Winding Factor 、Pitch Factor & Distribution Factor
Winding factor definition
The winding factor is defined as the product of the pitch factor and the distribution factor.
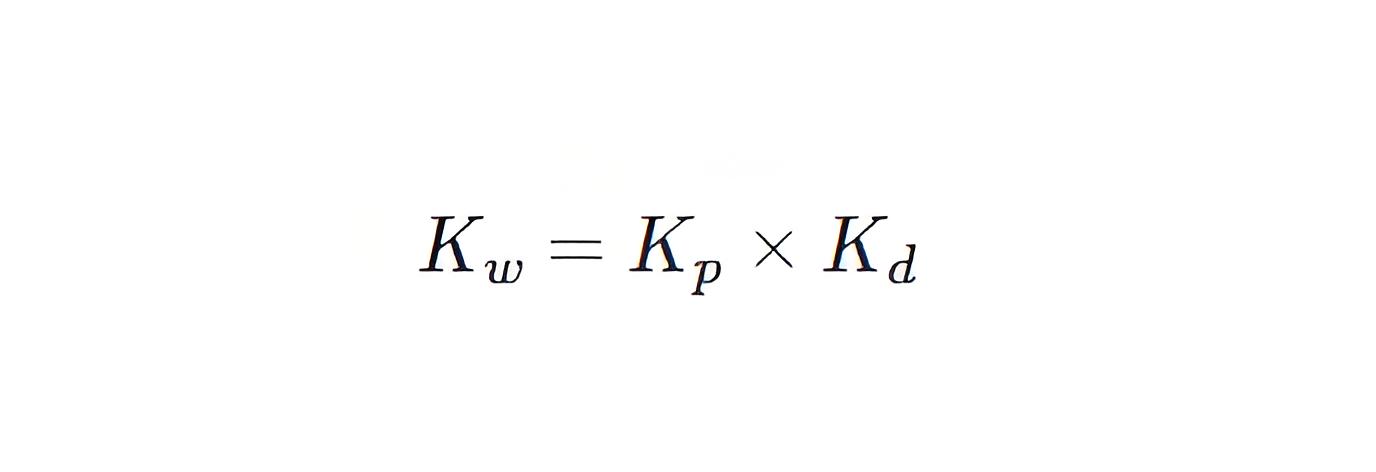
Pitch factor
The pitch factor is the phasor of the induced electromotive force and its ratio to its arithmetic sum, and is always less than the unit.
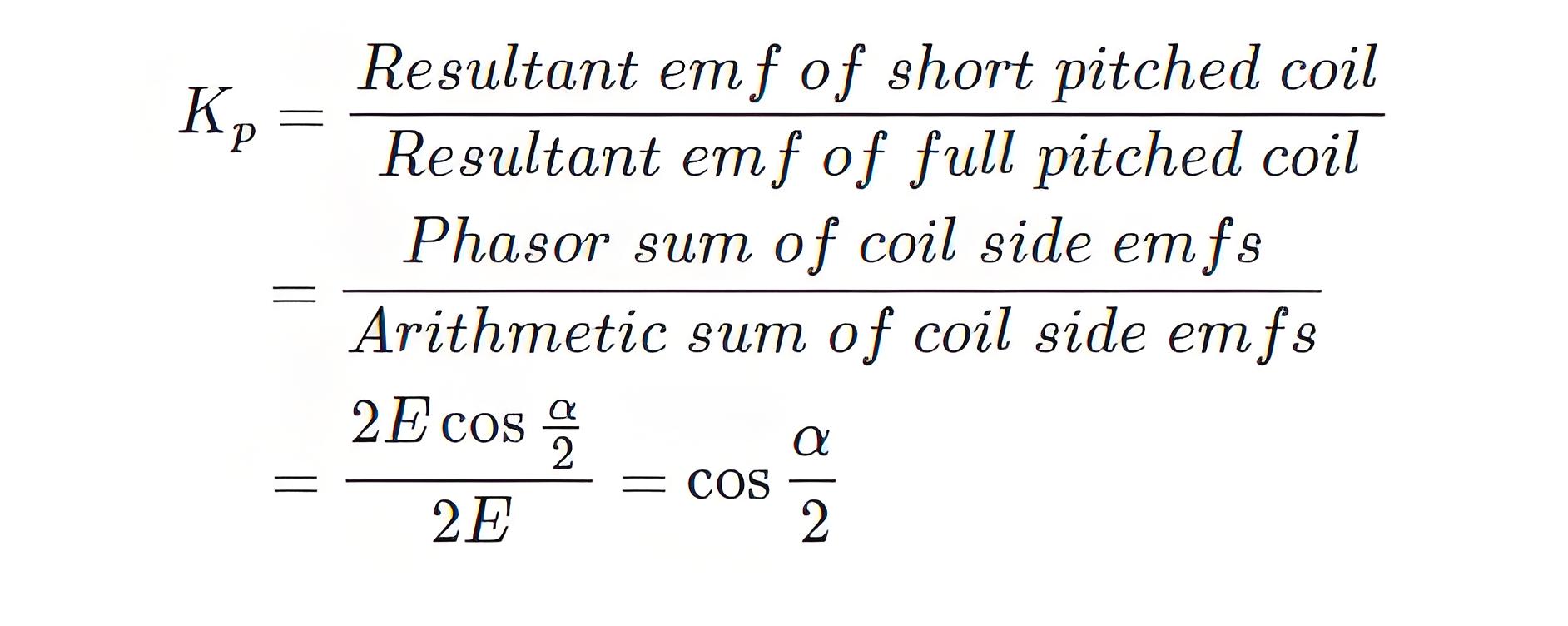
This pitch factor is the fundamental component of the electromotive force. Magnetic flux waves can also be composed of spatial field harmonics, which produce corresponding time harmonics in the generated voltage waveform.
