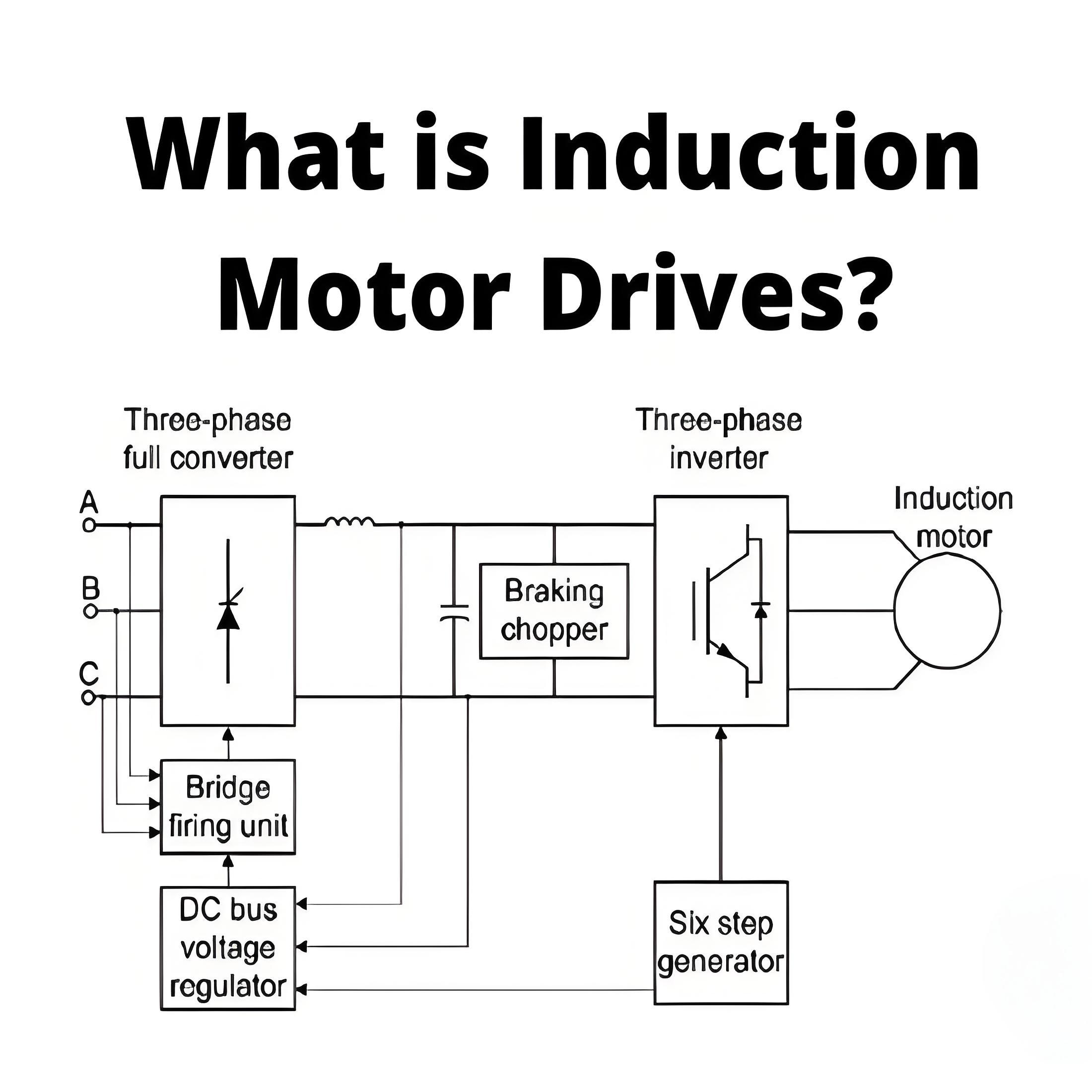
What is Rotor Resistance Control of Induction Motor?
What is Rotor Resistance Control of Induction Motor?
Rotor resistance control definition
Rotor resistance control is defined as a way to manage the speed of an induction motor by adjusting the resistance in its rotor circuit.
Induction motor basics
The working principle of the universal induction motor is that the motor speed can be adjusted by changing the resistance of the rotor.
Speed control of induction motor
Speed control is essential for applications that require variable motor speeds and can be effectively achieved with modern electronics.
Technology used
Techniques such as pulse width modulation (PWM) allow precise control of rotor resistance, thereby improving motor performance and energy efficiency.
