What is Linear Induction Motor?
What is Linear Induction Motor?
Linear induction motor definition
A linear induction motor is a special type of induction motor designed to produce linear motion rather than rotational motion.
 Design feature
Design feature
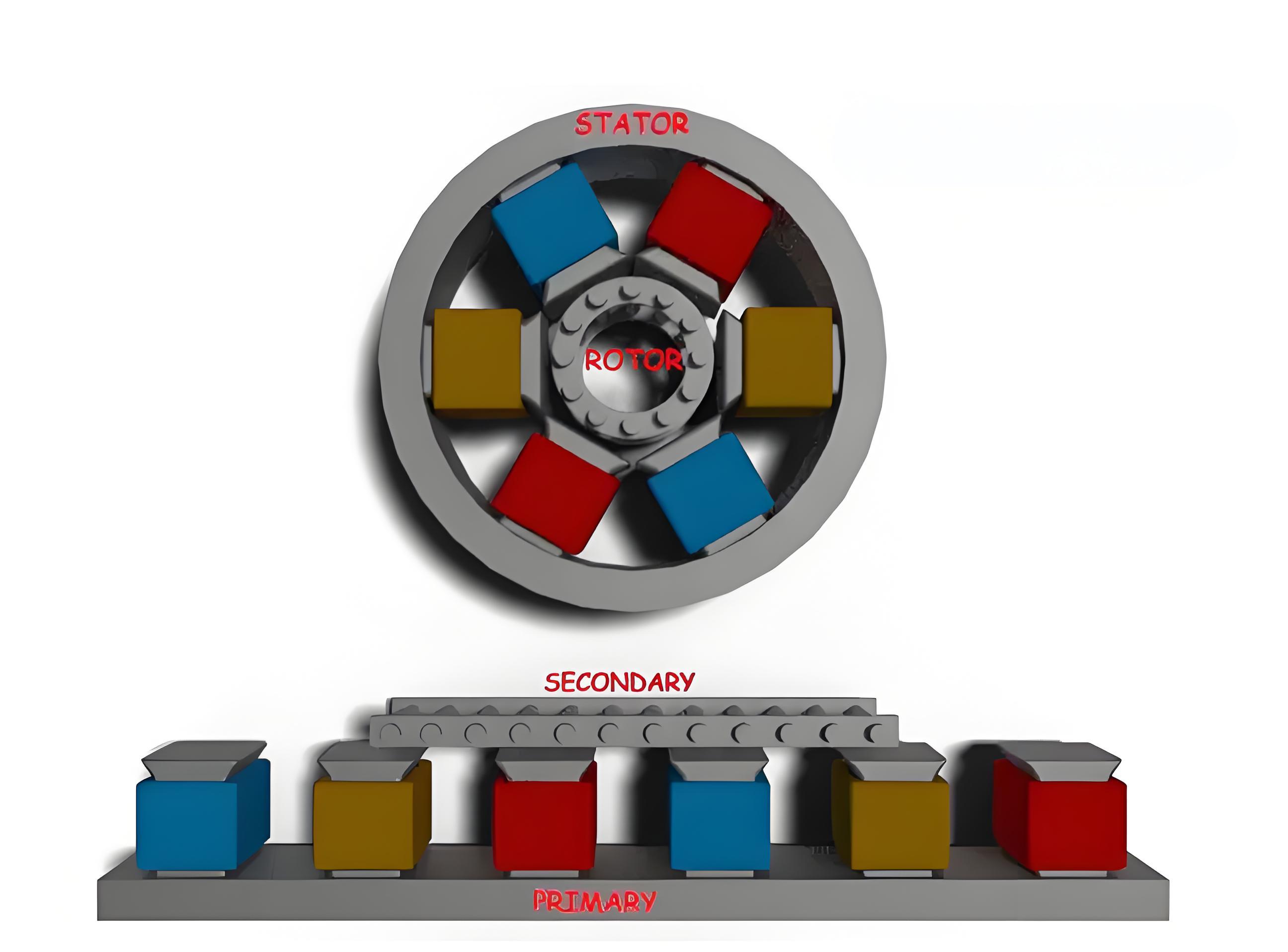
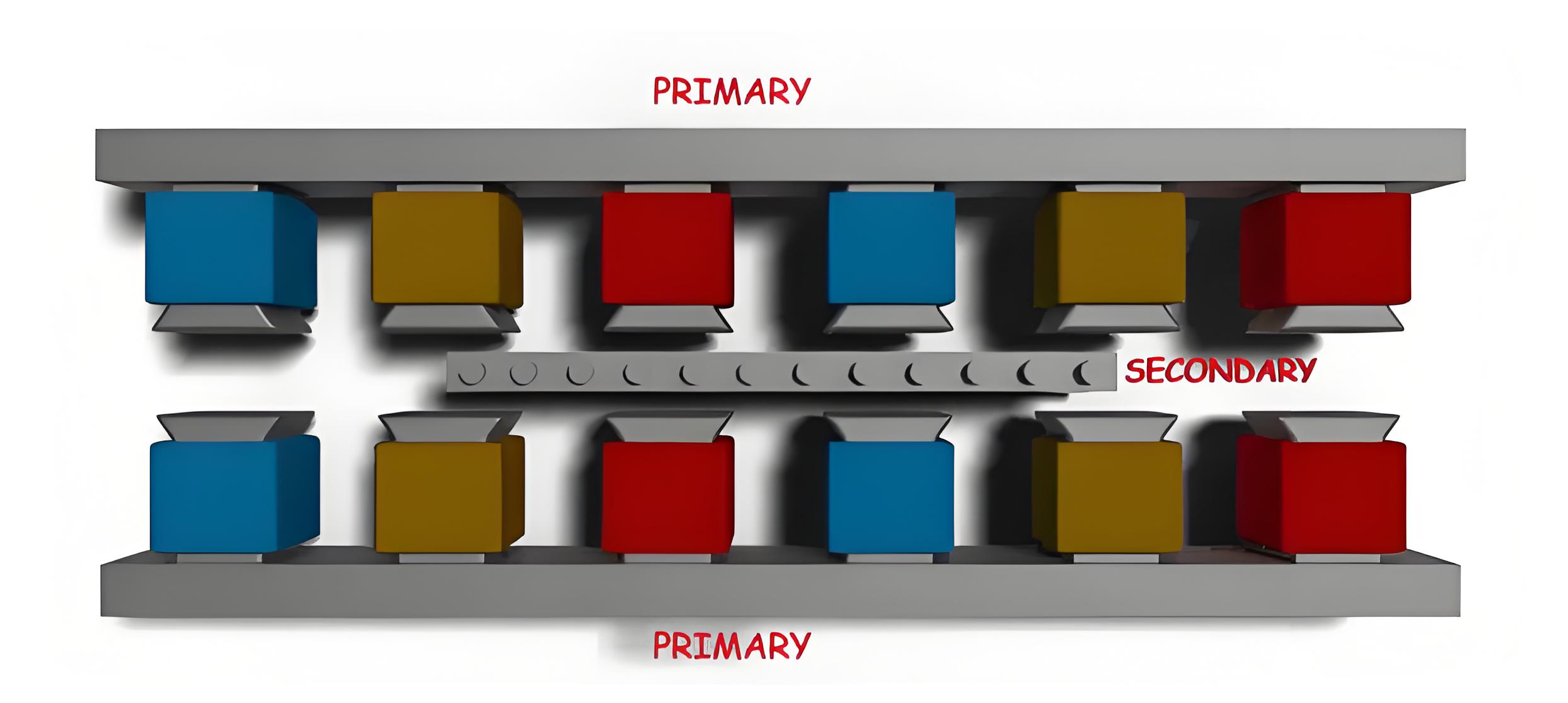
The design and construction of a linear induction motor is similar to the design and construction of a three-phase induction motor, albeit with a unique flat appearance. By cutting and flattening the stator of the polyphase induction motor, we form the main components of the system. Similarly, flattening the rotor creates a secondary component of the system. Another variant of LIM is also used to increase efficiency, called a double-sided linear induction motor or DLIM, as shown below. It has a primary on either side of the secondary in order to make more efficient use of the flux from both sides.
Working principle
