Speed Control of a Synchronous Motor
Synchronous Motor Definition
Synchronous motors are defined as constant speed motors that run at the synchronous speed of the supply. They are typically used for constant speed operations and to improve the power factor under no load conditions. Synchronous motors also have fewer losses compared to induction motors of the same rating.
The speed of a synchronous motor is given by
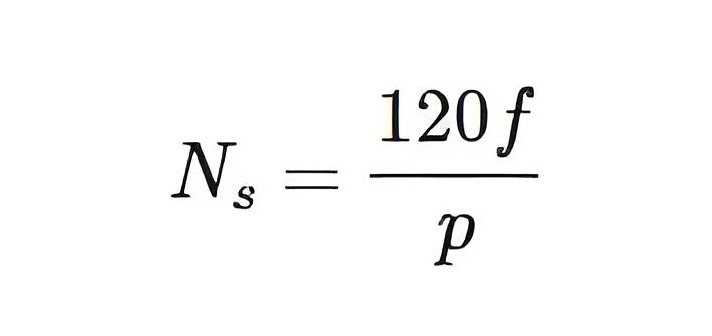
Where, f = supply frequency and p = number of poles.
The synchronous speed depends on the supply frequency and the number of poles on the rotor. Since changing the number of poles is difficult, it’s not used. However, with solid-state devices, we can vary the current frequency to the synchronous motor. This allows us to control the motor’s speed by changing the supply frequency.
Speed Control Factors
The speed of a synchronous motor depends on the supply frequency and the number of poles, with frequency adjustment being the practical method for speed control.
Open Loop Control
Inverter fed open loop synchronous motor drive uses variable frequency without feedback, suitable for less precise speed control needs.
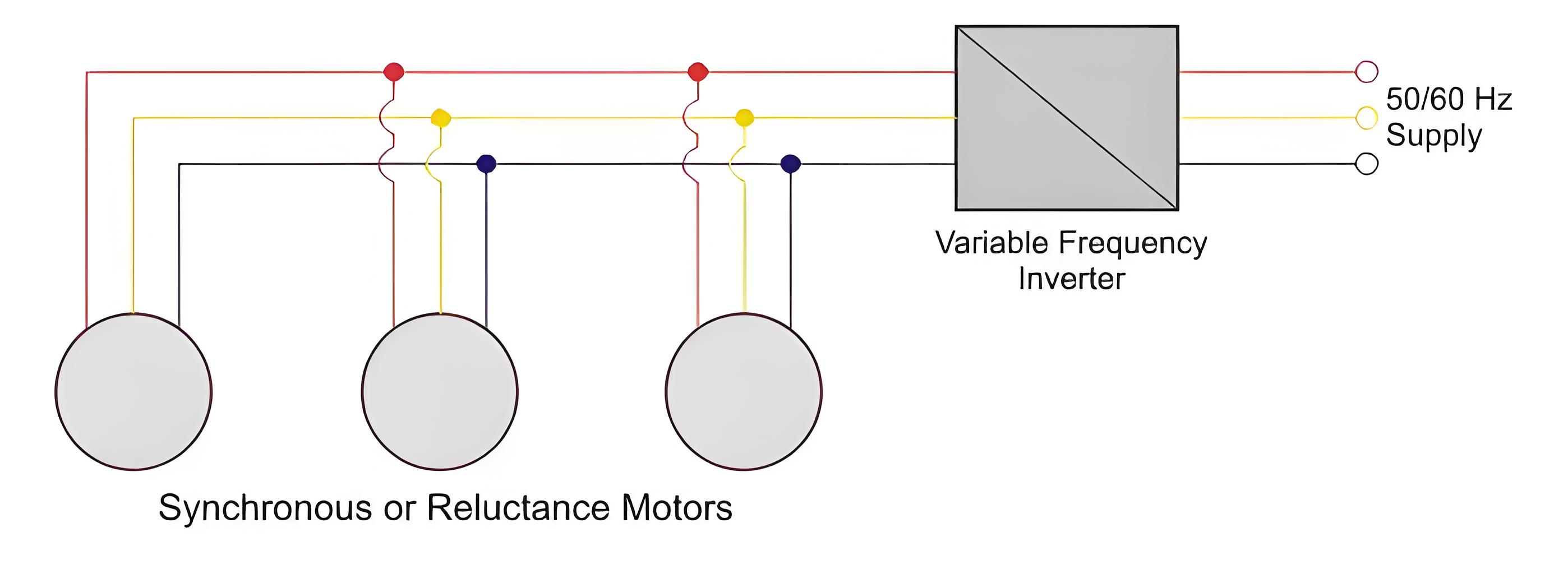
Closed Loop Operation
Self-synchronous (closed-loop) operation provides accurate speed control by adjusting frequency based on rotor speed feedback, avoiding oscillations.
