Types of Electrical Drives
Definition of Electrical Drives
Electrical drives are systems that control the motion of electrical motors by adjusting power and operational parameters.
Types of Electrical Drives
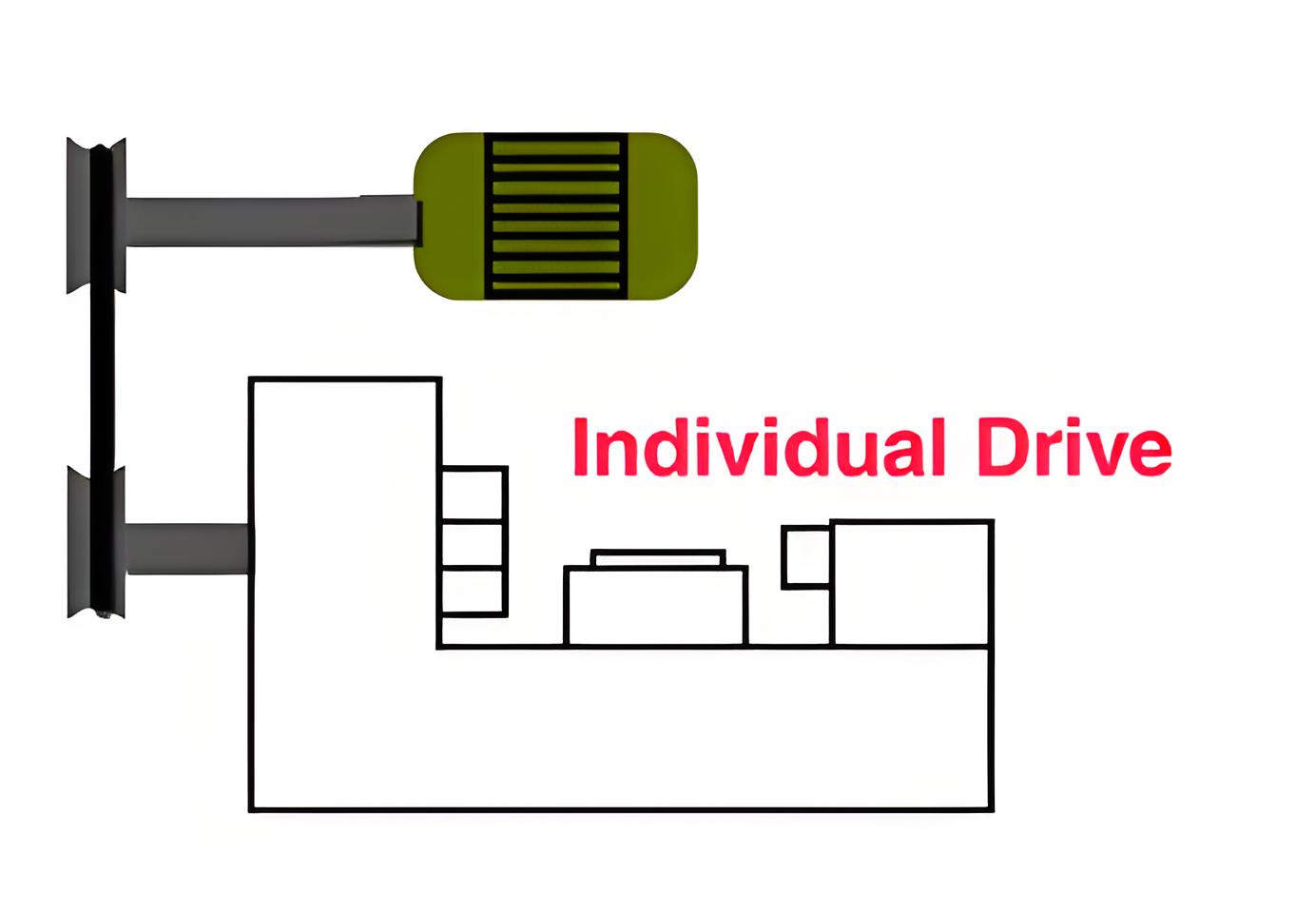
There are three main types—single-motor, group motor, and multi-motor drives, each suited for different applications.
Reversible vs. Non-Reversible Drives
Drives are classified as reversible or non-reversible based on their ability to change the direction of generated flux.