The primary of a LIM, when excited by a balanced three-phase power supply, produces a magnetic flux throughout its entire length. This magnetic flux moves linearly, parallel to the rotating magnetic field in a conventional three-phase induction motor or synchronous motor. The relative motion between the inlet flux and the secondary conductor induces a current, which interacts with the flux to produce a linear thrust.
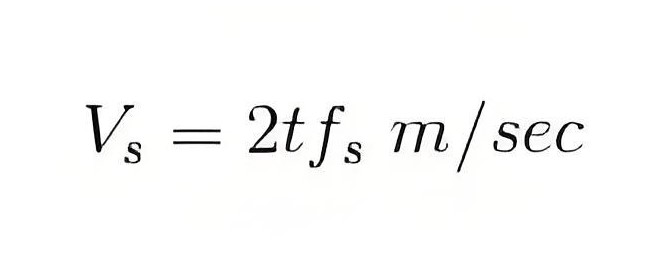
Velocity and slip
The speed of the LIM traveling field is determined by its supply frequency and polar distance, and the effect of slip on performance is similar to that of a conventional motor.
Application of linear induction motor
Automatic sliding doors in electric trains.
Mechanical handling of equipment, such as pushing a bathtub along a particular route.
Metal conveyor belt.
Liquid metal pumping, material handling in cranes, etc.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.