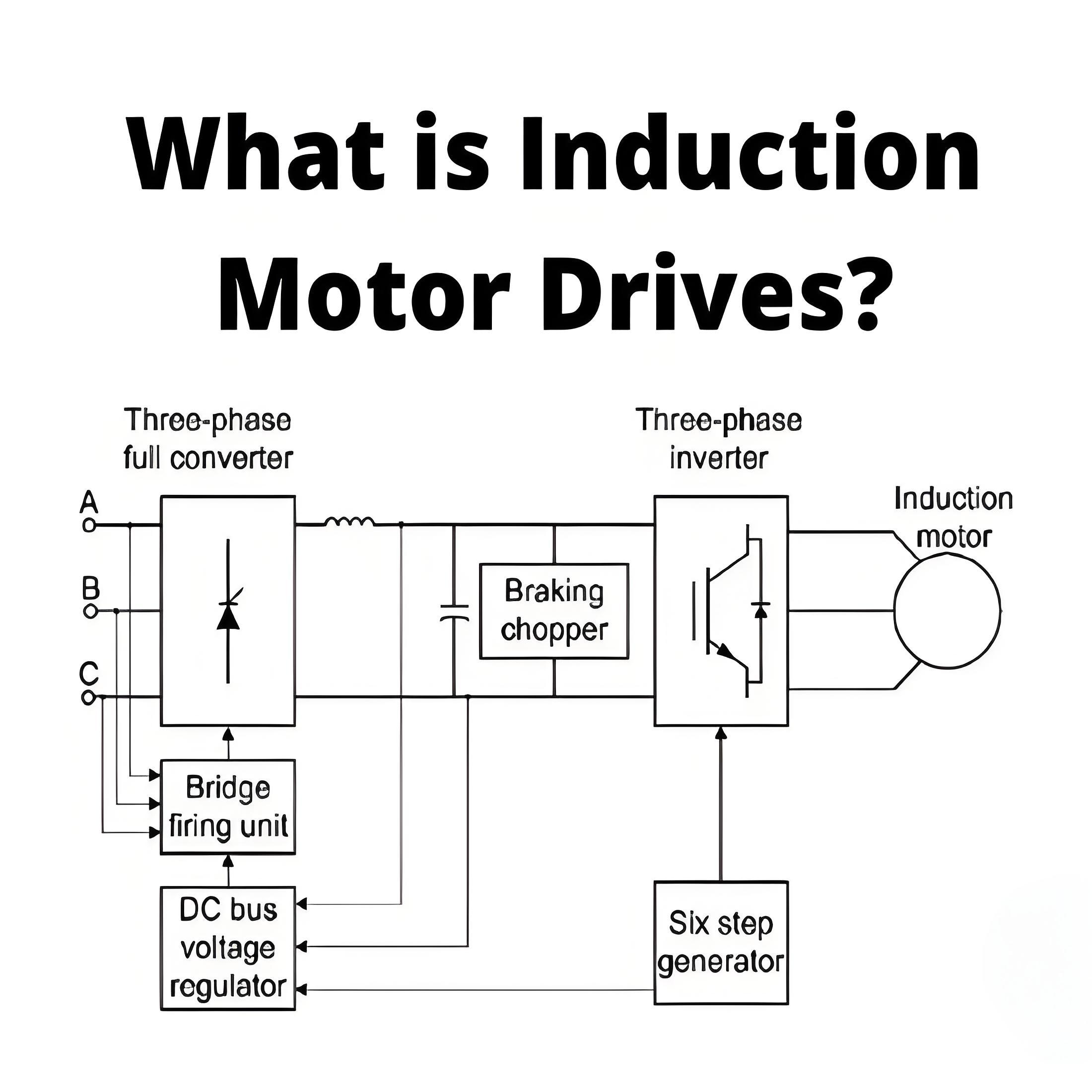
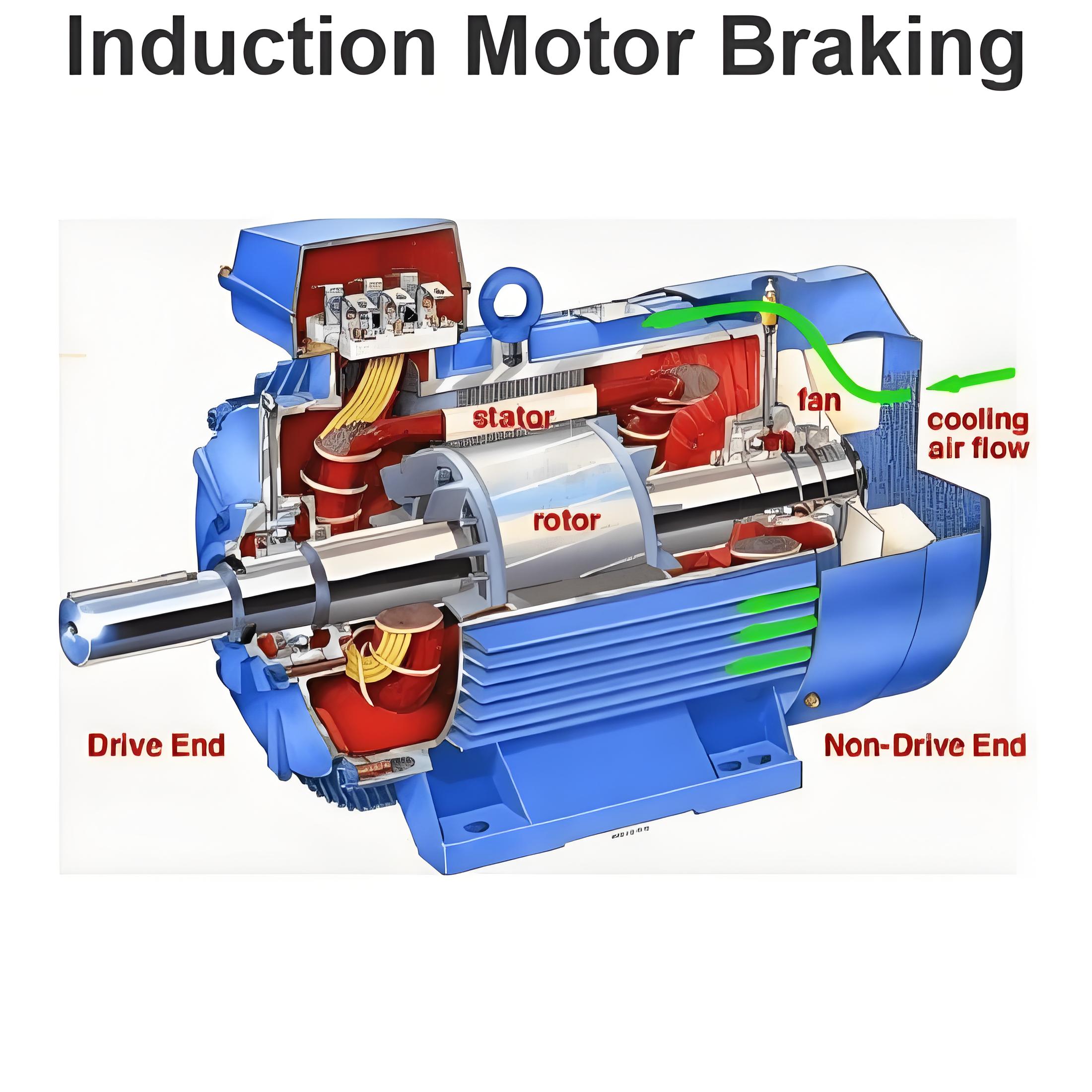
