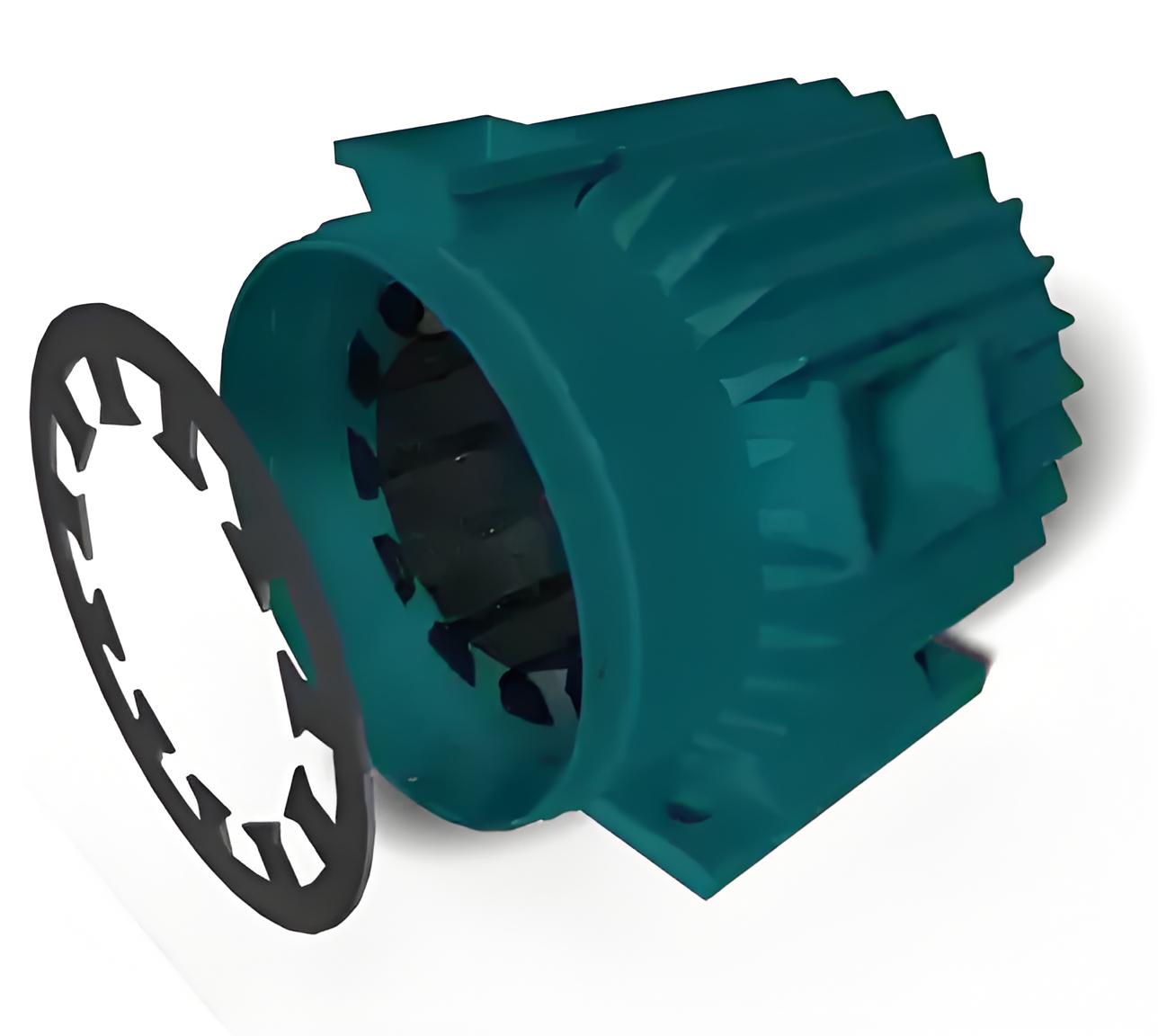
Three-phase asynchronous motor stator
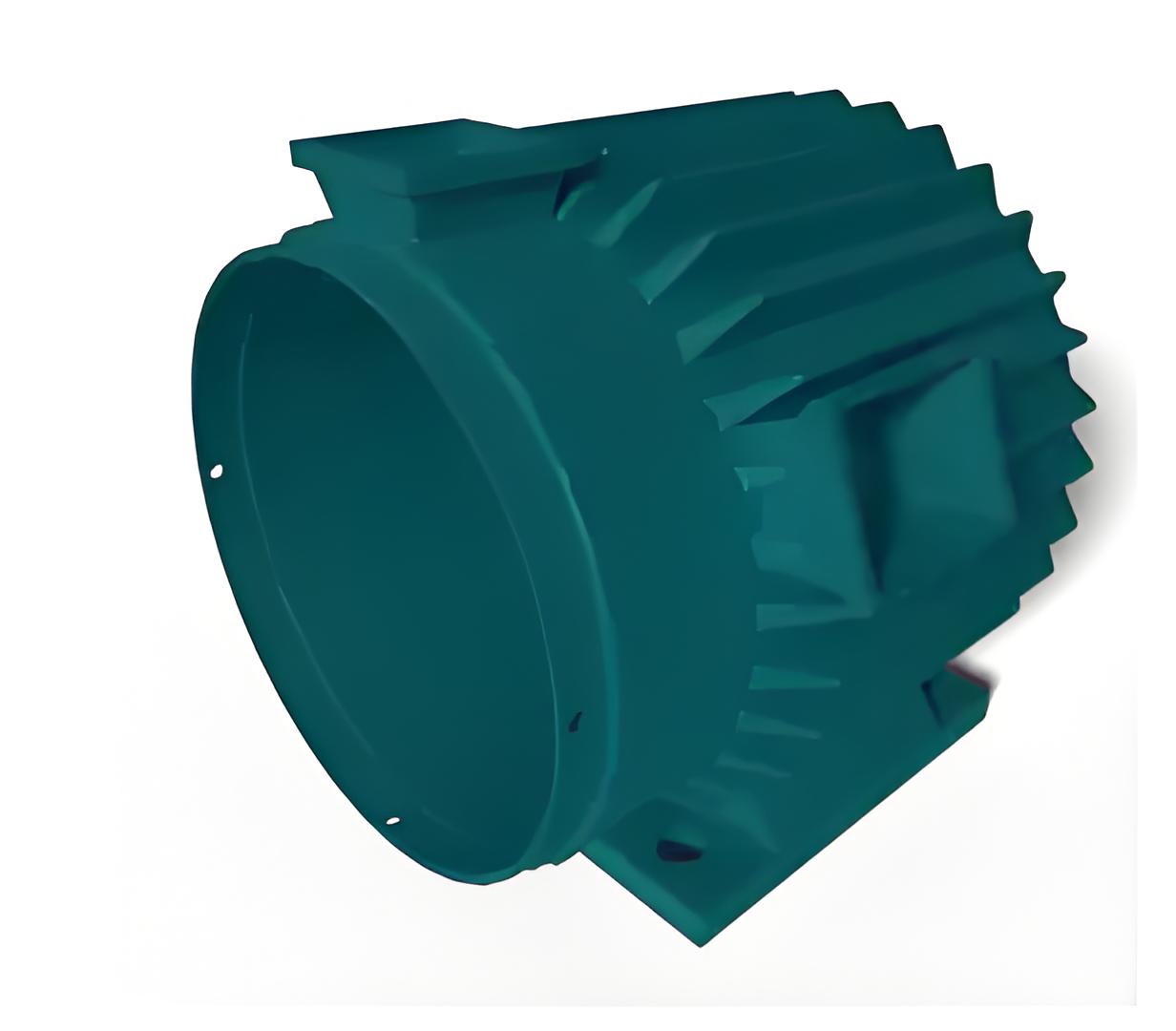
Stator frame
It is the exterior of the three-phase induction motor. Its main function is to support the stator core and the excitation winding. It acts as a covering and provides protection and mechanical strength to all internal components of the induction motor.

Stator core
The main function of the stator core is to carry AC magnetic flux. In order to reduce eddy current loss, the stator core is laminated.
