Application of Induction Generator
Induction Generator Definition
An induction generator (also known as an asynchronous generator) is defined as an induction machine used to generate electricity.
Operating Principle
Induction generators work when the slip is negative, achieved by increasing the prime mover speed beyond synchronous speed.
Magnetizing Current Requirement
They require external sources for magnetizing current and reactive power, often provided by supply mains or other generators.
Self-Excited Generators
This type, also known as a self excited generator, uses a capacitor bank connected across its stator terminals to provide necessary reactive power.
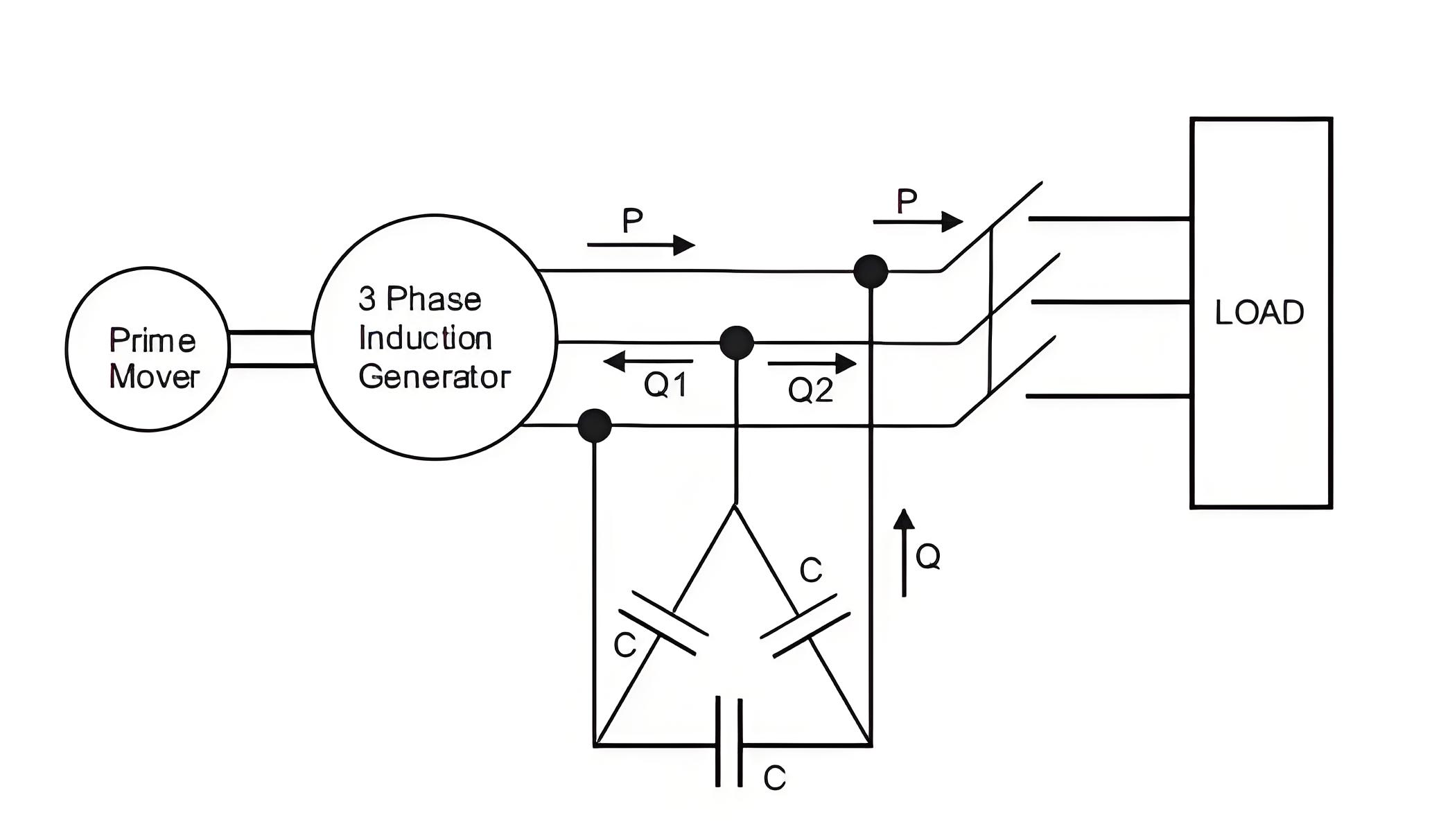
The function of the capacitor bank is to provide the lagging reactive power to the induction generator as well as load. So mathematically we can write total reactive power provided by the capacitor bank is equals to the summation of the reactive power consumed by the induction generator as well as the load.
