Duty Cycle of Motor
Motor Duty Class Definition
Nowadays, electric motors are used in almost every application, controlled by electrical drives. However, not all motors operate for the same amount of time. Some run continuously, while others have shorter run times with longer rest periods. This difference introduces the concept of motor duty class, which divides motor duty cycles into eight categories:
Continuous duty
Short time duty
Intermittent periodic duty
Intermittent periodic duty with starting
Intermittent periodic duty with starting and braking
Continuous duty with intermittent periodic loading
Continuous duty with starting and braking
Continuous duty with periodic speed changes
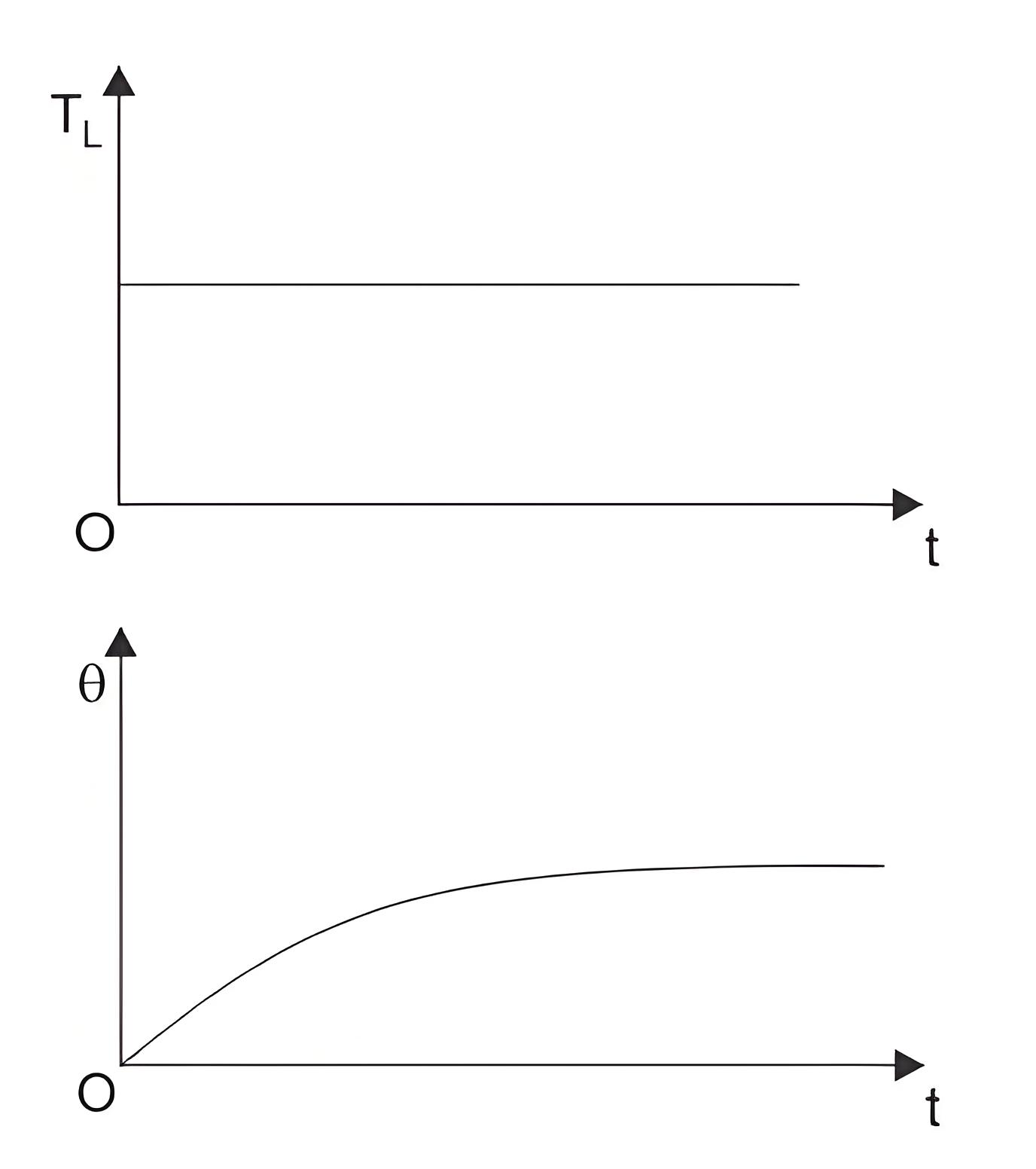
Continuous Duty
This duty denotes that, the motor is running long enough AND the electric motor temperature reaches the steady state value. These motors are used in paper mill drives, compressors, conveyors etc.
