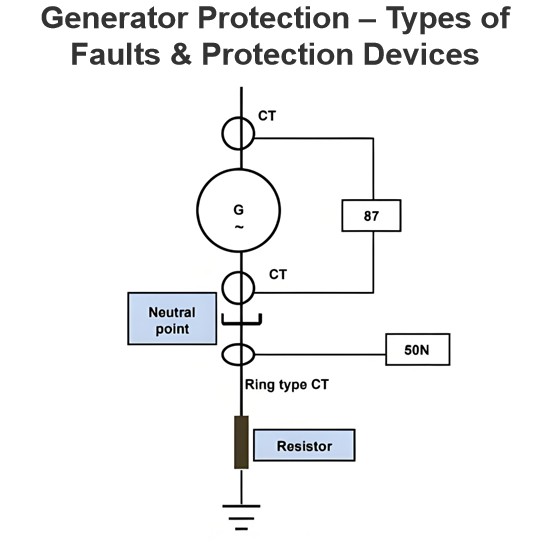
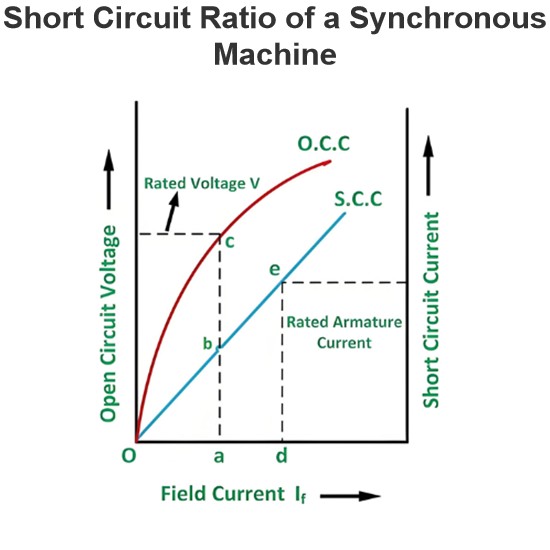
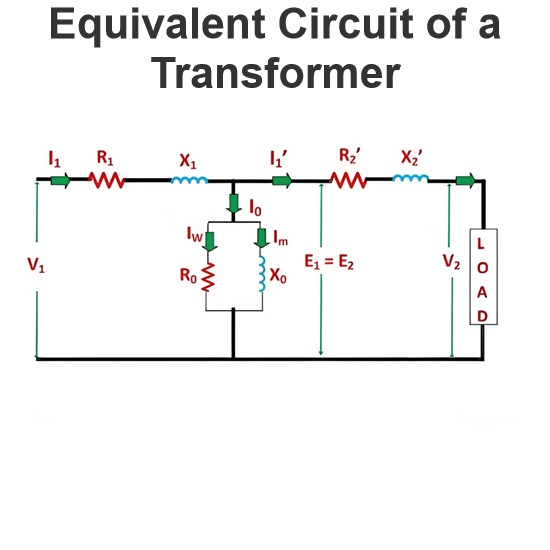
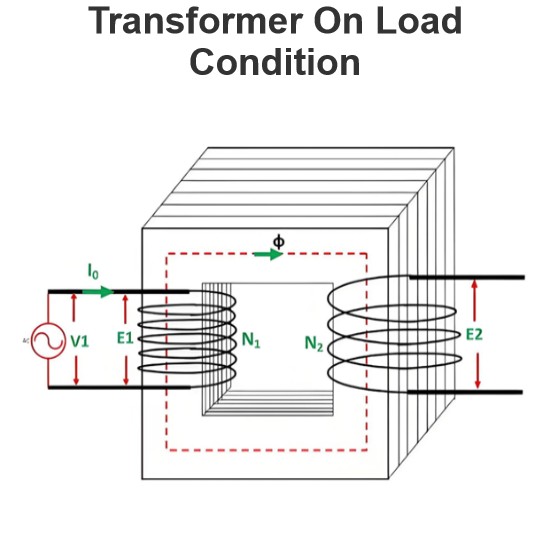
Rating of Alternator
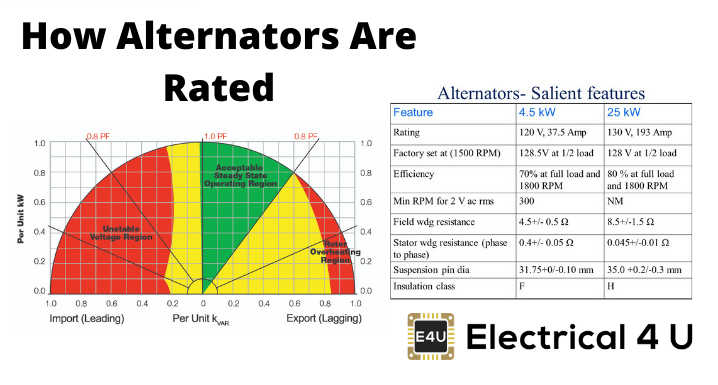
Power rating of an alternator is defined as the power which can be delivered by an alternator safely and efficiently under some specific conditions. Increasing load increases losses in the alternator, which leads to a temperature rise of the machine. The conductor and insulator parts of the machine have some specific overheating withstand limits. The manufacturer so specifies the power rating of an alternator that at that maximum load the temperature rise of different parts of the machine does not cross their specified safe limit.
