What is the maximum number of poles that an induction motor can have?
There is no fixed upper limit for the maximum number of poles in an induction motor. However, in practical applications, the choice of pole number is constrained by several factors, including motor size, design complexity, efficiency, and cost. Here are some considerations regarding the number of poles in induction motors:
1. Motor Size and Speed
Relationship Between Pole Number and Speed: The synchronous speed n of an induction motor can be calculated using the following formula:
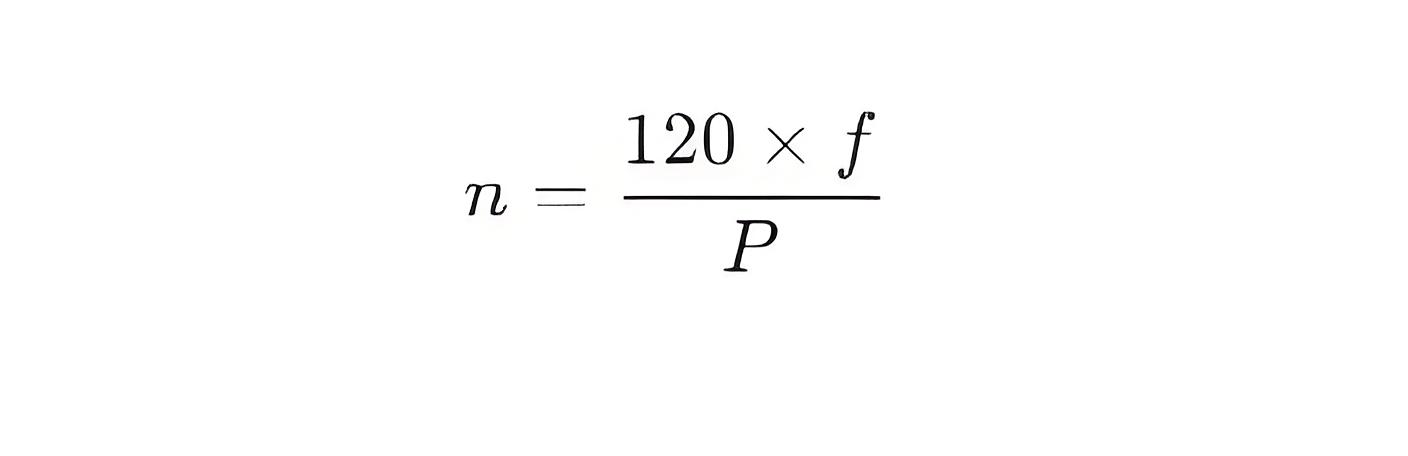
where f is the supply frequency (in Hz) and P is the number of poles.
Low-Speed Applications: For applications requiring low-speed operation, a higher number of poles can be chosen. For example, a 4-pole motor operating at 60 Hz has a synchronous speed of 1800 rpm, while a 12-pole motor has a synchronous speed of 600 rpm.
2. Design Complexity and Manufacturing Cost
Winding Design: As the number of poles increases, the design of the stator and rotor windings becomes more complex, leading to increased manufacturing difficulty and cost.
Heat Dissipation: More poles mean more windings and iron cores, which can cause heat dissipation issues, especially in high-power motors.
3. Efficiency and Performance
Efficiency: A higher number of poles can reduce the motor's efficiency due to increased copper and iron losses from more windings and iron cores.
Starting Performance: An increase in the number of poles may affect the motor's starting performance, particularly during low-speed starting.
4. Practical Applications
Common Pole Numbers: In practical applications, common pole numbers include 2-pole, 4-pole, 6-pole, 8-pole, 10-pole, and 12-pole motors. These pole numbers meet the requirements of most industrial and commercial applications.
Special Applications: In some specialized applications, such as low-speed high-torque applications, motors with more poles may be used. For example, motors in wind turbines and ship propulsion systems sometimes have more poles.
5. Extreme Cases
Theoretical Limit: Theoretically, the number of poles in an induction motor can be very high, but in practical applications, it is rarely more than 24 poles.
Extreme Examples: In some extreme cases, such as specialty motors or experimental motors, motors with even more poles may be designed, but these are typically not used in conventional industrial applications.
Summary
While there is no strict theoretical upper limit, in practical applications, the number of poles in an induction motor is usually not more than 24. Common pole numbers range from 2 to 12, which meet the requirements of most industrial and commercial applications. Choosing the appropriate number of poles involves a comprehensive consideration of motor size, speed requirements, design complexity, efficiency, and cost.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













