What is Lap Winding ?
What is Lap Winding ?
Lap Winding Definition
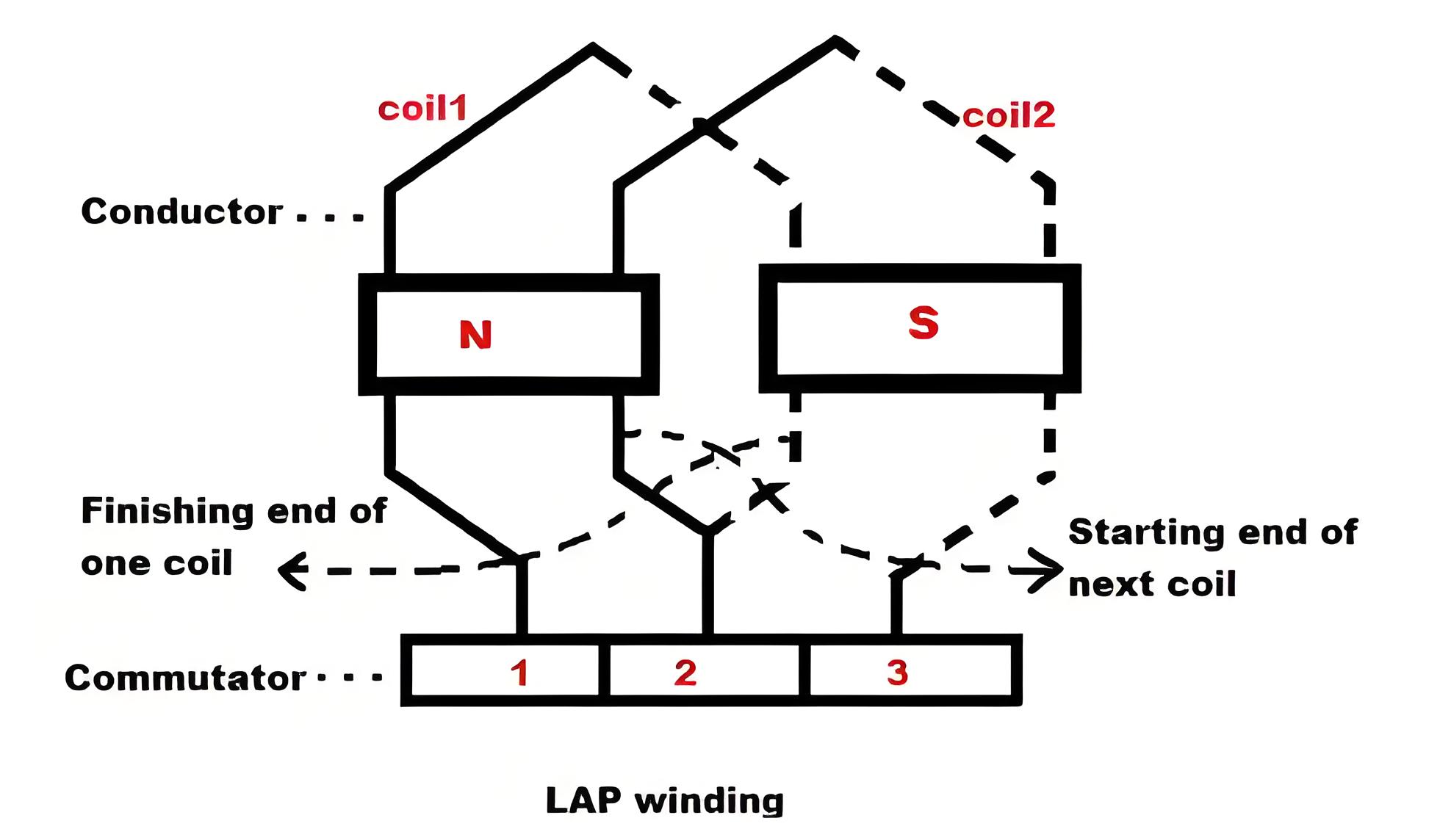
Lap Winding Definition: A lap winding is defined as a winding where successive coils overlap and connect to the same commutator segment under the same magnetic pole.
Simplex Lap Winding: In Simplex Lap Winding, the number of parallel paths between the brushes equals the number of poles.
Duplex Lap Winding: In Duplex Lap Winding, the number of parallel paths between the brushes is twice the number of poles.
Lap Winding Formula: Important formulae include Back pitch (YB), Front pitch (YF), Resultant pitch (YR), and Commutator pitch (YC).