Operational restriction
While this method is effective for changing the motor speed, it generates energy loss and heat, making it unsuitable for continuous, demanding applications.
Advantages of using static devices to control the speed of induction motors
Smooth change in rotor resistance.
Use closed loop control, easy to operate.
The system responds quickly.
The use of power electronics can eliminate rotor resistance imbalances.
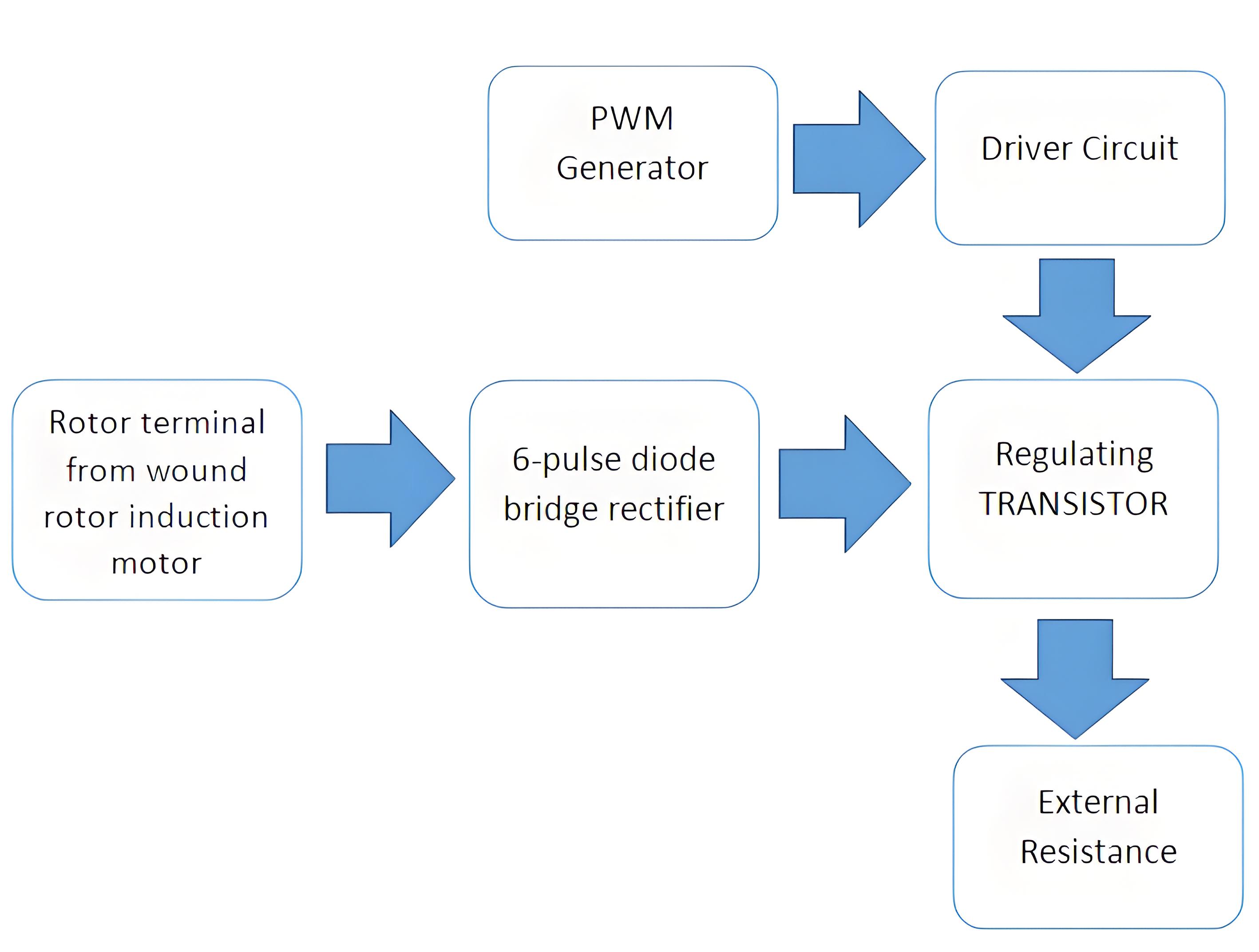
Conclusion
Although the use of resistance to control the motor speed is effective, it will also lead to resistance loss, resulting in unnecessary heating and efficiency reduction to a certain extent. This is why it cannot run continuously, it is used for intermittent applications such as bridge cranes, load fluctuations, etc.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.