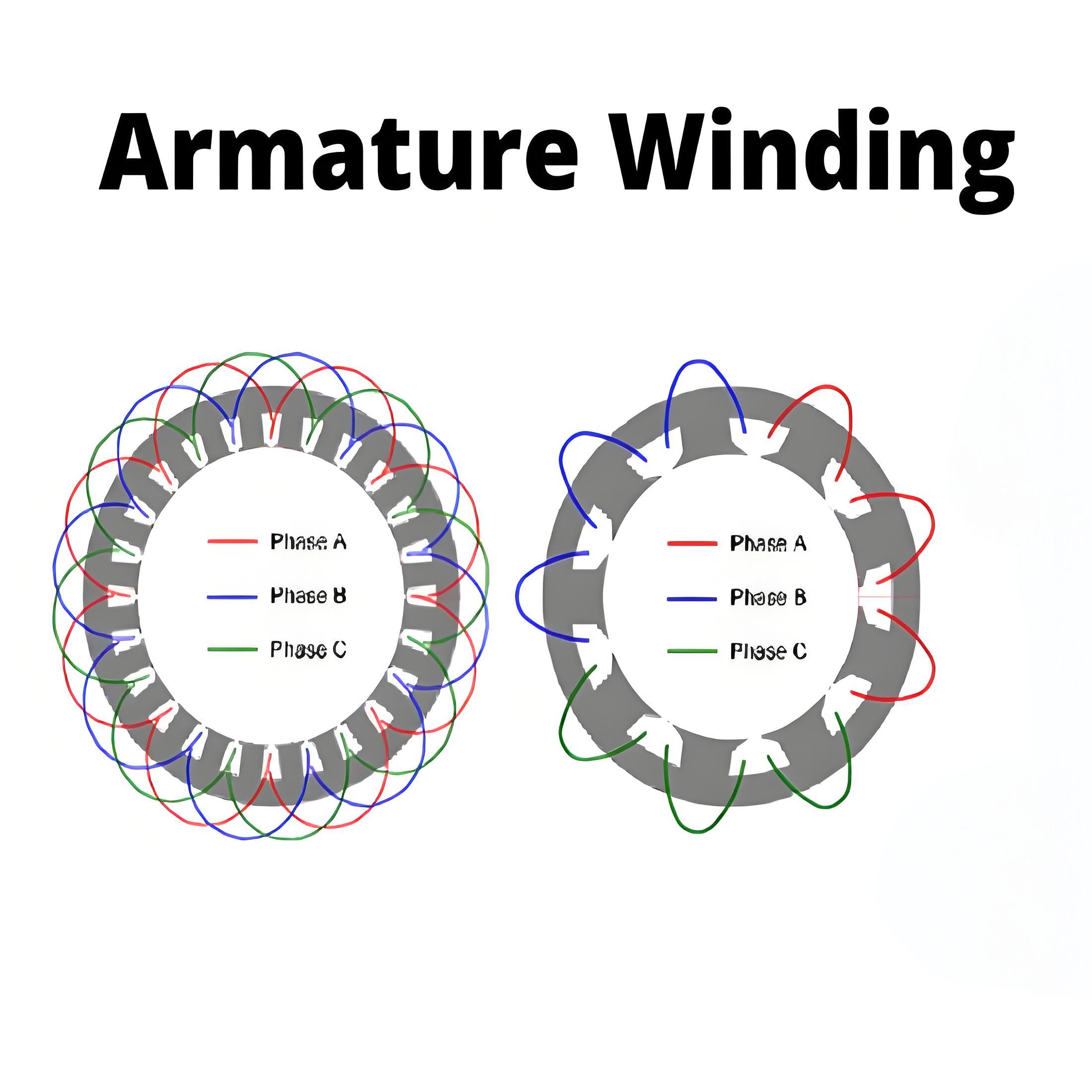
What is an Induction Motor?
