What is a Servo Motor Controller ?
What is a Servo Motor Controller ?
Servo Motor Controller Definition
A servo motor controller (or servo motor driver) is defined as a circuit used to control the position of a servo motor.
Servo Motor Driver Circuit
The servo motor driver circuit includes a micro-controller, power supply, potentiometer, and connectors, ensuring precise motor control.
Micro-controller Role
The micro-controller generates PWM pulses at specific intervals to control the servo motor’s position accurately.
Power Supply
The power supply design for a servo motor controller depends on the number of connected motors. Servo motors typically use a 4.8V to 6V supply, with 5V being standard. Exceeding the supply voltage can damage the motor. The current draw varies with the torque and is lower in idle mode and higher when running. The maximum current draw, known as stall current, can reach up to 1A for some motors.
For single motor control, use a voltage regulator like LM317 with a heat sink. For multiple motors, a high-quality power supply with a higher current rating is necessary. An SMPS (Switched Mode Power Supply) is a good choice.
Block Diagram below-showing interconnections in a Servo Motor Driver
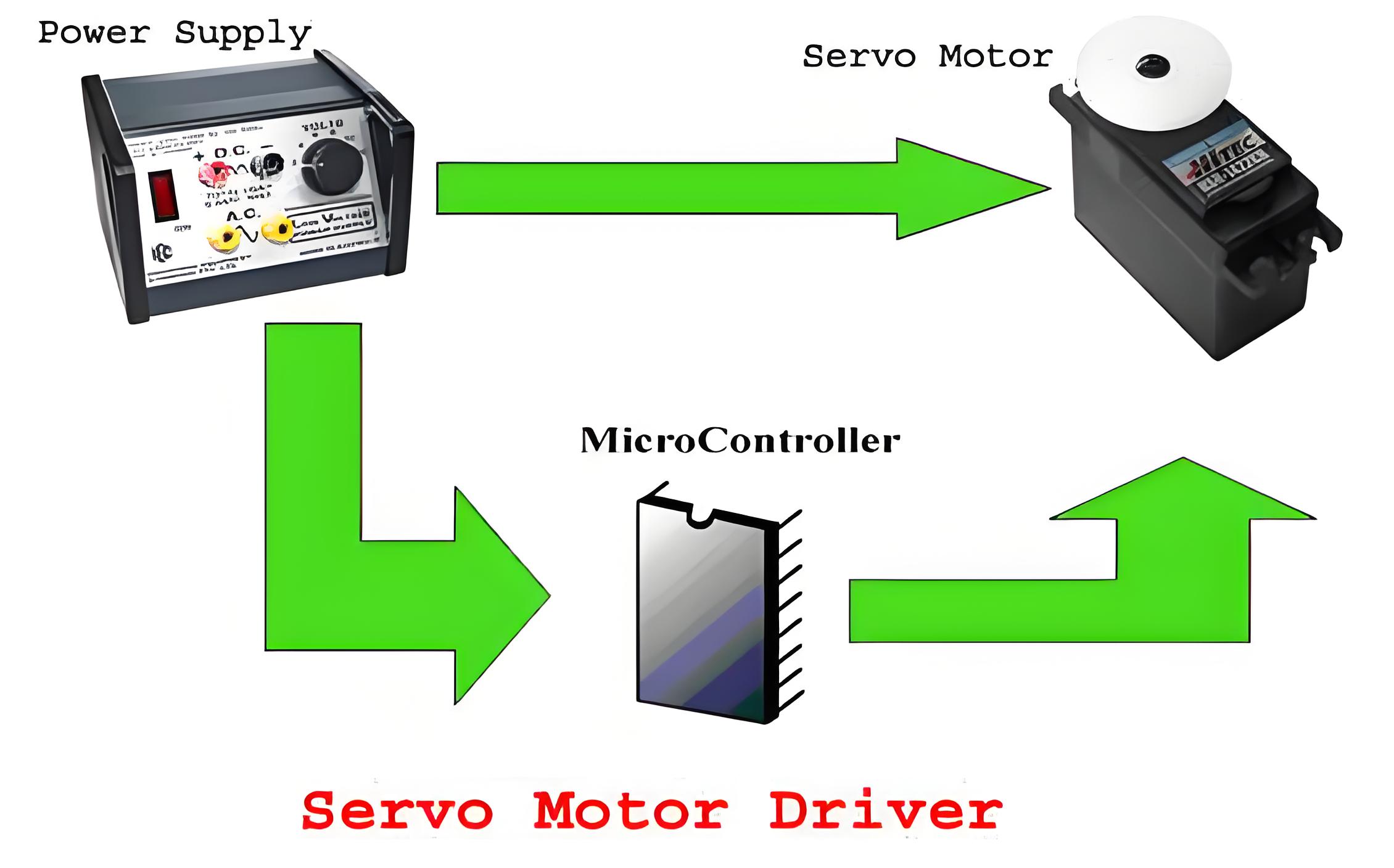
Controlling Servo Motor
The servo motor has three terminals.