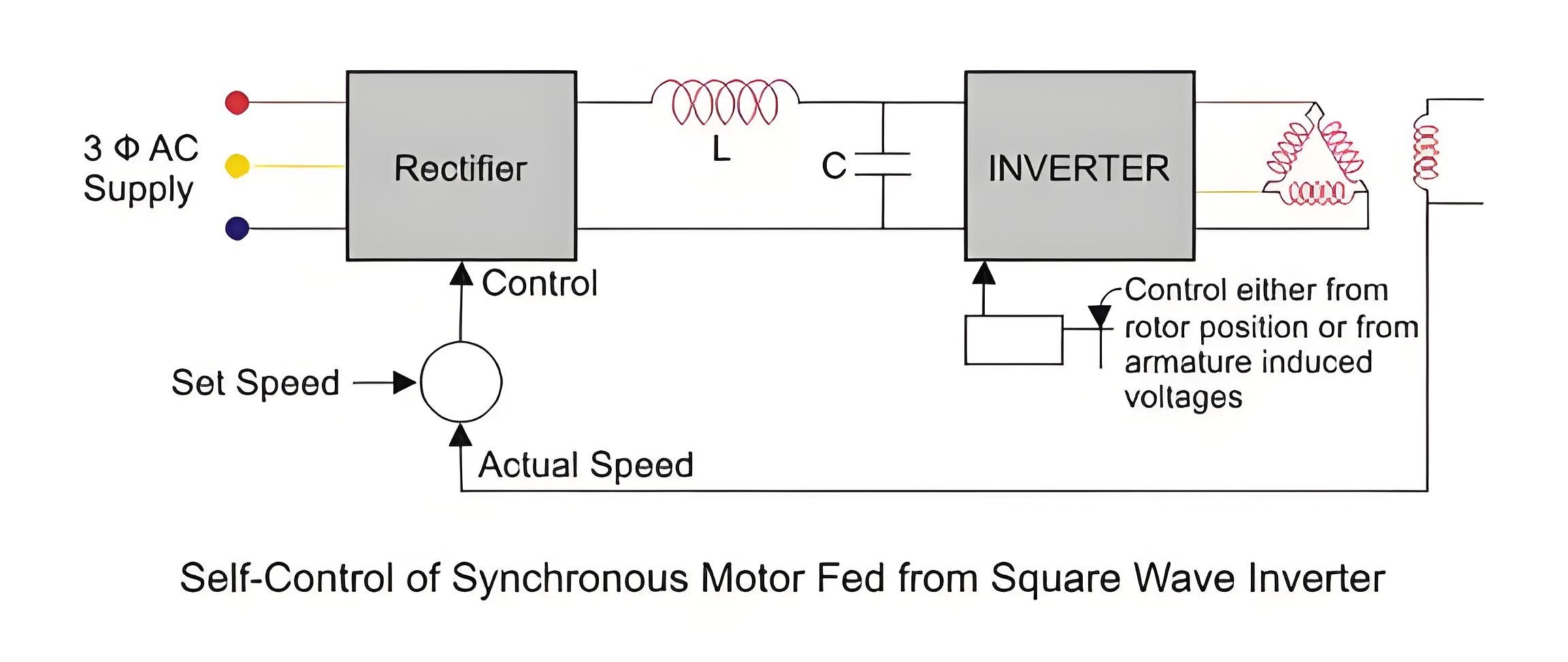
Speed Control of Synchronous Motor
Speed control of synchronous motor is achieved through varying the supply frequency using solid-state devices, rectifiers, and inverters.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













