Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor
The Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motor also features a cage rotor, and it has two windings, namely the main winding and the auxiliary winding, which are similar to those in a Capacitor Start motor and a Capacitor Start Capacitor Run motor. However, in a PSC motor, there is only one capacitor that is connected in series with the starting winding. This capacitor remains permanently connected within the circuit, functioning both during the starting process and when the motor is running.
The connection diagram of a Permanent Split Capacitor motor is illustrated as follows:
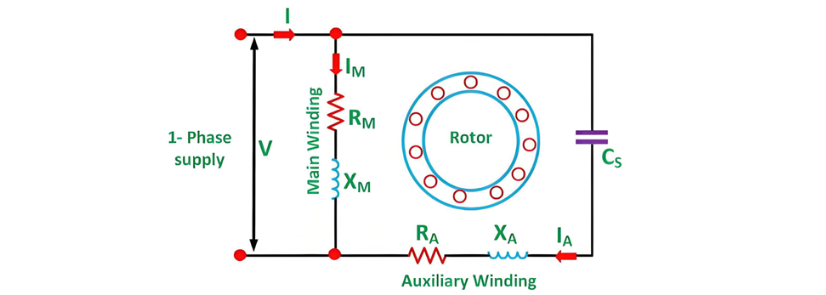
It is also known as a Single Value Capacitor motor. Since the capacitor remains constantly in the circuit, this type of motor does not incorporate any starting switch. The auxiliary winding is always present in the circuit. As a result, the motor functions as a balanced two-phase motor, generating a uniform torque and operating without noise.
Advantages of Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor
The Single Value Capacitor motor offers the following benefits:
- There is no requirement for a centrifugal switch.
- It has a high efficiency.
- With the capacitor permanently connected in the circuit, it exhibits a high power factor.
- It possesses a relatively high pullout torque.
Limitations of Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor
The limitations of this motor are as follows:
In this motor, a paper capacitor is utilized because an electrolytic capacitor cannot be used for continuous operation. The cost of the paper capacitor is higher, and its size is larger compared to an electrolytic capacitor of the same rating.
It has a low starting torque, which is less than the full load torque.
Applications of Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) Motor
The Permanent Split Capacitor motor has diverse applications, as listed below:
- It is used in fans and blowers of heaters and air conditioners.
- It is employed in the compressors of refrigerators.
- It is applied in office machinery.
This concludes the introduction to the Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motor.