Full pitch coil and short pitch coil
In a full-pitch coil, emfs sum arithmetically due to a phase Angle of 180°, while in a short-pitch coil, they sum in a phase Angle vector of less than 180°.
Distribution factor
The distribution factor measures the resultant electromotive force of the distributed winding compared to the concentrated winding and is always less than the unit.
As a spacing factor, the distribution factor is also always smaller than the unit.
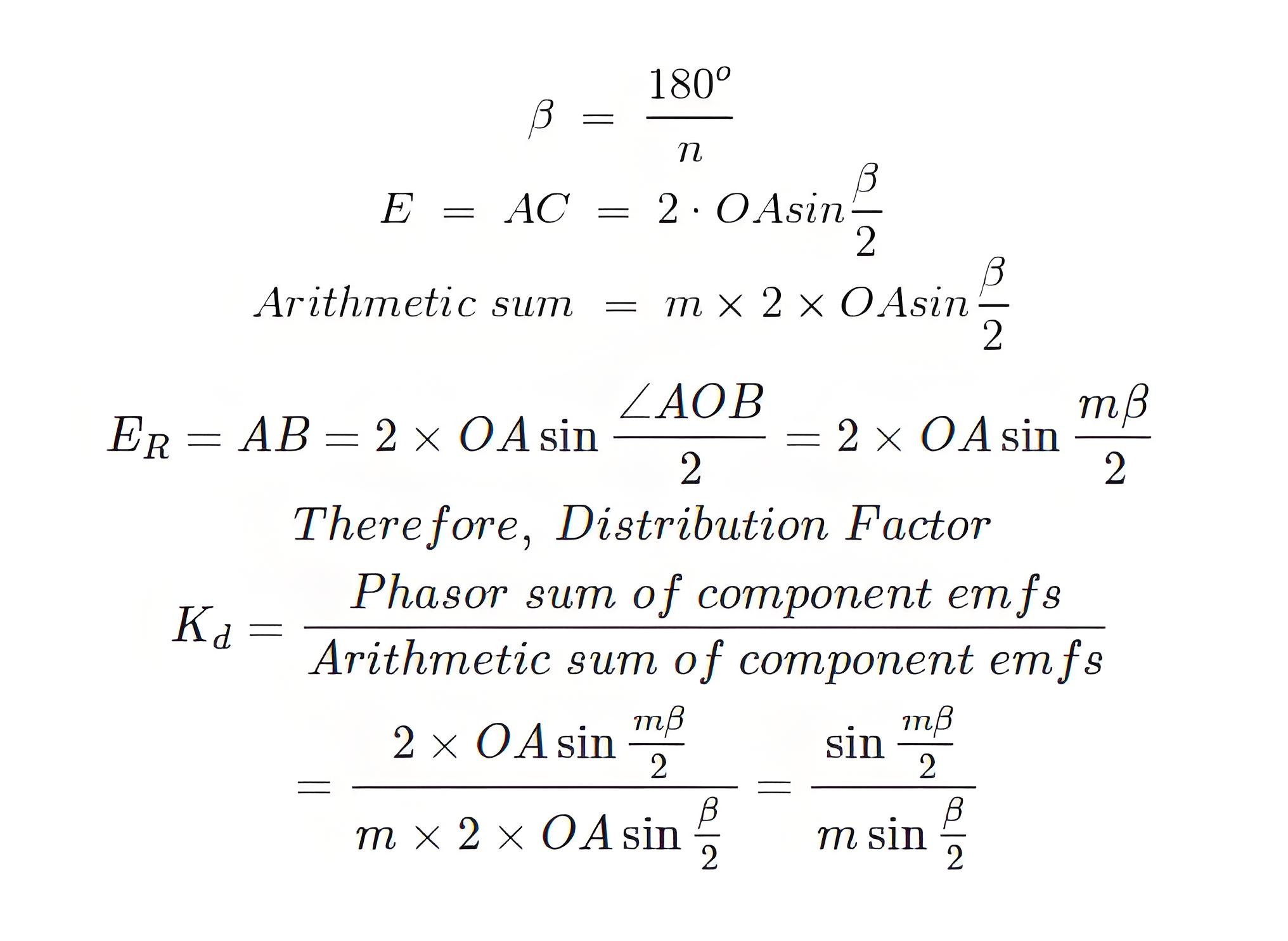
Let the number of slots per pole be n.
