What is a Hysteresis Motor?
What is a Hysteresis Motor?
Hysteresis Motor Definition
A hysteresis motor is defined as a synchronous motor that uses hysteresis losses in its rotor A hysteresis motor is defined as a synchronous motor with a cylindrical rotor that operates using hysteresis losses in the rotor made of hardened steel with high retentivity. It is a single-phase motor, and its rotor is made of ferromagnetic material with non-magnetic support over the shaft.
Hysteresis Motor Construction
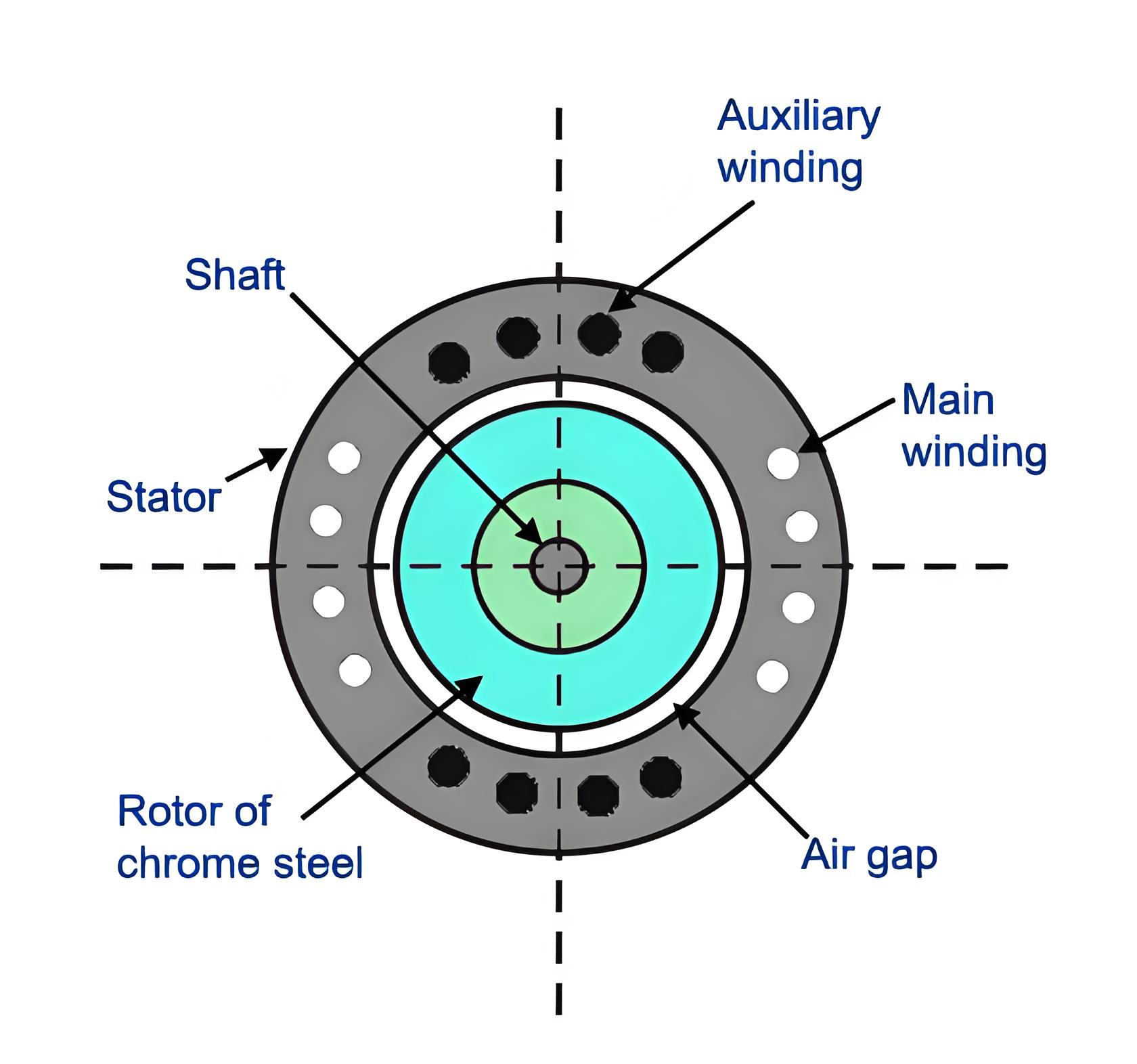
Single phase stator winding
Shaft
Shading coil
Stator
The stator of a hysteresis motor is designed to produce a synchronous revolving field from a single-phase supply. It carries two windings: the main winding and the auxiliary winding. In some designs, the stator also includes shaded poles.