Lap Winding Diagrams: Diagrams illustrate the coil connections in both Simplex and Duplex Lap Windings.
There are two different types of Lap Windings:
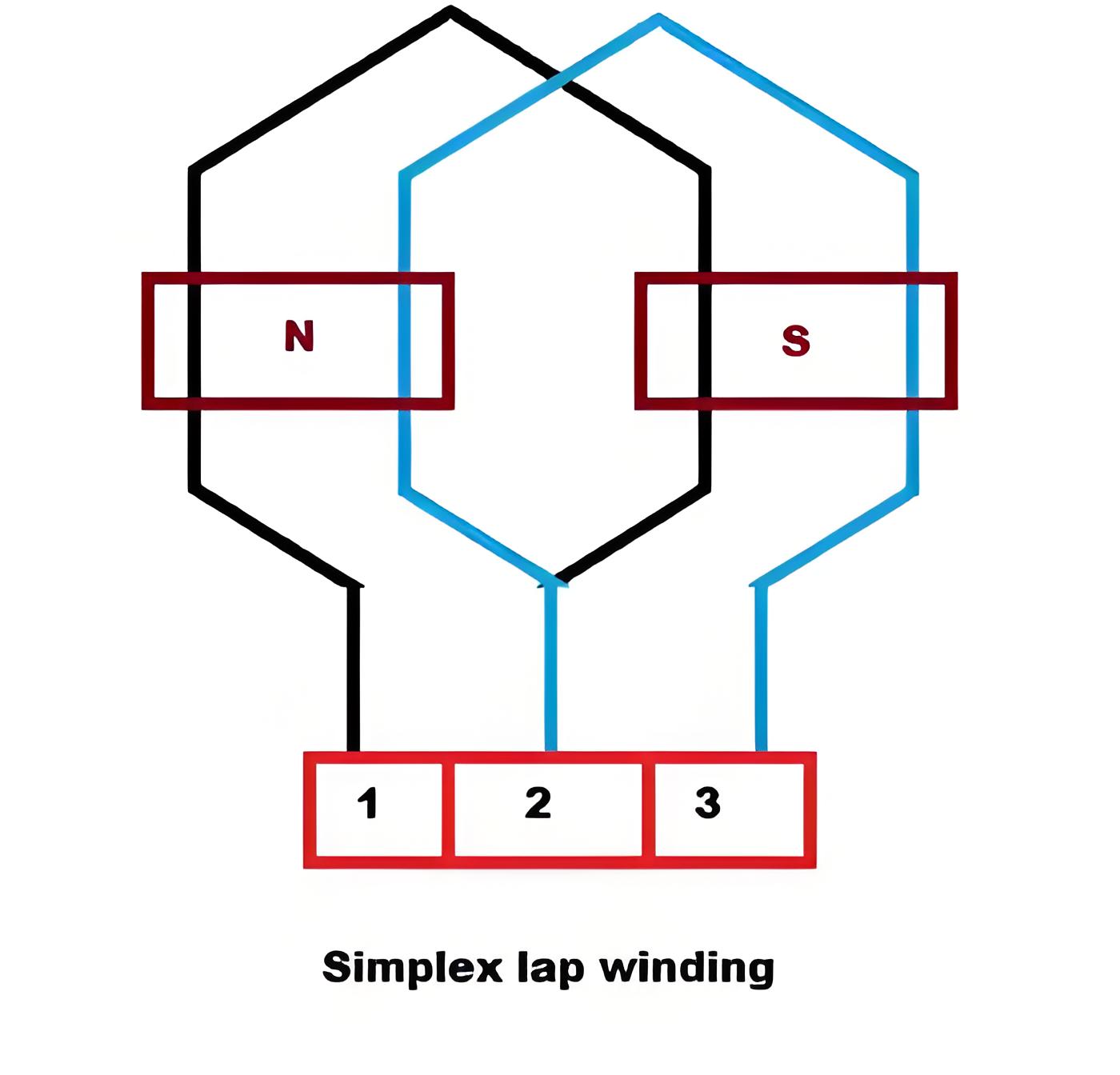
Simplex Lap Winding
Duplex Lap Winding
Simplex Lap Winding
In Simplex Lap Winding, the number of parallel paths between the brushes equals the number of poles.