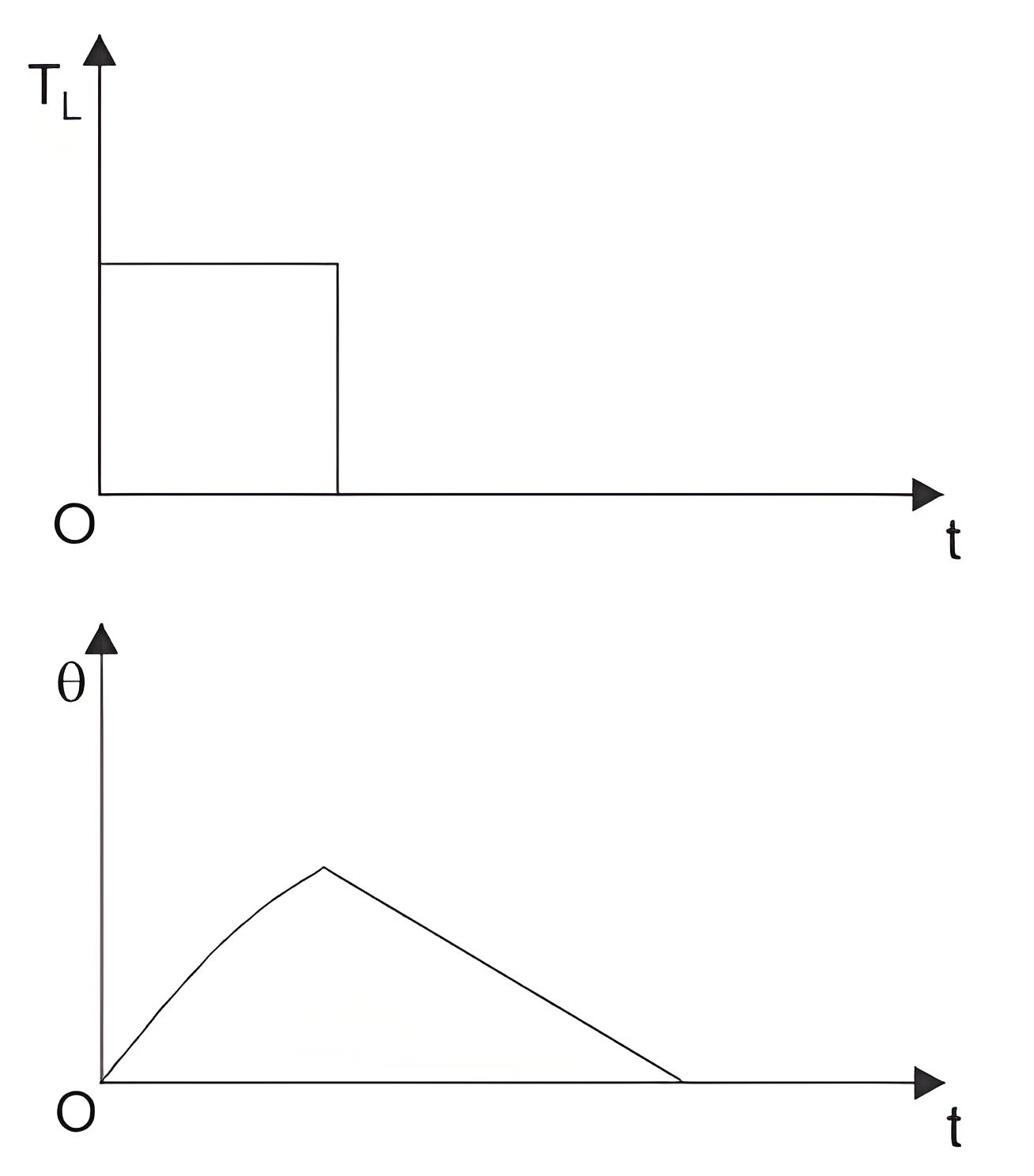
Short Time Duty
These motors operate for short periods, and their heating time is much less than their cooling time. Thus, the motor cools down to ambient temperature before operating again. These motors are used in crane drives, household appliances, and valve drives.