Position signal(PWM Pulses)
Vcc (From Power Supply)
Ground
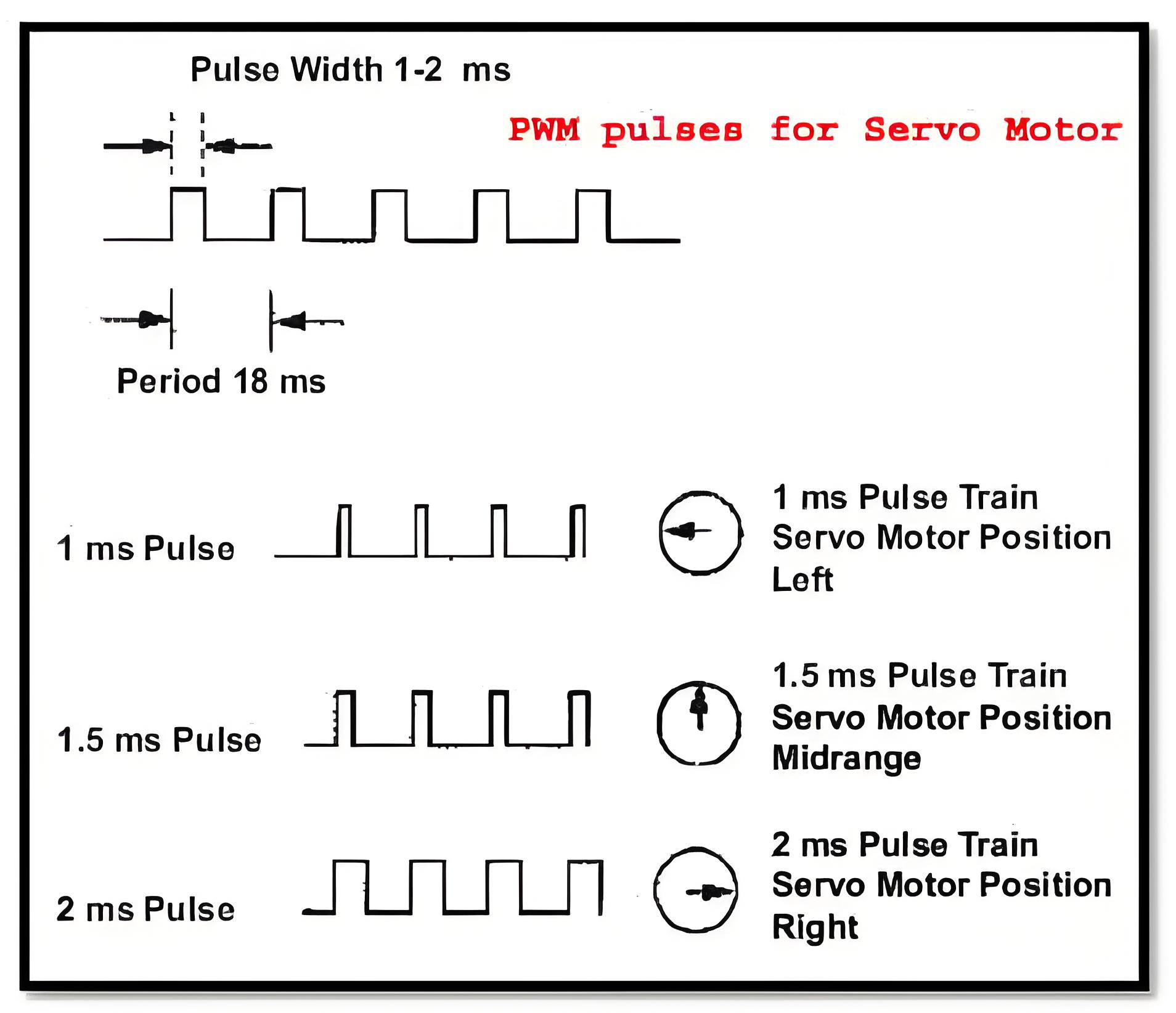
The servo motor’s angular position is controlled by applying PWM pulses of specific widths. The pulse duration ranges from about 0.5ms for 0-degree rotation to 2.2ms for 180-degree rotation. The pulses should be given at frequencies around 50Hz to 60Hz.
In order to generate the PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) waveform, as shown in the figure below, one can use either the internal PWM module of the micro-controller or the timers can be used. Using the PWM block is more flexible as most micro-controller families design, and this PWM block better suits the needs of applications such as a servo motor. For different widths of PWM pulses, we need to program the internal registers accordingly.
Now, we also need to tell the microcontroller how much it has to rotate. For this purpose, we can use a simple potentiometer and use an ADC to get the rotation angle or for more complex applications an accelerometer can be used.
Program Algorithm
Let us design the Program to control a single servo and the position input is given via the potentiometer connected to a pin of controller.
Nitialize the port pins for input/output.
Read the ADC for desired servo position.
Program the PWM registers for the desired value.
As soon as you trigger the PWM module, the selected PWM channel pin goes high (logic 1) and after the required width is reached, it will again go low (logic 0). So after triggering the PWM, you must start a timer with a delay of about 19 ms and wait until the timer overflowsGo to step 2
There are various modes of PWM available which you can use depending on the microcontroller you choose. Some degree of optimization should be done in the code to control the servo.
If you plan to use more than one servo than you will require as many PWM channels. Each servo can be given the PWM signal sequentially. But you must take care that the pulse repetition rate for each servo is maintained. Otherwise the servo will run out of synchronization.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













