How can we identify the poles in induction motors?
Identifying the poles (magnetic poles) in an induction motor is an important step in understanding the motor's structure and operating principles. The position and number of poles determine the motor's performance and characteristics. The following are common methods to identify the poles in an induction motor:
1. Check the Motor Nameplate
Nameplate Information: The motor nameplate usually indicates the number of poles (P). For example, the nameplate might state "4P," indicating a 4-pole motor.
Pole Calculation: Using the number of poles and the frequency, you can calculate the synchronous speed of the motor. The formula for synchronous speed (n) is:
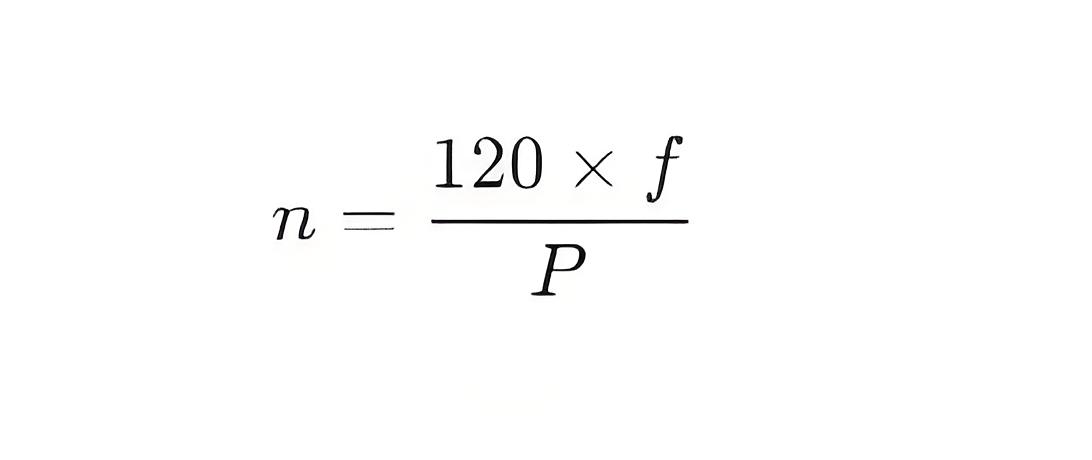
where
f is the supply frequency (in Hz) and
P is the number of poles.
2. Inspect the Stator Windings
Winding Distribution: The distribution of the stator windings can provide clues about the positions of the poles. Each pole corresponds to a set of windings, and the arrangement is typically symmetrical.
Winding Connections: Check the connections of the windings, particularly whether they are connected in a star (Y) or delta (Δ) configuration. The connection method can provide information about the number and position of the poles.
3. Use a Flux Detector
Flux Detector: Using a flux detector (such as a Hall effect sensor) can help detect the magnetic field distribution on the surface of the motor. By measuring the strength and direction of the magnetic field, you can determine the positions of the poles.
Procedure:
Place the flux detector close to the surface of the stator.
Move the detector along the stator surface and record changes in the magnetic field strength and direction.
Determine the positions of the poles based on the changes in the magnetic field.
4. Use Doppler Effect
Ultrasonic Sensor: Using an ultrasonic sensor can detect changes in the magnetic field while the motor is running. By analyzing the Doppler effect of the ultrasonic signals, you can determine the positions of the poles.
Procedure:
Place the ultrasonic sensor near the motor.
Start the motor and record changes in the ultrasonic signals.
Analyze the signal changes to determine the positions of the poles.
5. Inspect the Rotor Slots
Rotor Slots: The slots (or teeth) on the rotor can also provide clues about the positions of the poles. The number and distribution of rotor slots typically correspond to the poles of the stator windings.
Slot Distribution: Inspect the distribution of the rotor slots, especially when the motor is stopped. The distribution of the slots can indicate the positions of the poles.
6. Use an Oscilloscope
Oscilloscope: Using an oscilloscope to observe the voltage waveforms of the motor windings can help determine the positions of the poles.
Procedure:
Connect the oscilloscope probes to the terminals of the motor windings.
Start the motor and record the voltage waveforms of the windings.
Analyze the waveform changes to determine the positions of the poles.
7. Consult the Motor Manual
Technical Manual: Consult the technical manual or documentation provided by the manufacturer, which often includes detailed information about the motor's poles.
Diagrams and Charts: The technical manual may contain diagrams and charts showing the motor's structure and winding distribution, which can visually display the positions of the poles.
Summary
Identifying the poles in an induction motor can be achieved through various methods, including checking the motor nameplate, inspecting the stator windings, using a flux detector, using the Doppler effect, inspecting the rotor slots, using an oscilloscope, and consulting the motor manual. Each method has its own advantages and applicable scenarios, and combining multiple methods can provide a more accurate determination of the pole positions.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