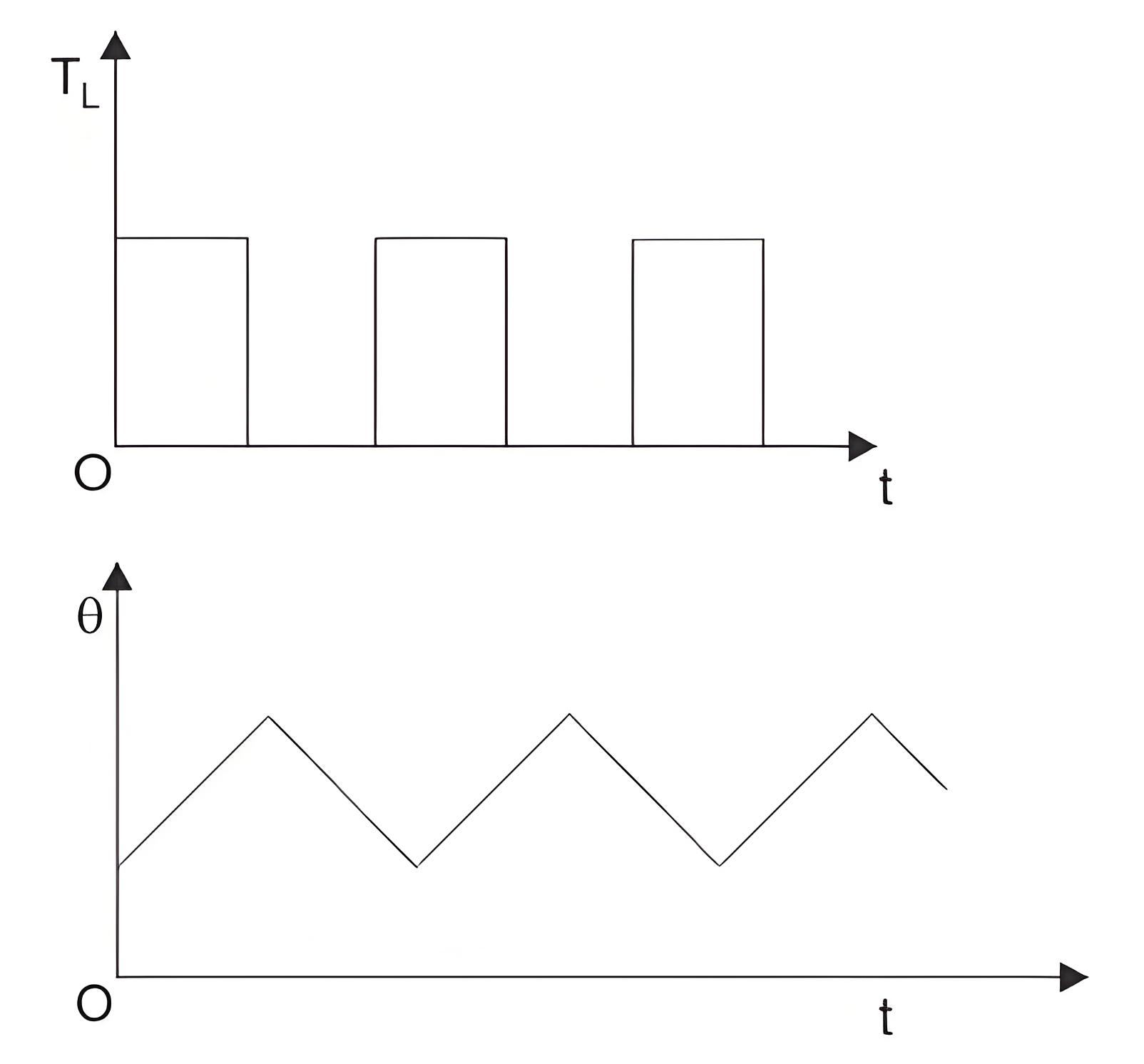
Intermittent Periodic Duty
In this duty, the motor runs for a while and then rests. Neither period is long enough to reach steady state temperature or cool down completely. This type is used in press and drilling machine drives.