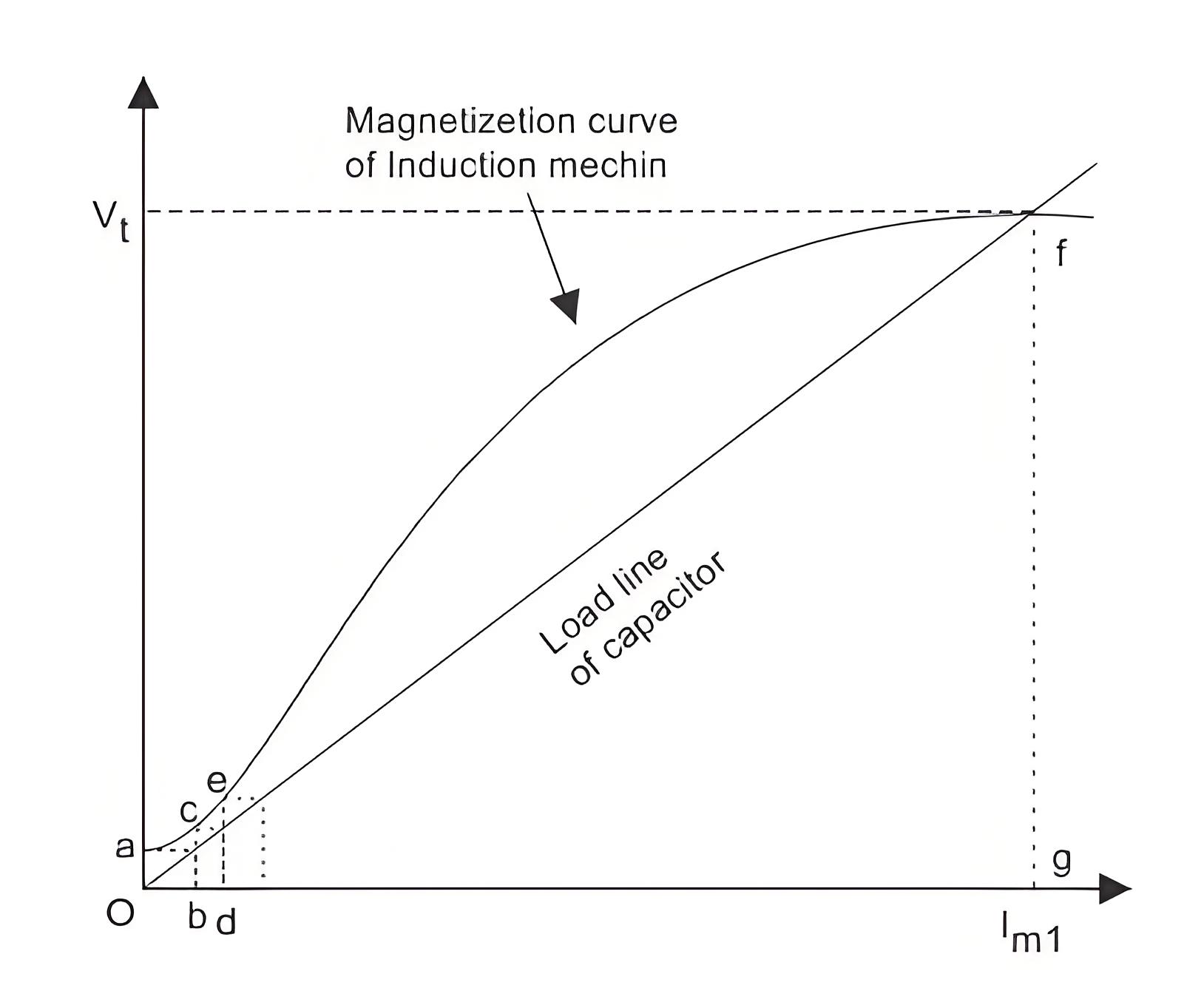
There is generation of small terminal voltage oa (as in figure given below) across the stator terminal due the residual magnetism when the rotor of the induction machine runs at the required speed. Due to this voltage oa the capacitor current ob is produced. The current bc sends current od which generates the voltage de.