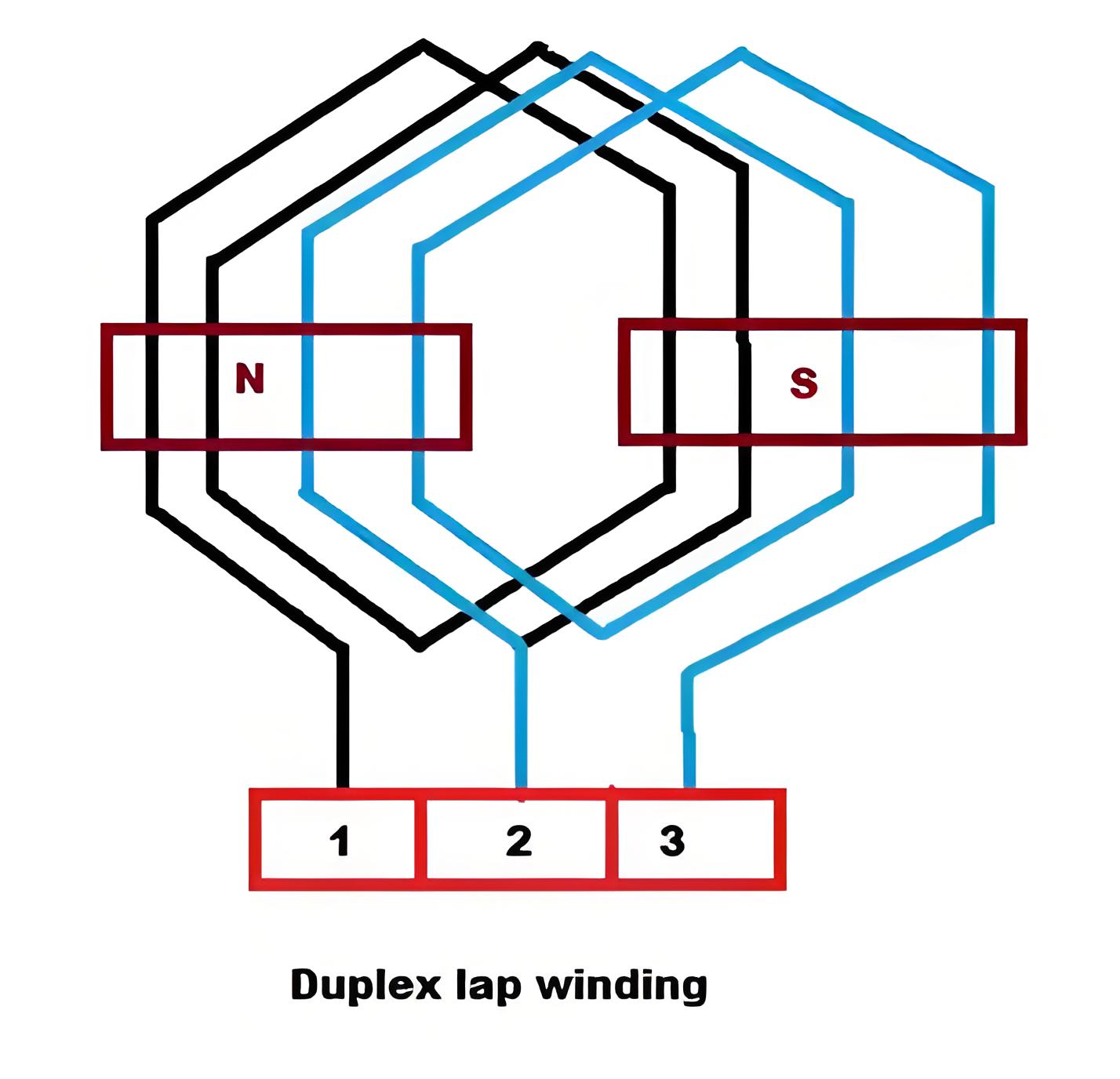
Duplex Lap Winding
In Duplex Lap Winding, the number of parallel paths between the brushes is twice the number of poles.