Rotor
Rotor of hysteresis motor is made of magnetic material that has high hysteresis loss property. Example of this type of materials is chrome, cobalt steel or alnico or alloy. Hysteresis loss becomes high due to large area of hysteresis loop.
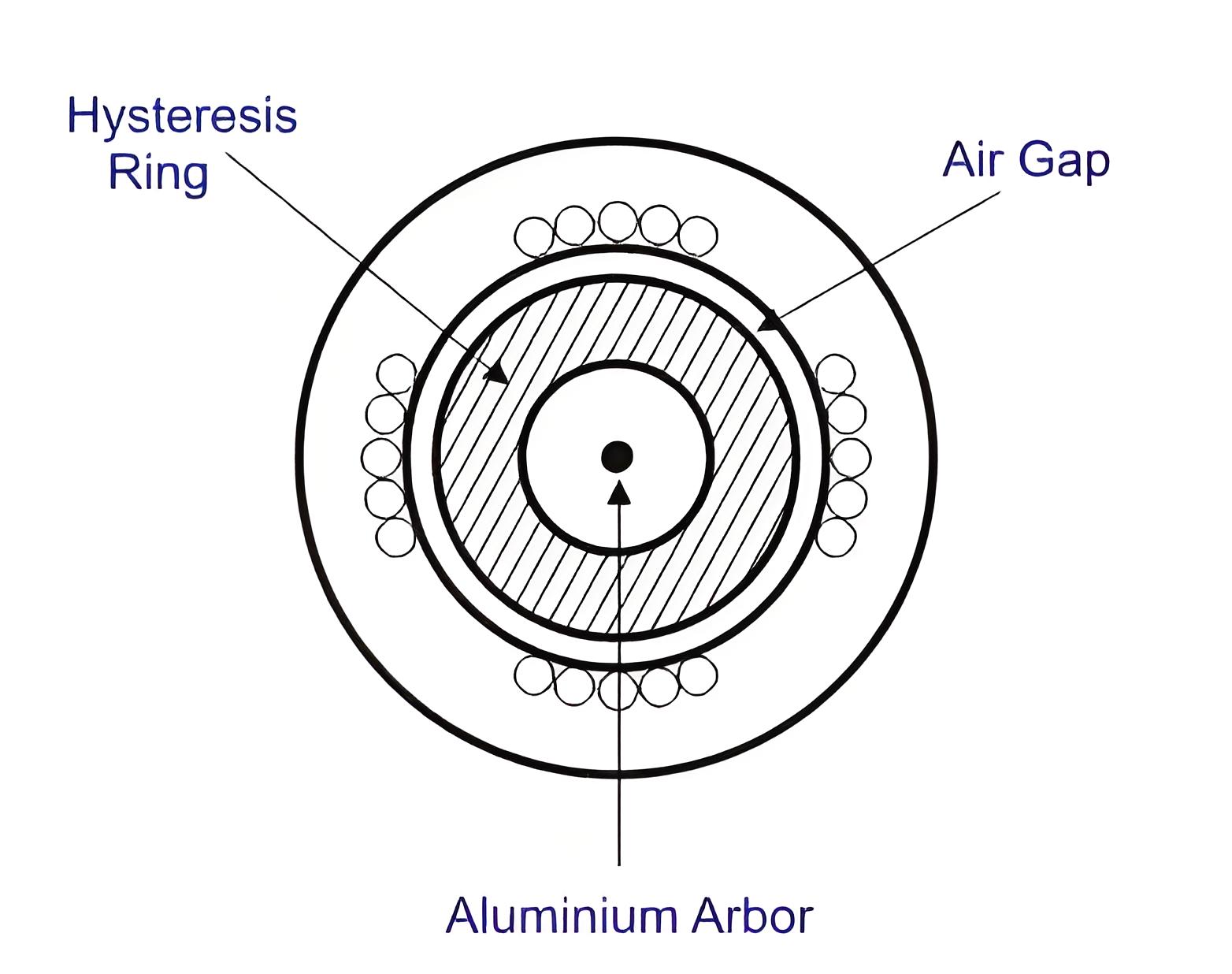
Working Principle
Starting behavior of a hysteresis motor is like a single phase induction motor and running behavior is same as a synchronous motor. Step by step its behavior can be realized in the working principle that is given below.
