What is a Current Transformer ?
What is a Current Transformer ?
Current Transformer Definition
A current transformer (CT) is defined as an instrument transformer where the secondary current is proportional to the primary current and ideally has zero phase difference.
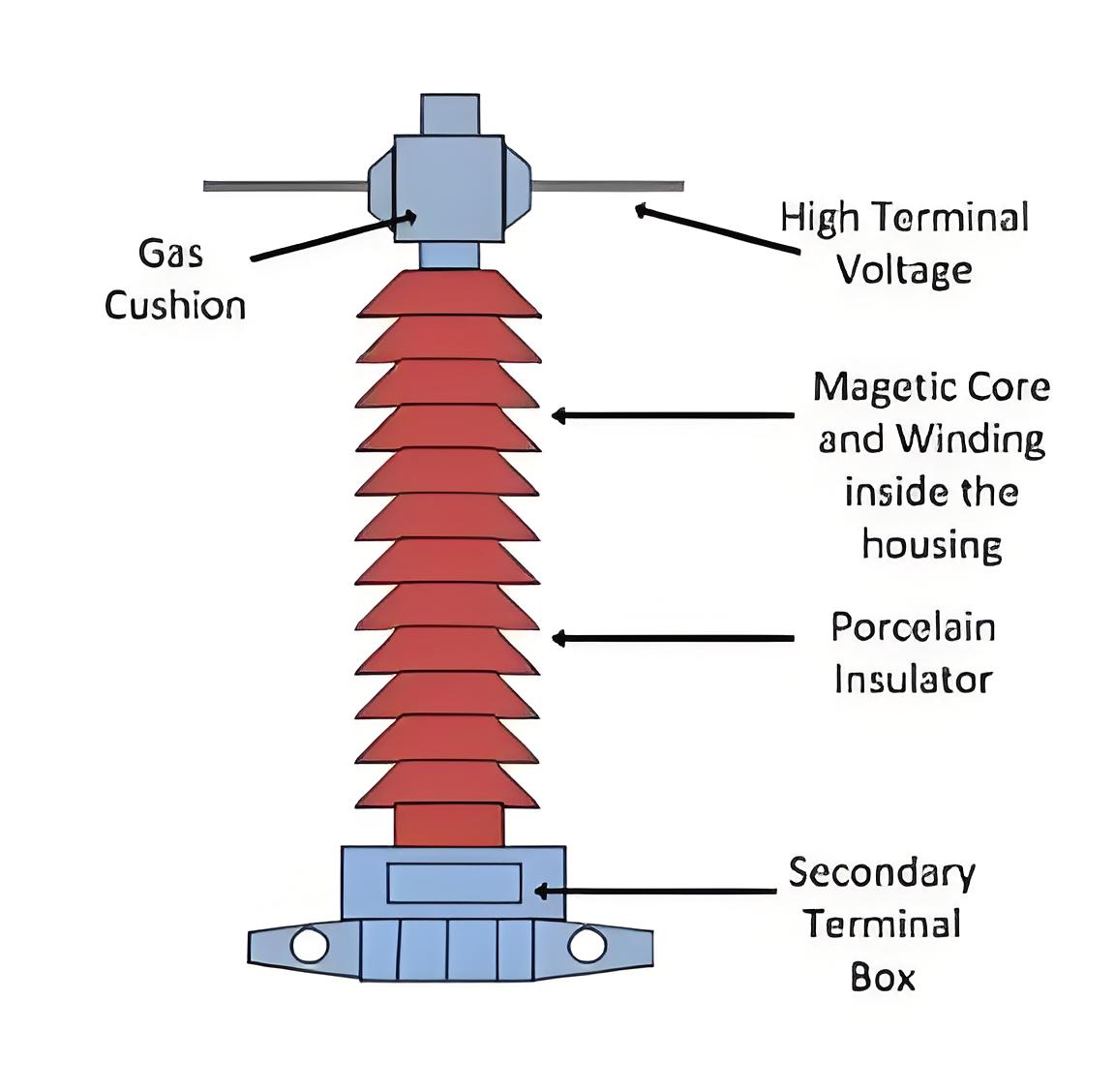
CT Accuracy Clas
The accuracy class of a current transformer measures how accurately the CT replicates the primary current in its secondary, crucial for precise metering.
Working Principle
Current transformers operate on the principle of a power transformer, where the primary current is the system current, and the secondary current depends on the primary current.
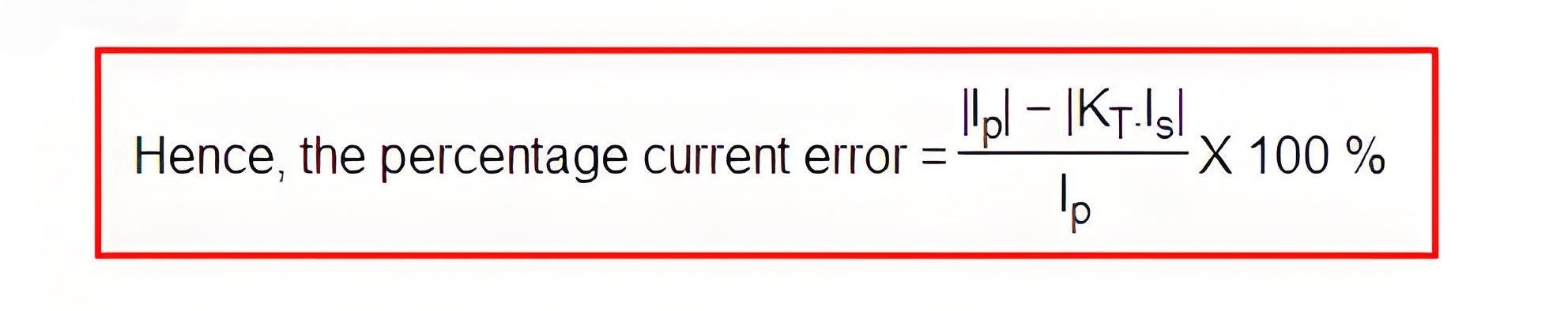
Ratio Error in Current Transformer
Ratio error in current transformer occurs when the primary current isn’t perfectly mirrored in the secondary current due to core excitation.
