What is the normal slip of an induction motor?
The slip (s) of an induction motor is an important parameter that measures the difference between the rotor speed and the synchronous speed of the rotating magnetic field. Slip is typically expressed as a percentage and is calculated using the following formula:
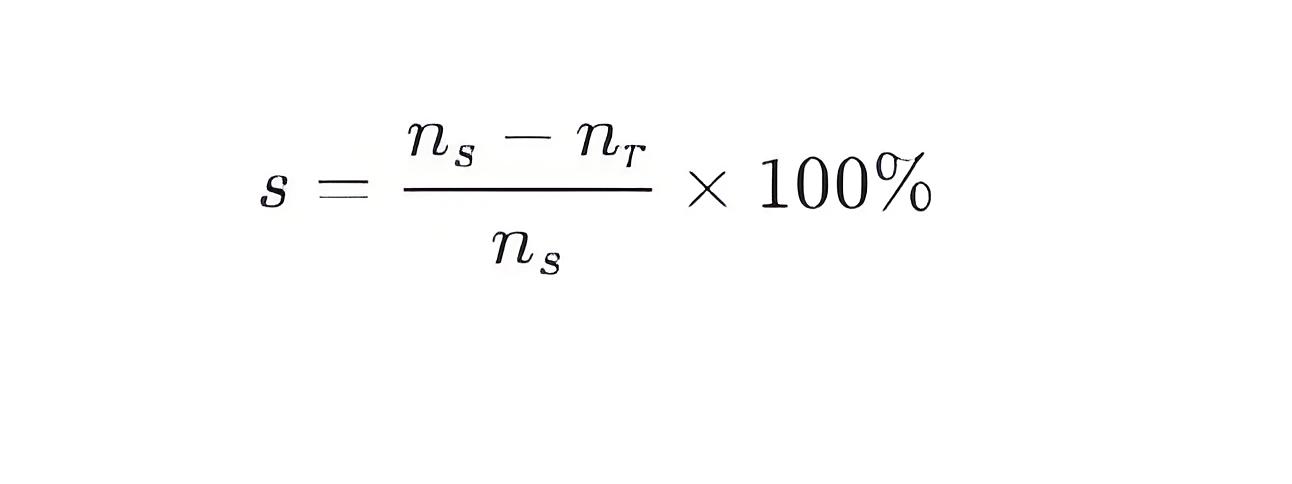
Where:
s is the slip (%)
ns is the synchronous speed (rpm)
nr is the actual rotor speed (rpm)
Normal Slip Range
For most induction motors, the normal slip range is typically between 0.5% and 5%, depending on the motor design and application. Here are some typical slip ranges for common types of induction motors:
Standard Design Induction Motors:
Slip is usually between 0.5% and 3%.
For example, a 2-pole induction motor operating at 50 Hz has a synchronous speed of 3000 rpm. Under normal operating conditions, the rotor speed might be between 2970 rpm and 2995 rpm.
High Starting Torque Design Induction Motors:
Slip may be slightly higher, typically between 1% and 5%.
These motors are designed for applications requiring high starting torque, such as pumps and compressors.
Low-Speed Design Induction Motors:
Slip is generally lower, typically between 0.5% and 2%.
These motors are designed for low-speed, high-torque applications, such as heavy machinery and conveyors.
Factors Affecting Slip
Load:
An increase in load causes the rotor speed to decrease, resulting in a higher slip.
At light loads, the slip is lower; at heavy loads, the slip is higher.
Motor Design:
Different designs and manufacturing processes can affect the slip of the motor. For example, high-efficiency motors typically have lower slip.
Supply Frequency:
Changes in supply frequency affect the synchronous speed, which in turn affects the slip.
Temperature:
Temperature variations can affect the resistance and magnetic properties of the motor, thereby influencing the slip.
Summary
The normal slip of an induction motor is typically between 0.5% and 5%, with the specific range depending on the motor design and application. Understanding and monitoring the slip helps ensure that the motor operates optimally, improving system efficiency and reliability.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