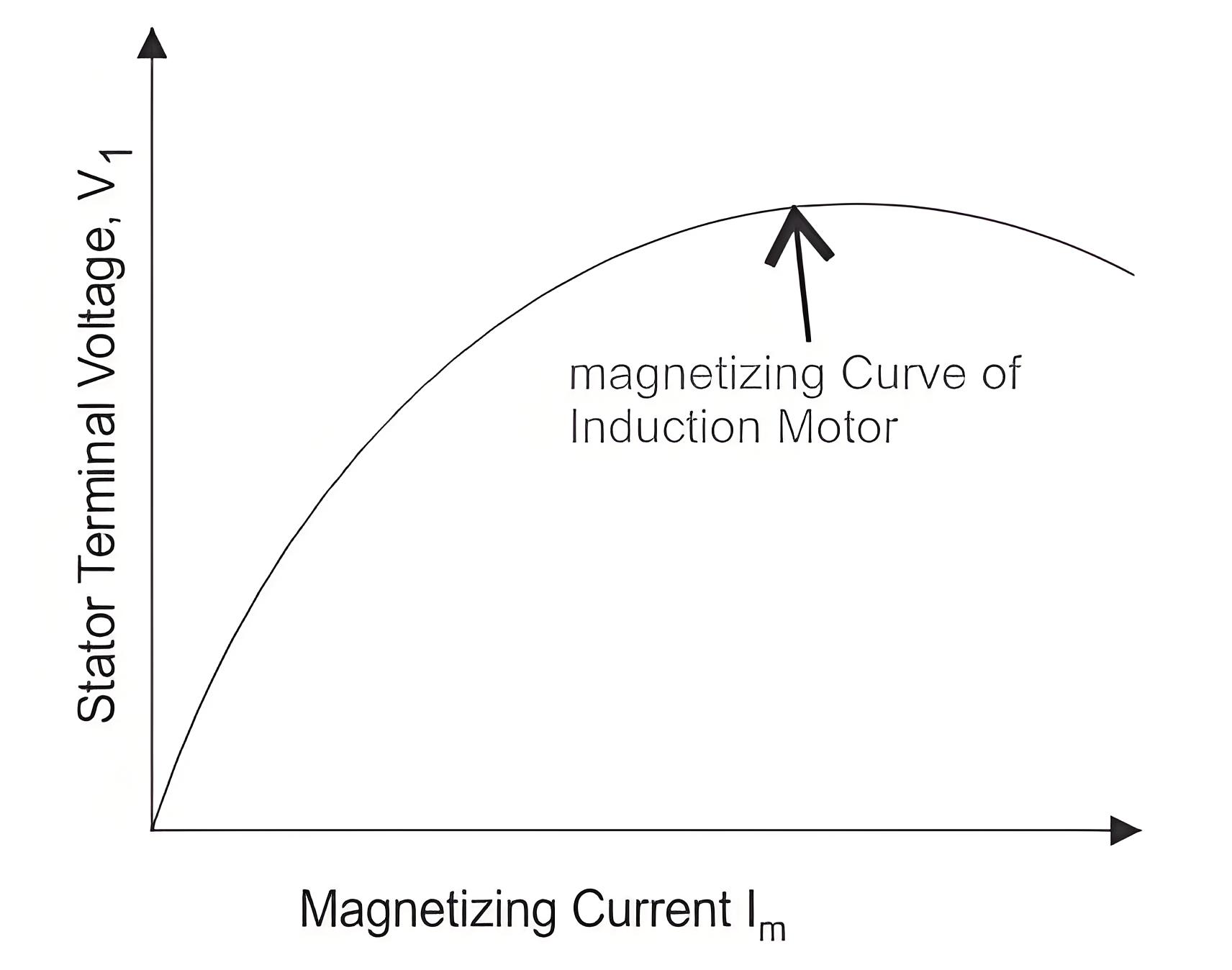
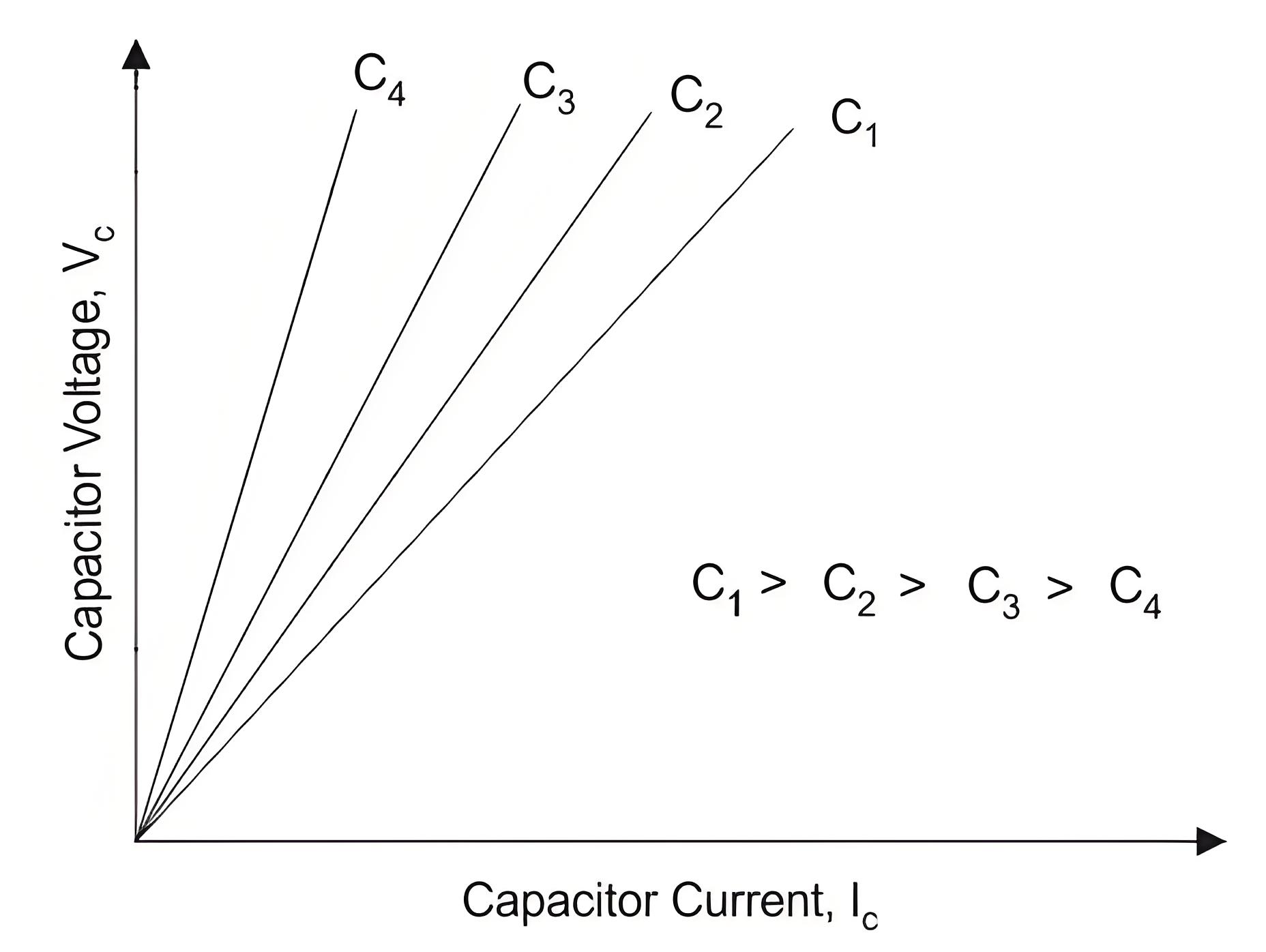
The cumulative process of voltage generation continues till the saturation curve of the induction generator cuts the capacitor load line at some point. This point is marked as f in the given curve.
Application of Induction Generator
Let us discuss application of induction generator: We have two types of induction generator let us discuss the application of each type of generator separately: Externally excited generators are widely used for regenerative breaking of hoists driven by the three phase induction motors.
Self-excited generators are used in the wind mills. Thus this type of generator helps in converting the unconventional sources of energy into electrical energy.
Now let us discuss some disadvantages of externally excited generator:
The efficiency of the externally excited generator is not so good.
We cannot use externally excited generator at lagging power factor which major drawback of this type of generator.
The amount of reactive power used to run these types of generator required is quite large.
Advantages of Induction Generators
It has robust construction requiring less maintenance
Relatively cheaper
Small size per kW output power (i.e. high energy density)
It runs in parallel without hunting
No synchronization to the supply line is required like a synchronous generator
Disadvantages of Induction Generators
It cannot generate reactive voltamperes. It requires reactive voltamperes from the supply line to furnish its excitation.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