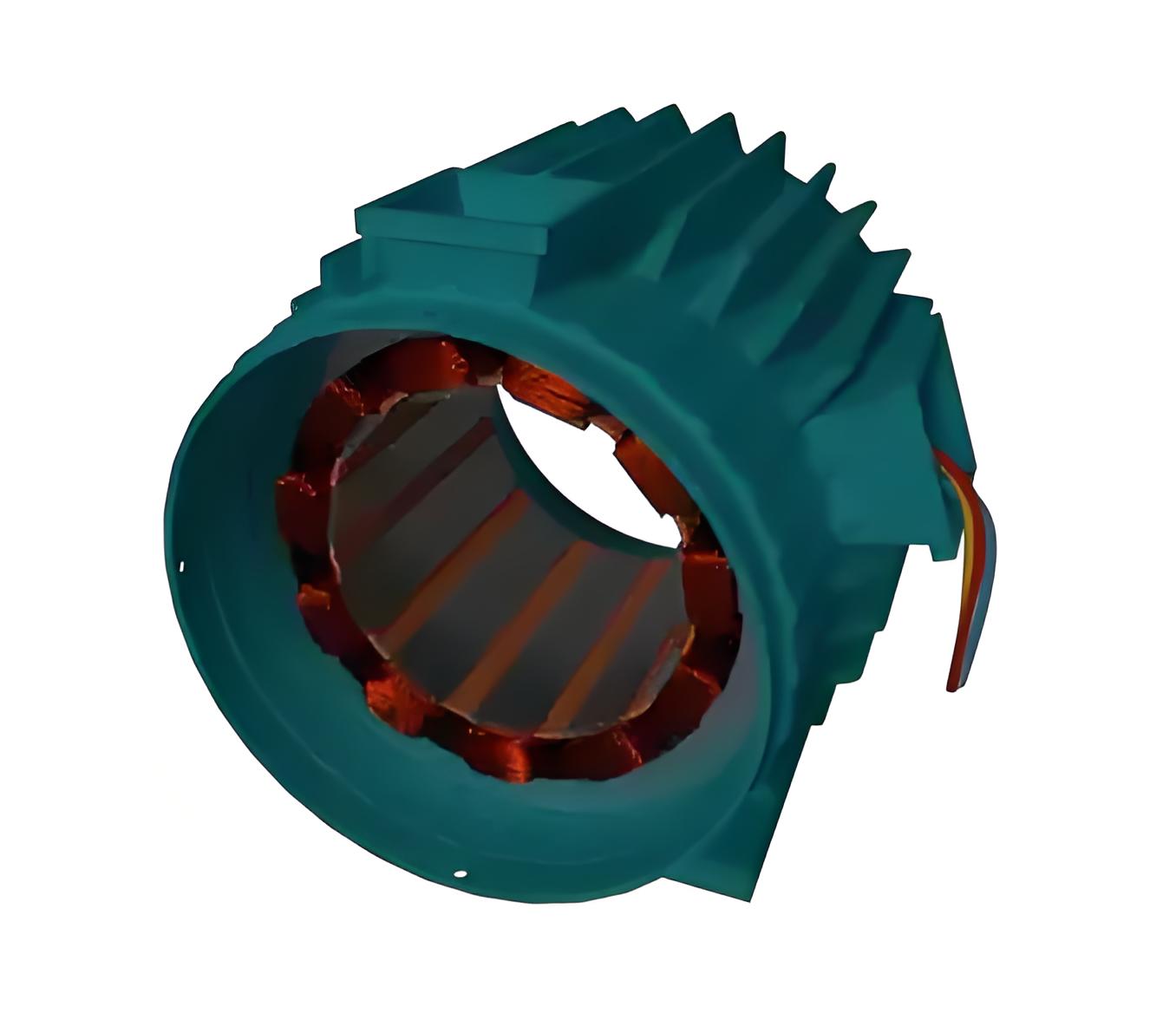
Stator winding or field winding
The groove outside the stator core of the three-phase induction motor has a three-phase winding. We use a three-phase AC power supply for this three-phase winding. The three phases of the winding are connected in a star or triangle shape, depending on the type of starting method we use.

Rotor type
Rotor models include squirrel cage rotors, which are maintenance-free and rugged, and slip-ring or wire-wound rotors, which allow for external resistance and provide better control when starting.
Apply
Three-phase induction motors power a wide variety of machinery in a wide range of industries, including lathes, drill presses, fans and elevators.
Operational advantage
Squirrel-cage motors are favored for their simplicity and low maintenance costs, while slip-ring motors are chosen for applications requiring high starting torque and adjustable speeds.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













