Why is it that when an inductor produces high voltage and not a high current?
When an inductor collapses (for example, when a switch in the inductor circuit suddenly opens), it produces a high voltage rather than a high current. This can be explained by the basic properties of an inductor and its energy storage mechanism. Here is a detailed explanation:
Basic Properties of an Inductor
The fundamental property of an inductor can be expressed by the following formula:
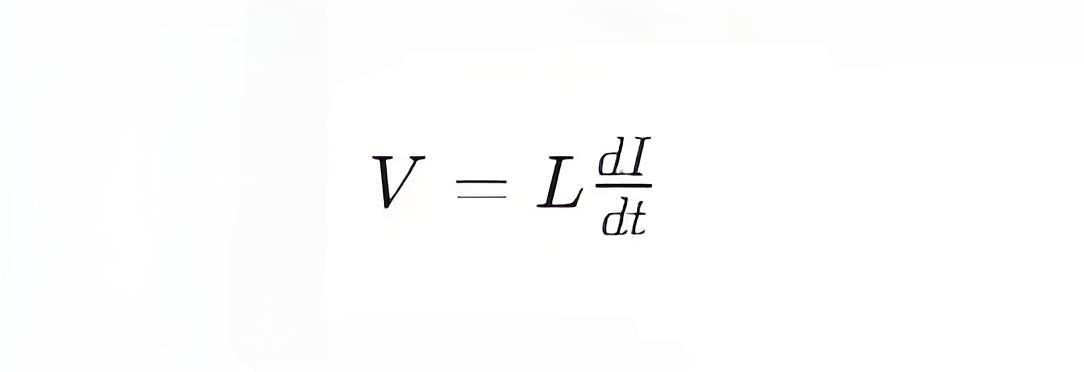
where:
V is the voltage across the inductor.
L is the inductance of the inductor.dI/dt is the rate of change of current with respect to time.
This formula indicates that the voltage across the inductor is proportional to the rate of change of current. In other words, an inductor resists rapid changes in current.
Energy Storage
An inductor stores energy when current flows through it, and this energy is stored in the magnetic field. The energy
E stored in an inductor can be expressed by the following formula:
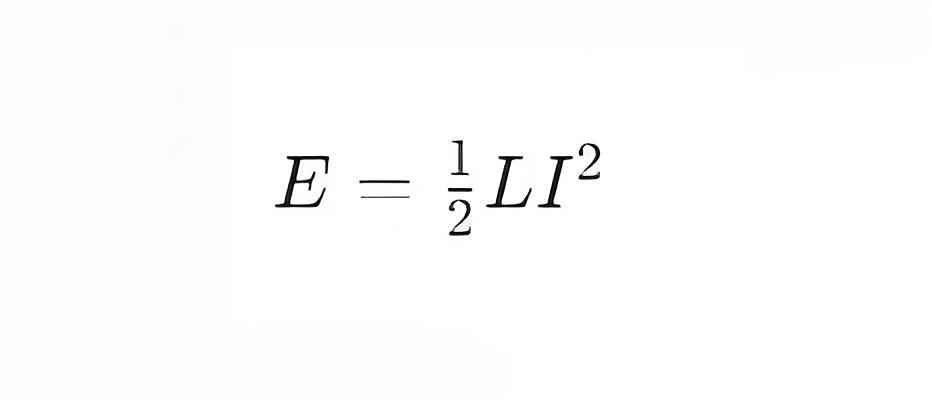
where:
E is the stored energy.
L is the inductance.
I is the current flowing through the inductor.
When the Switch Opens
When a switch in the inductor circuit suddenly opens, the current cannot instantly drop to zero because the magnetic field in the inductor needs time to release its stored energy. Since the current cannot change instantaneously, the inductor attempts to maintain the existing current flow.
However, because the switch has opened, the path for the current is cut off. The inductor cannot continue to maintain the current, so it generates a very high voltage across its terminals. This high voltage tries to force the current to continue flowing, but since the circuit is broken, the current cannot pass, and the inductor releases its stored energy through the high voltage.
Mathematical Explanation
According to the voltage-current relationship of an inductor V=L(dI/dt)when the switch suddenly opens, the current I must drop to zero very quickly. This means that the rate of change of current dI/dt becomes very large, resulting in a very high voltage V.
Practical Phenomenon
In practical circuits, this high voltage can cause spark discharges or damage other components in the circuit. To prevent this, a diode (known as a flyback diode or freewheeling diode) is often connected in parallel with the inductor. This allows the current to continue flowing through the diode when the switch opens, thus avoiding the generation of excessively high voltages.
Summary
When a switch in an inductor circuit suddenly opens, a high voltage is produced instead of a high current because the inductor tries to maintain the existing current flow. However, since the circuit is broken, the current cannot continue to flow, and the inductor releases its stored energy by generating a high voltage. This high voltage is due to the very large rate of change of current dI/dt.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