The number of slots per phase per pole is m.
The induced electromotive force on the coil side is Ec.

The angular displacement between the slots,
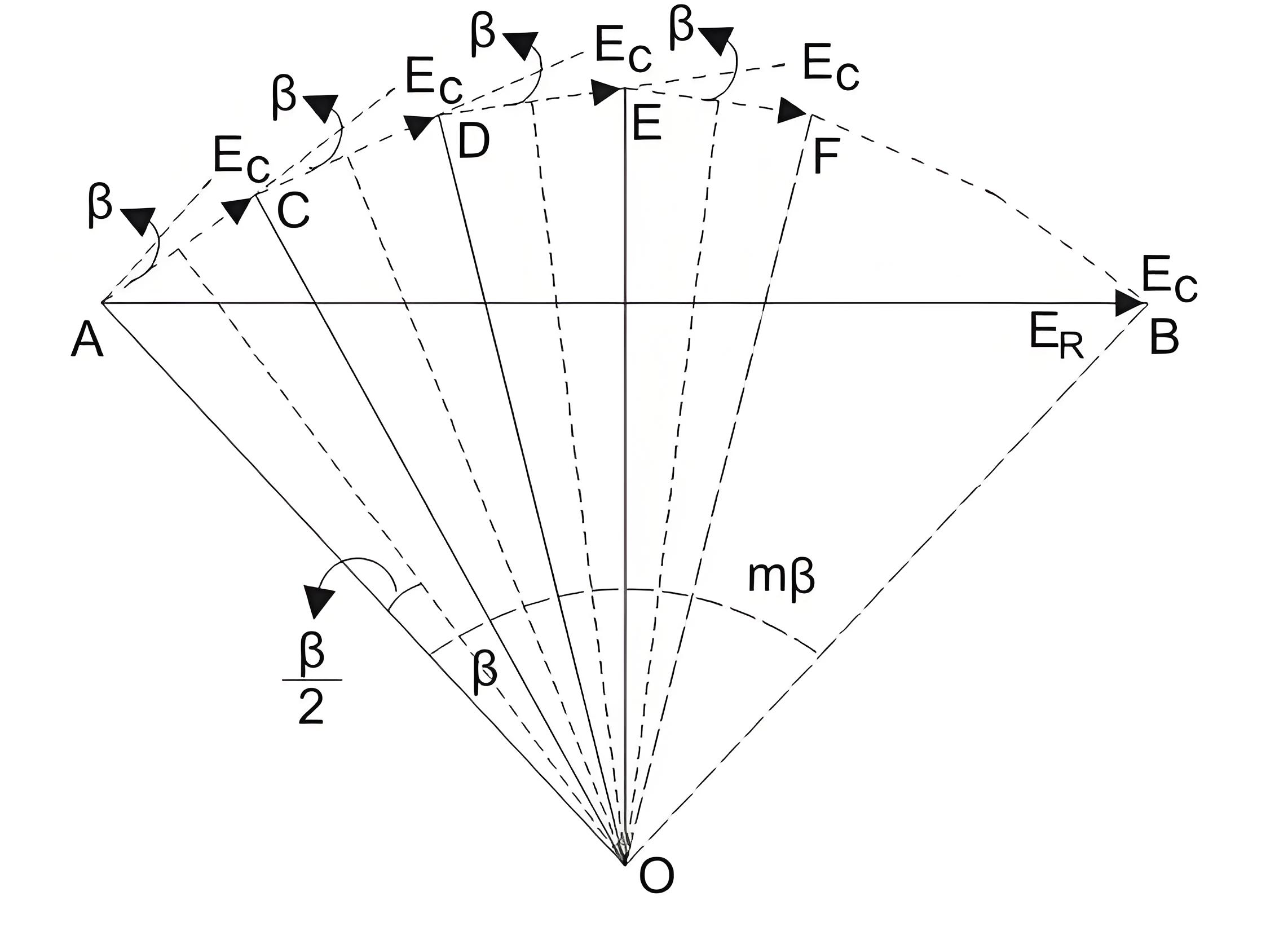
We represent the electromotive force induced by a phase of different coils under one pole, such as AC, DC, DE, EF, etc. They are equal in size, but they differ from each other by an Angle β.