The copper losses i.e. I2R loss varies with armature current and core losses vary with voltage. The temperature rise or heating of alternator depends upon cumulative effect of copper losses and core losses. As there is no role of power factor upon these losses, the rating of alternator generally given in the order of VA or KVA or MVA.
In other words, as the losses of the alternator are independent of electrical power factor, hence power factor does not come into picture while we calculate and estimate the power rating of an alternator. Although losses of the alternator depend upon its KVA or MVA rating, actual output varies with electrical power factor.
The electrical output of an alternator is a product of power factor and VA. We express the output in KW.
Sometimes alternators are also rated by its power instead of VA rating. That time electrical power factor of the alternator must be specified too.
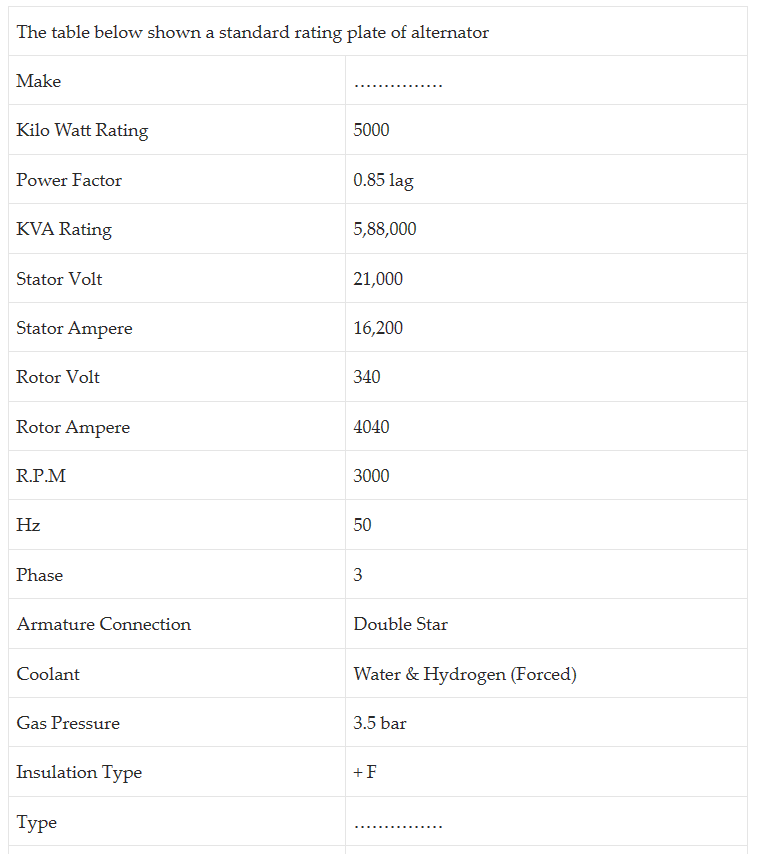
In addition to KVA rating, an alternator has also voltage, electric current, frequency, speed, number of phases, number of poles, field ampere, excitation voltage, maximum temperature rise limit ratings, etc.

Statement: Respect the original, good articles worth sharing, if there is infringement please contact delete.
Electrical4U is dedicated to the teaching and sharing of all things related to electrical and electronics engineering.