Loss and Efficiency of Induction Motors
Loss and Efficiency of Induction Motors
Loss type
Fixed loss
Variable loss
Fixed loss definition
Fixed loss is the loss that remains unchanged during normal operation, including iron loss, mechanical loss, brush friction loss.
Loss of iron or core
Iron loss or core loss is divided into hysteresis loss and eddy current loss. By laminating the core, eddy current losses can be reduced, thereby increasing resistance and reducing eddy currents. The use of high-grade silicon steel minimizes hysteresis losses.
Mechanical and brush friction loss
The mechanical loss occurs in the bearing, and the brush friction loss occurs in the winding rotor induction motor. These losses are minimal at startup, but increase with speed. In a three-phase induction motor, the speed is usually kept constant, so these losses are also kept almost constant.
Variable loss definition
Variable loss, also known as copper loss, varies with load and depends on the current in the stator and rotor windings.
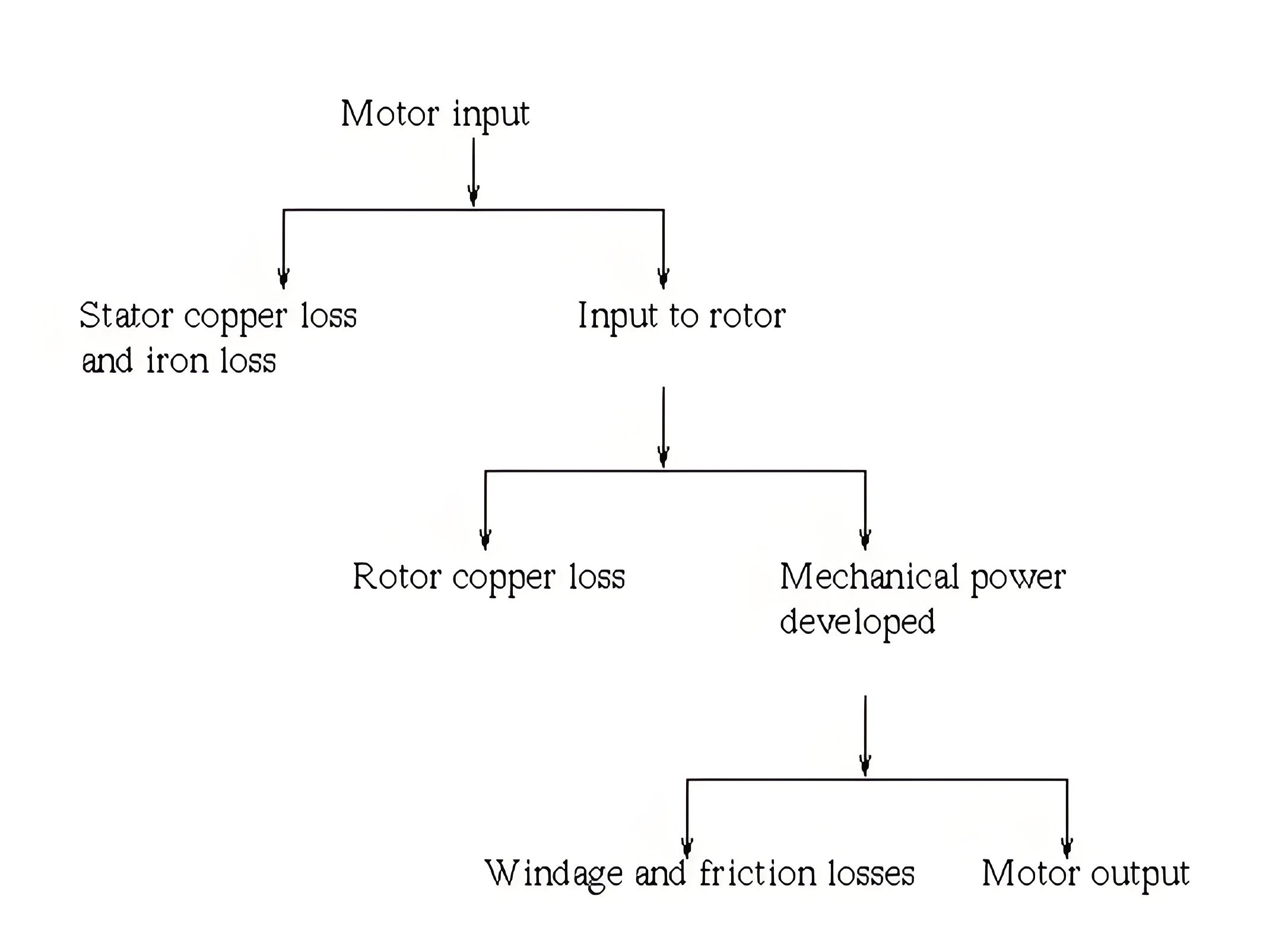
Power flow in a motor
The power flow diagram shows the stages at which electricity is converted into mechanical power, highlighting the different losses.
