What is the effect of increasing the number of poles in an induction motor?
Increasing the number of poles in an induction motor can have several impacts on the motor's performance. Here are the main effects:
1. Reduced Speed
Synchronous Speed Formula: The synchronous speed ns of an induction motor can be calculated using the following formula:
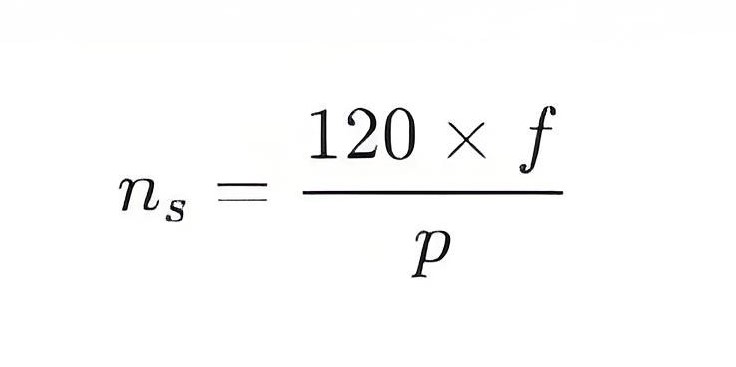
where f is the supply frequency (in Hz) and p is the number of pole pairs (half the number of poles).
Speed Reduction: Increasing the number of poles means increasing the number of pole pairs p, which reduces the synchronous speed ns. For example, increasing the number of poles from 4 (2 pole pairs) to 6 (3 pole pairs) at a supply frequency of 50 Hz would reduce the synchronous speed from 1500 rpm to 1000 rpm.
2.Increased Torque
Torque Density: Increasing the number of poles can enhance the motor's torque density. More poles mean a denser magnetic flux distribution, resulting in greater torque for the same current.
Starting Torque: Increasing the number of poles typically increases the motor's starting torque, making it easier to start heavy loads.
3. Changes in Mechanical Characteristics
Torque-Speed Characteristic: Increasing the number of poles alters the motor's torque-speed characteristic curve. Generally, multipole motors exhibit higher torque at lower speeds, making them suitable for applications requiring high starting torque.
Slip: Slip s is the difference between the actual speed
n and the synchronous speed ns. Increasing the number of poles can increase slip, as the motor is more likely to produce slip at lower speeds.
4. Size and Weight
Size Increase: Increasing the number of poles typically increases the physical size of the motor. More poles require more space for magnetic poles and windings, which can increase the diameter and length of the motor.
Weight Increase: Due to the increase in size, the weight of the motor will also increase, which can affect installation and transportation.
5. Efficiency and Power Factor
Efficiency: Increasing the number of poles may slightly reduce the motor's efficiency due to higher iron losses and copper losses from the additional poles and windings.
Power Factor: Multipole motors typically have a lower power factor because they require more reactive power to establish strong magnetic fields.
6. Application Domains
Low-Speed Applications: Multipole motors are suitable for applications that require low speed and high torque, such as pumps, fans, conveyors, and heavy machinery.
High-Speed Applications: Few-pole motors are suitable for applications that require high speed and low torque, such as fans, centrifuges, and high-speed machine tools.
Summary
Increasing the number of poles in an induction motor reduces its synchronous speed, increases torque density and starting torque, changes the torque-speed characteristics, increases mechanical size and weight, and may slightly reduce efficiency and power factor. Multipole motors are better suited for low-speed, high-torque applications, while few-pole motors are better for high-speed, low-torque applications.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