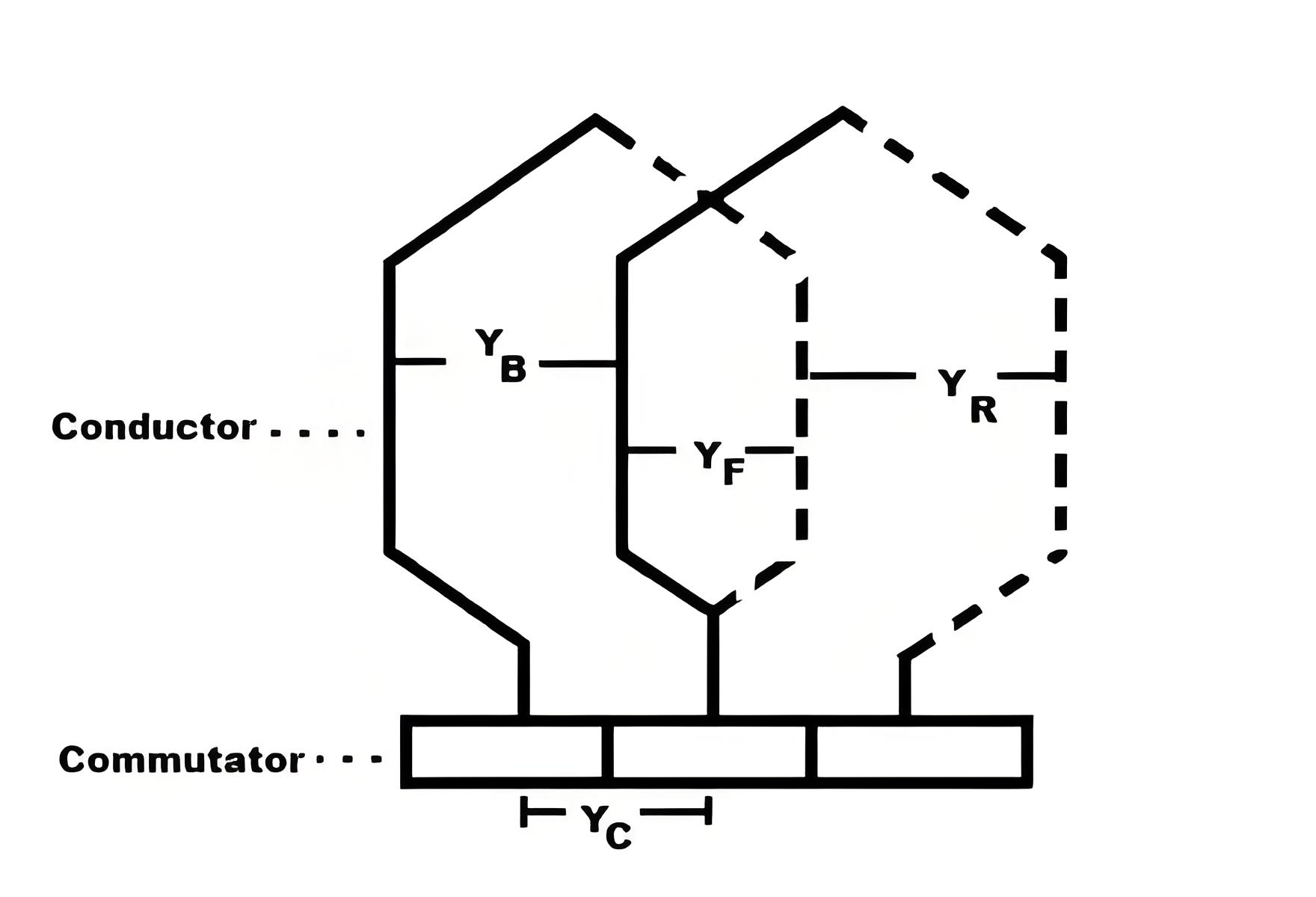
Some important points to remember while designing the Lap winding:
If,
Z = the number of conductors
P = number of poles
YB = Back pitch
YF = Front pitch
YC = Commutator pitch
YA = Average pole pitch
YP = Pole pitch
YR = Resultant pitch
Then, the back and front pitches are of opposite sign and they cannot be equal.
YB = YF ± 2m
m = multiplicity of the winding.
m = 1 for Simplex Lap winding
m = 2 for Duplex Lap winding
When,
YB > YF, it is called progressive winding.
YB < YF, it is called retrogressive winding.
The back pitch and front pitch must be odd.
Resultant pitch (YR) = YB – YF = 2m
YR is even because it is the difference between two odd numbers.
Commutator pitch (YC) = ±m
Number of parallel path in the Lap winding = mP
Let us start from 1st conductor.
Advantages of Lap Winding
This winding is necessarily required for large current applications because it has more parallel paths.
It is suitable for low voltage and high current generators.
Disadvantages of Lap Winding
It produces less emf compared to wave winding. This winding needs more conductors to produce the same emf, leading to higher winding costs.
It has less efficient utilization of space in the armature slots.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