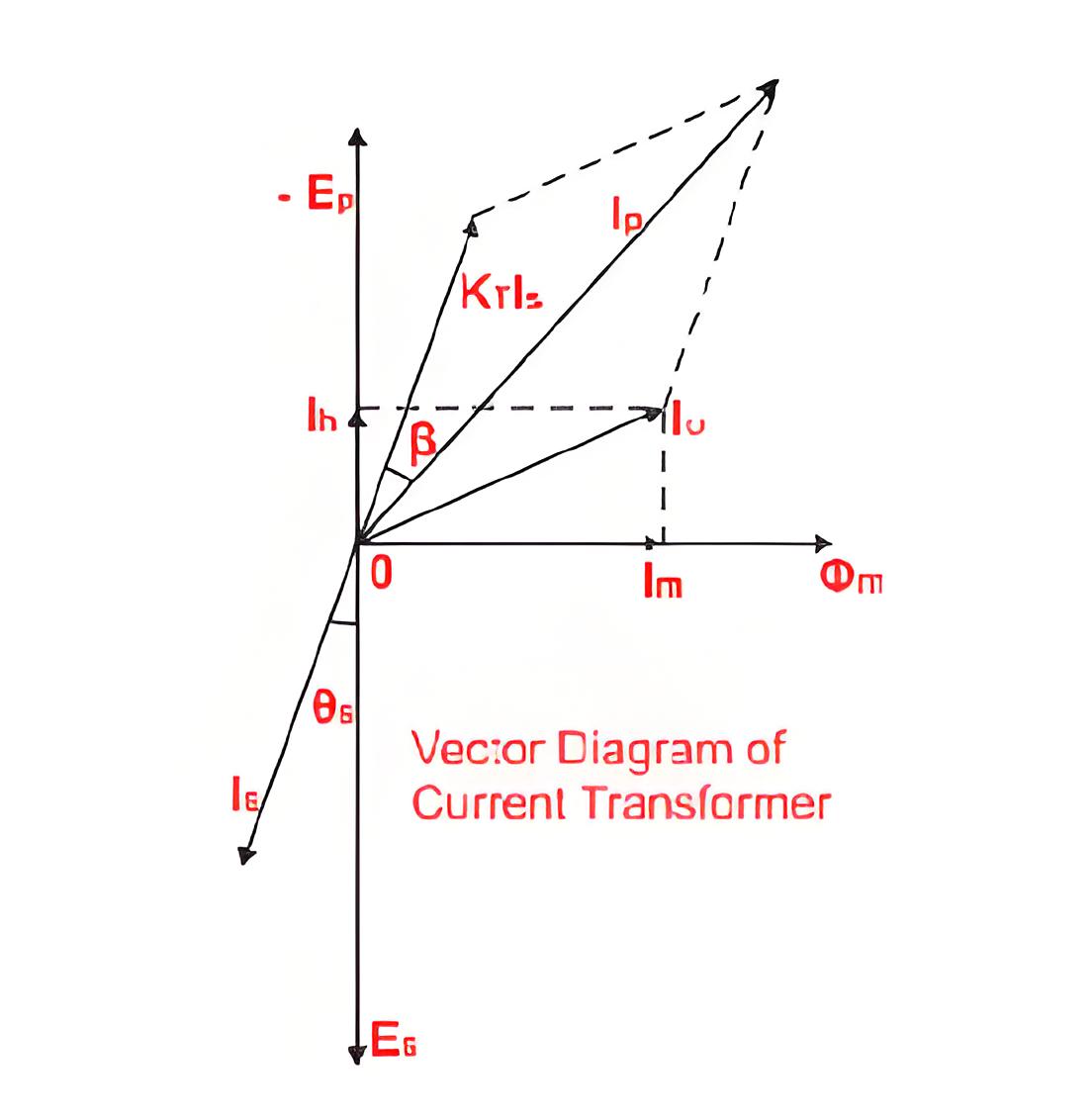
Is – Secondary current.
Es – Secondary induced emf.
Ip – Primary current.
Ep – Primary induced emf.
KT – Turns ratio = Numbers of secondary turns/number of primary turns.
I0 – Excitation current.
Im – Magnetizing component of I0.
Iw – Core loss component of I0.
Φm – Main flux.
Reducing CT Errors
Using a core of high permeability and low hysteresis loss magnetic materials.
Keeping the rated burden to the nearer value of the actual burden.
Ensuring minimum length of flux path and increasing cross-sectional area of the core, minimizing joint of the core.
Lowering the secondary internal impedance.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