What is an Induction Motor?
Induction motor definition
An induction motor is a type of AC motor in which torque is generated from the rotating magnetic field of the stator to the rotor by electromagnetic induction.
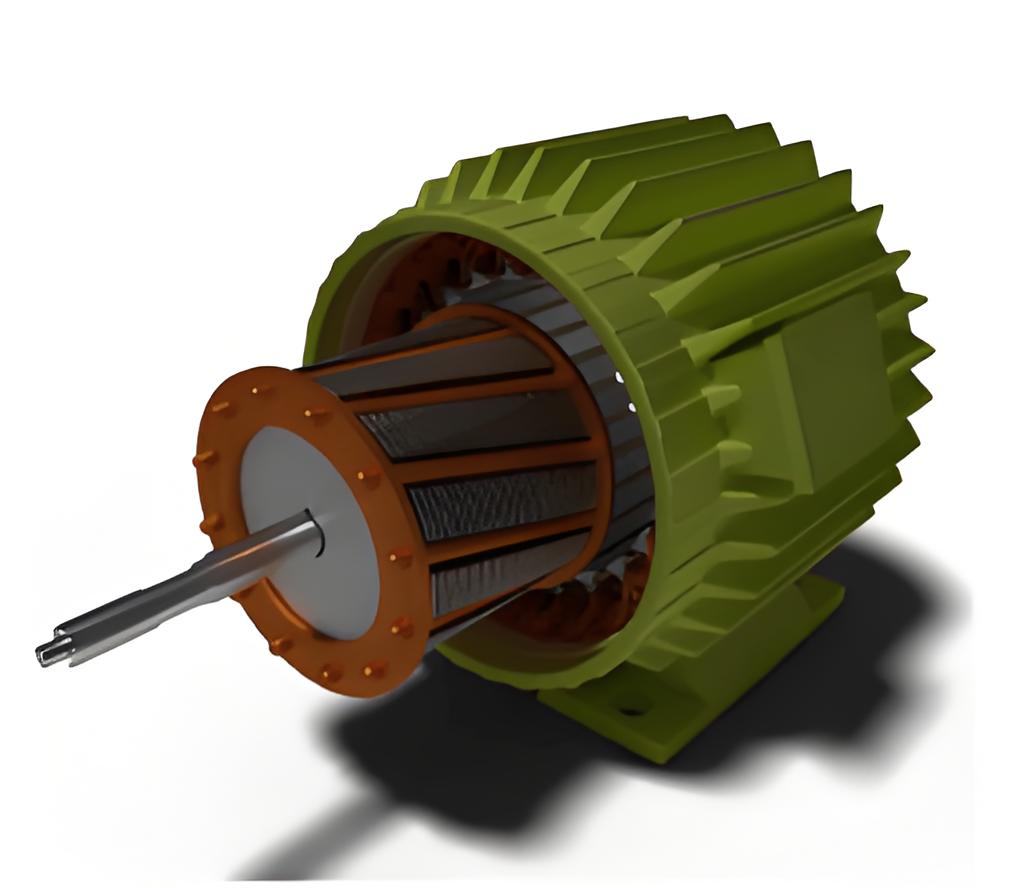
Working principle
The working principle of the induction motor is that the alternating current induces a magnetic field in the stator, and then induces a current in the rotor, generating torque and making the rotor rotate.
Type of induction motor
Type of single-phase induction motor
Split phase induction motor
Capacitor start induction motor
Capacitor start and capacitor run induction motor
Shaded pole induction motor
Type of three-phase induction motor
Squirrel cage induction motor
Slip ring induction motor
Self-starting characteristic
Three-phase induction motors are self-starting because the phase difference between three single-phase lines creates a rotating magnetic field, and single-phase motors often require capacitors to start.
Speed control and efficiency
Induction motors offer high efficiency through variable speed control options, making them suitable for a variety of industrial applications, although their speed will vary with the load.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.