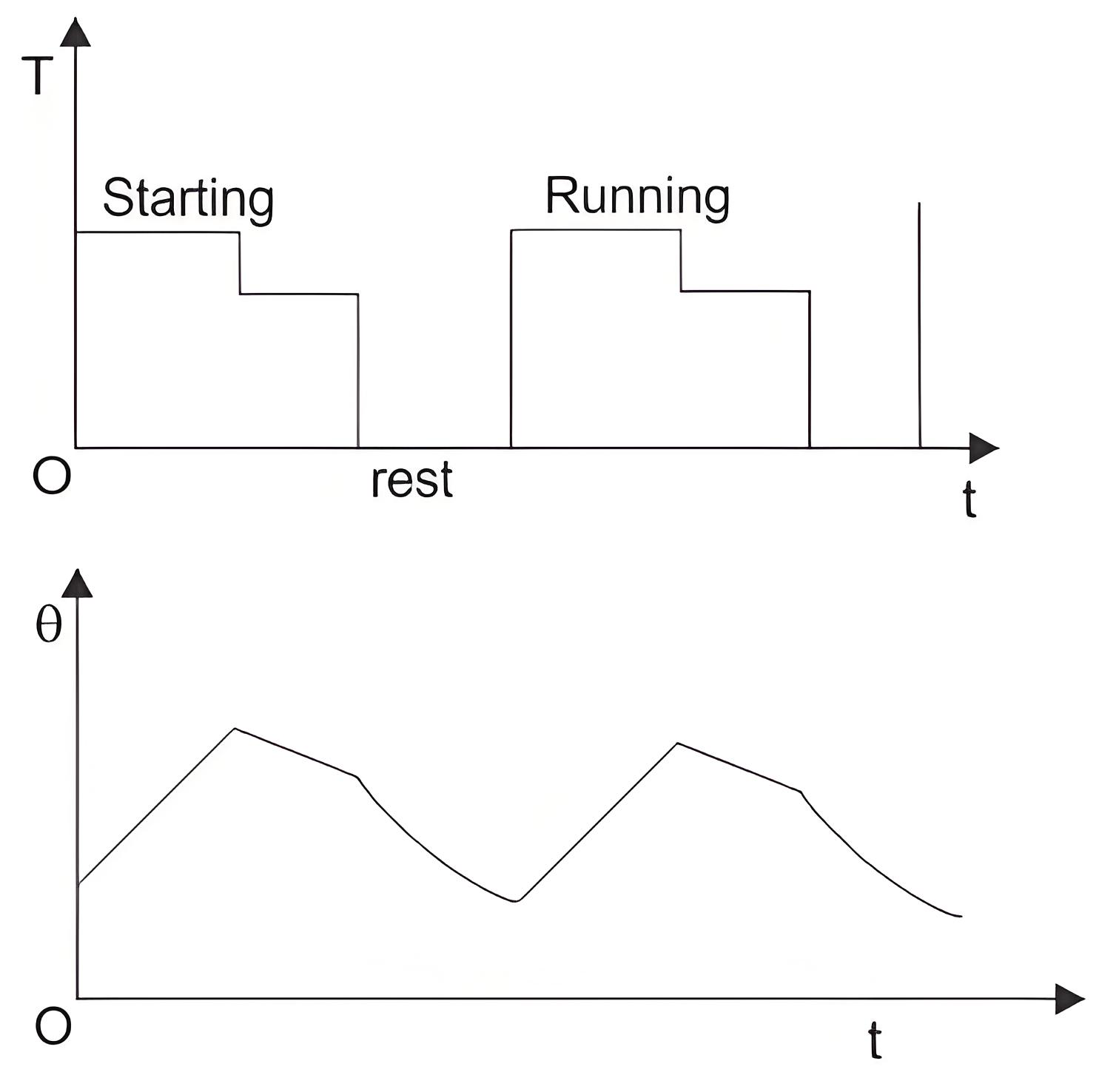
Intermittent Period Duty with Starting
In this type of drives, heat loss during starting and braking cannot be ignored. So, the corresponding periods are starting period, operating period, braking period and resting period, but all the periods are too short to attain the respective steady state temperatures, these techniques are used in billet mill drive, manipulator drive, mine hoist etc.
Continuous Duty with Intermittent Periodic Loading
This motor duty is similar to periodic duty, but it includes a no-load running period instead of a rest period. Examples include pressing and cutting machines.
Continuous Duty with Starting and Braking
It is also a period of starting, running and braking and there is no resting period. The main drive of a blooming mill is an example.
Continuous Duty with Periodic Speed Changes
In this type of motor duty, there are different running periods at different loads and speeds. But there is no rest period and all the periods are too short to attain the steady state temperatures.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