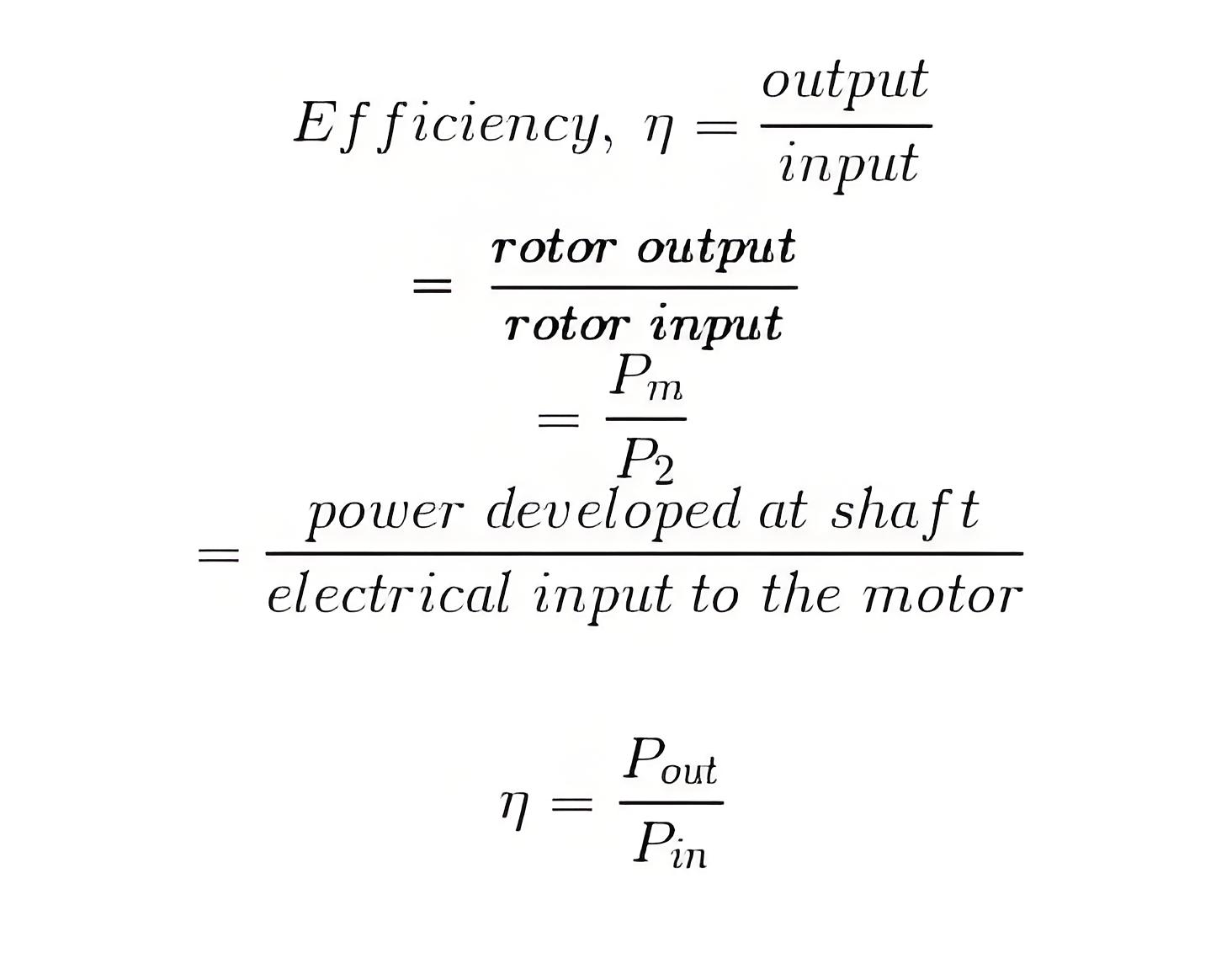
Induction motor efficiency
Efficiency is defined as the ratio of output power to input power and is important for evaluating motor performance.
Efficiency of three-phase induction motor
Rotor efficiency of the three phase induction motor ,
= Gross mechanical power developed / rotor input
Three phase induction motor efficiency,
Three phase induction motor efficiency
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.