When stator is energized with single phase AC supply, rotating magnetic field is produced in stator.
To maintain the rotating magnetic field the main and auxiliary windings must be supplied continuously at start as well as in running conditions.
At the start, the rotating magnetic field in the stator induces a secondary voltage in the rotor. This generates eddy currents in the rotor, causing it to develop torque and start rotating.
Thus eddy current torque is developed along with the hysteresis torque in the rotor. Hysteresis torque in the rotor develops as the rotor magnetic material is with high hysteresis loss property and high retentivity.
The rotor goes under the slip frequency before going to the steady state running condition.
So it can be said that when the rotor starts to rotate with the help of these eddy current torque due to induction phenomenon, it behalves like a single phase induction motor.
Hysteresis Power Loss
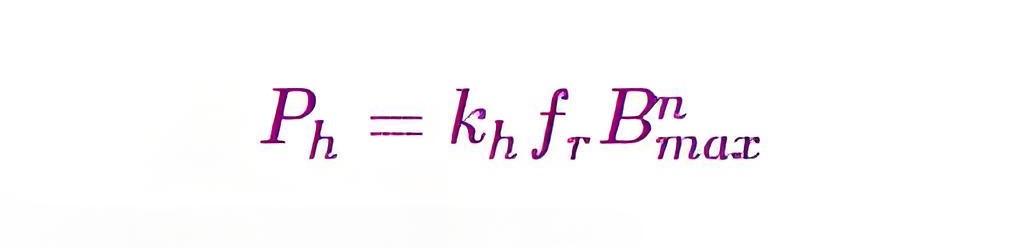
f r is the frequency of flux reversal in the rotor (Hz)
Bmax is the maximum value of flux density in the air gap (T)
Ph is the heat-power loss due to hysteresis (W)
kh is the hysteresis constant
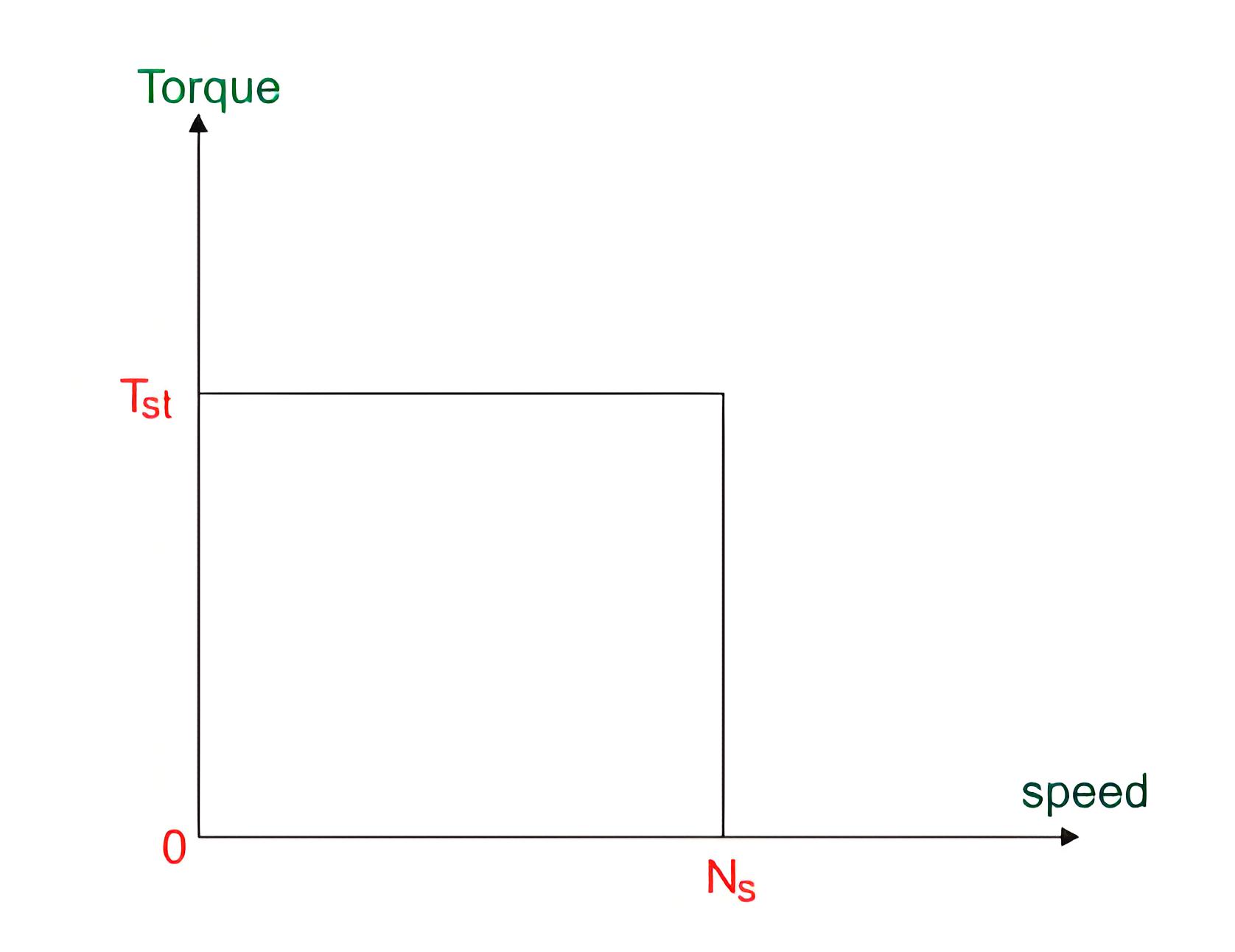
Torque-Speed Characteristics
The hysteresis motor has a constant torque-speed characteristic, making it reliable for various loads.
Types of Hysteresis Motors
Cylindrical hysteresis motors: It has cylindrical rotor.
Disk hysteresis motors: It has annular ring shaped rotor.
Circumferential-Field hysteresis motor: It has rotor supported by a ring of non magnetic material with zero magnetic permeability.
Axial-Field hysteresis motor: It has rotor supported by a ring of magnetic material with infinite magnetic permeability.
Advantages of Hysteresis Motor
As no teeth and no winding in rotor, no mechanical vibrations take place during its operation.
Its operation is quiet and noiseless as there is no vibration.
It is suitable to accelerate inertia loads.
Multi-speed operation can be achieved by employing gear train.
Disadvantages of Hysteresis Motor
Hysteresis motor has poor output that is one-quarter of output of an induction motor with same dimension.
Low efficiency
Low torque.
Low power factor
This type of motor is available in very small size only.
Applications
Sound producing equipments
Sound recording instruments
High quality record players
Timing devices
Electric clocks
Teleprinters
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













