Types Frog Leg & Wave Winding
Frog Leg Winding Definition
A frog leg winding is a combination of a multiplex wave and a simplex lap winding in the same slots. It retains the advantages of both lap windings and wave windings without their inherent disadvantages.
Lap and wave windings each have an equal number of parallel paths, which are connected to the same commutator.
The frog-leg winding has as many parallel paths as duplex lap windings because the simplex lap winding portion supplies ‘P’ number of parallel paths and the multiplex-wave section also provides ‘P’ number of parallel paths. Hence the total is 2P number of paths in parallel (which is the same number as a duplex lap winding).
Advantages of Frog Leg Winding
This winding has more no. of parallel paths and the current and the voltage rating is higher than that of lap or wave winding. These frog-leg wound armatures are designed for the use with moderate current and moderate voltage.
These windings are connected in series-parallel. Any wave element and the succeeding lap element connected on the commutator exactly two pole pitches apart in a series combination. This two commutator segments are exactly 360 electrical degrees apart and develop zero net voltage. Therefore, this lap-wave combination of a frog leg winding is fully equalized and eliminates the use of an equalizer. That is why most large DC machines use frog-leg wound armatures.
Drum Winding Definition
This is the type of winding in which the conductors are placed in slots over the drum-shaped armature surface and connected to one another by front and back connections at coil ends. Drum winding is introduced mainly to overcome the shortcomings of ring-type winding.
Advantages of Drum Winding
Each winding, placed on the armature slots, surrounds the core and so that the entire length of the conductor, except the end connections, cut the main magnetic flux. Therefore the voltage induced in this type of armature winding is larger than the Gramme-ring winding.
The coils, before placing on the armature slots, can be pre-formed and insulated. Hence cost can be reduced.
The two sides of the coil placed under two different poles, one North Pole and another South Pole, hence the emf induced in them are always additive with the help of the end connection.
Fractional pitch winding can be used in drum winding. The advantage of fractional pitch winding is that it gives substantial savings in the copper of end connections. Commutation is also improved because of the lesser mutual inductor between the coils.
Fractional pitch winding: To get the maximum emf, the coil span should match the pole pitch. However, reducing the coil span to eight-tenths (8/10) of the pole pitch can still induce significant emf. This is called fractional-pitch winding.
Because of several conductors are placed in a single slot, the nos. of the slot get reduced in the armature core, the armature core teeth become mechanically stronger. The lamination and the protection of coils are also improved.
The manufacturing cost will be reduced in the drum type winding because here we have to construct fewer coils.
Gramme Ring Winding Definition
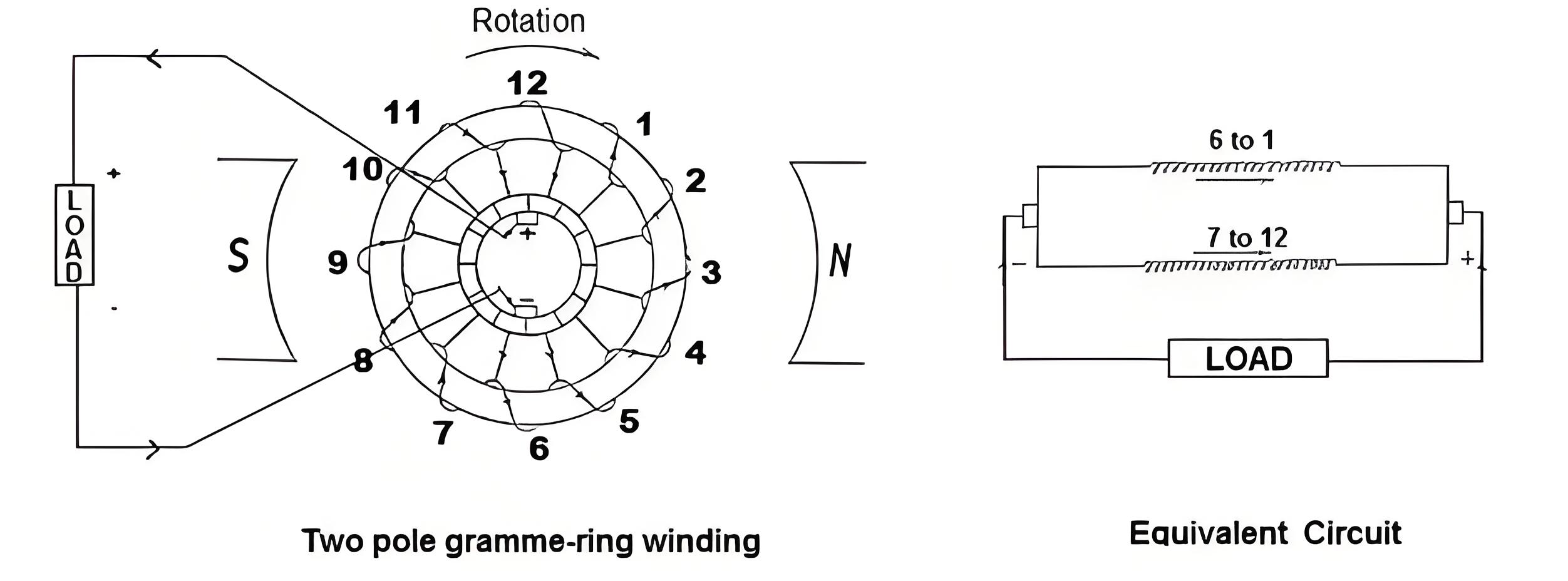
A ring winding is the type of armature winding in which the wire is wound around the outer and inner surfaces alternately of a cylindrical or ring-shaped core. The Gramme-ring type of armature winding is an old type of armature winding. In this winding, the armature consists of a hollow cylinder or ring made up of iron lamination. The core is wound with insulated wire spirally about the ring.
The winding is continuous, and hence it is closed. We connect the coils between brushes in series. The figure shows Gramme-Ring type winding and its equivalent circuit. We can see that there is an equal number of voltage-generating conductors placed on each side of the armature.
We tap the wire at regular intervals and connect them to the commutator segments. There are two paths between the positive and negative brushes, connected in parallel. Coils 1 to 6 form one path, while coils 7 to 12 form the other.
When the armature rotates in the clockwise direction, then the emf is induced in the conductors. The direction of induced emf and the direction of current will be inward in case of the conductors under N-pole by Fleming’s right-hand rule. In the case of the conductors under S-pole, the direction of induced emf and the direction of current will be outward.
According to Fleming’s right-hand rule, hold your right hand with the thumb, forefinger, and middle finger at right angles. The forefinger shows the magnetic field direction, the thumb indicates motion, and the middle finger points to the induced current.
Thus the EMF generated in two paths are in the opposite direction as shown in the above figure. The emf generated on each path is additive from bottom to top on each side. Since there are two parallel paths, the voltage per path is the generated voltage of the machine, and each path provides half of the current output in the external circuit.
Advantages of Gramme Ring Winding
Operating principle of the armature is simpler because there is no crossing of conductors in the winding.
Same winding can be employed with 2, 4, 6 or 8 poles theoretically.
Disadvantages of Gramme Ring Winding
The part of this winding located on the inner side of the iron ring cut very few lines of flux. Thus they have very little voltage induced in them. For this reason, it is not widely used.
With the same no. of poles the same velocity of the armature winding the induced emf in Gramme-ring winding is half of the induced emf in the drum type winding.
As the portion lying inside the inner ring acts only as connectors so, there is a wastage of copper.
Repairs and maintenance are very costly.
Insulation of winding is much difficult.
Strong field excitation needed to produce the require flux because the construction requires a large air gap.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