If we draw bisectors on AC, CD, DE, EF -- They will sense the common point O.EMM on each coil side
To meet,
Since the slot per phase per pole is m, that is, the total arithmetic sum of all induced electromotive forces per pole on each phase coil side,
The resultant electromotive force is AB, as shown in the figure.
Therefore, the electromotive force is synthesized
mβ is also known as electrical phase spread.
The distribution factor Kd is given by the equation as the fundamental component of EMF.
If the magnetic flux distribution contains spatial harmonics, then the slot Angle spacing of β on the fundamental wave scale will become the rβ harmonic component, so the distribution factor harmonic of r will be.
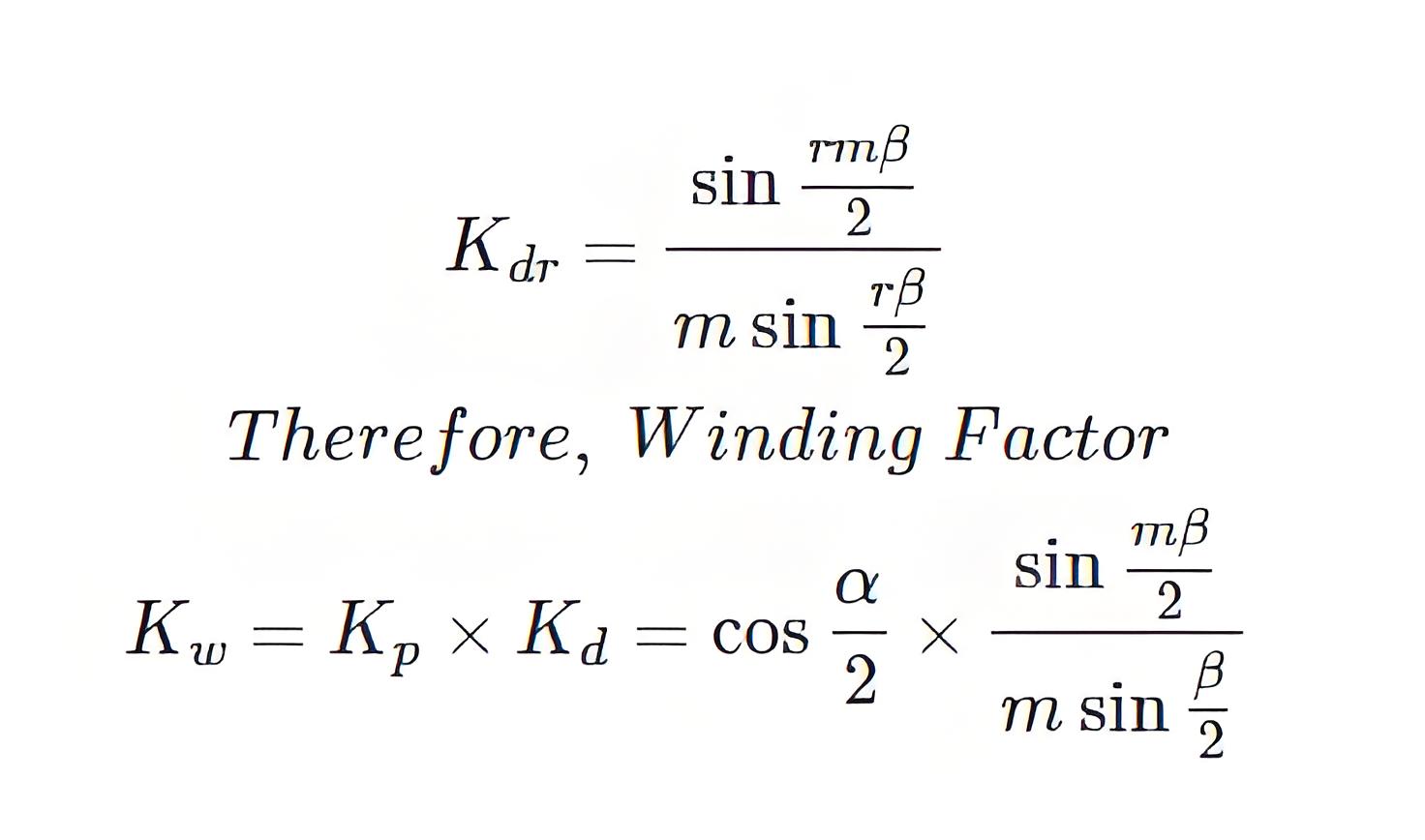
Harmonics in design
By choosing the appropriate chord Angle, designers can optimize the windings to reduce unnecessary harmonic effects.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