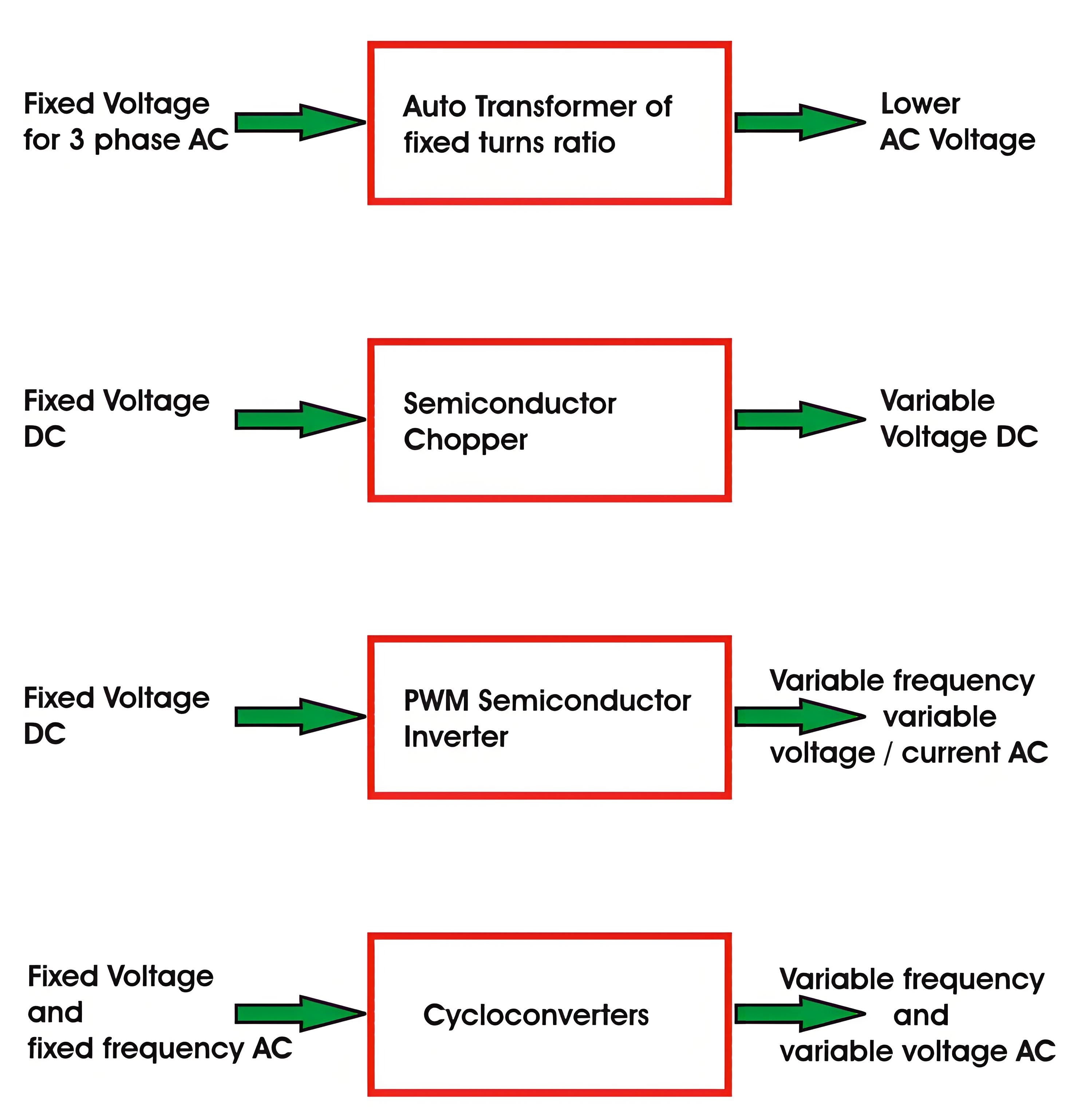
Converters can be divided into 5 types
AC to DC converters
AC regulators
Choppers or DC-DC converters (i.e. a DC Chopper)
Inverters
Cycloconverters

Parts of Electrical Drives
The primary components include load, motor, power modulator, control unit, and source, all crucial for the drive’s operation.
Advantages of Electrical Drives
These drives are available in wide range torque, speed and power.The control characteristics of these drives are flexible. According to load requirements these can be shaped to steady state and dynamic characteristics. As well as speed control, electric braking, gearing, starting many things can be accomplished.
The are adaptable to any type of operating conditions, no matter how much vigorous or rough it is.
They can operate in all the four quadrants of speed torque plane, which is not applicable for other prime movers.
They do not pollute the environment.
They do not need refueling or preheating, they can be started instantly and can be loaded immediately.
They are powered by electrical energy which is atmosphere friendly and cheap source of power.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













