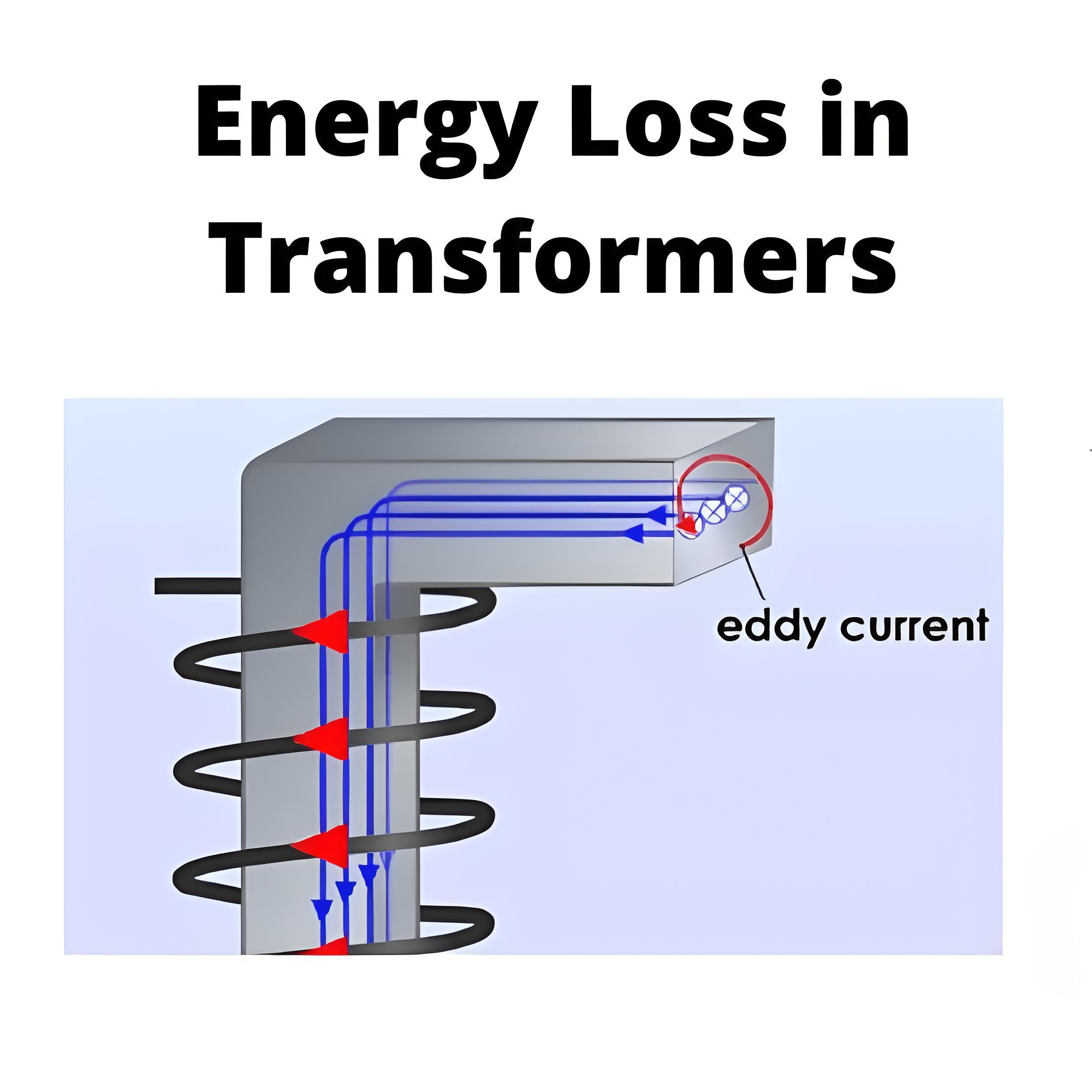
Loss evaluation in transformers based on IEC 60076
I. Definitions of Losses in IEC 6007
IEC 60076-1 (General Requirements) and IEC 60076-7 (Loading Guidelines) specify two core types of losses:
No-load Loss (P0)
Definition: Losses measured when the primary winding is energized at rated voltage and the secondary winding is open-circuited (dominated by core losses).
Test Conditions
- Measured at rated frequency and voltage (typically sinusoidal power frequency).
- Corrected to reference temperature (75°C for oil-immersed transformers, 115°C for dry-type).
Load Loss (Pk)
Definition: Losses measured when the secondary winding is short-circuited and rated current flows through the primary winding (dominated by copper losses).
Test Conditions:
- Measured at rated current and frequency.
- Corrected to reference temperature (75°C for oil-immersed; varies for dry-type based on insulation class).
II. Testing and Calculation of Losses
No-load Loss Test (IEC 60076-1 Clause 10)
Method
- Direct measurement using a power analyzer (instrument losses must be subtracted).
- Test voltage: rated voltage ±5%, with the lowest value used.
Temperature Correction Formula:
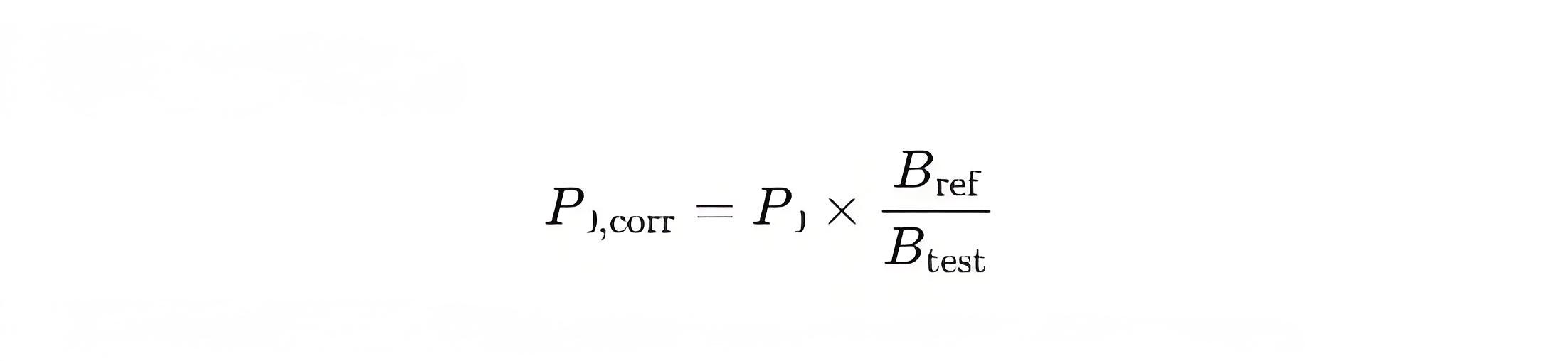
Bref: Flux density at reference temperature; B test : Measured flux density.
2. Load Loss Test (IEC 60076-1 Clause 11)
Method:
- Measured during short-circuit impedance testing.
- Test current: rated current; frequency deviation ≤ ±5%.
Temperature Correction Formula (for copper windings)

Tref: Reference temperature (75°C); T test : Winding temperature during testing.
Key Parameters and Tolerances
Loss Tolerances (IEC 60076-1 Clause 4.2):
- No-load loss: +15% allowed (measured value must not exceed guaranteed value).
- Load loss: +15% allowed (measured value must not exceed guaranteed value).
Stray Losses:
Losses caused by leakage flux in structural components, evaluated via high-frequency component separation or thermal imaging.
Energy Efficiency Classes and Loss Optimization
Per IEC 60076-14 (Energy Efficiency Guidelines for Power Transformers):
Total Losses (P total):
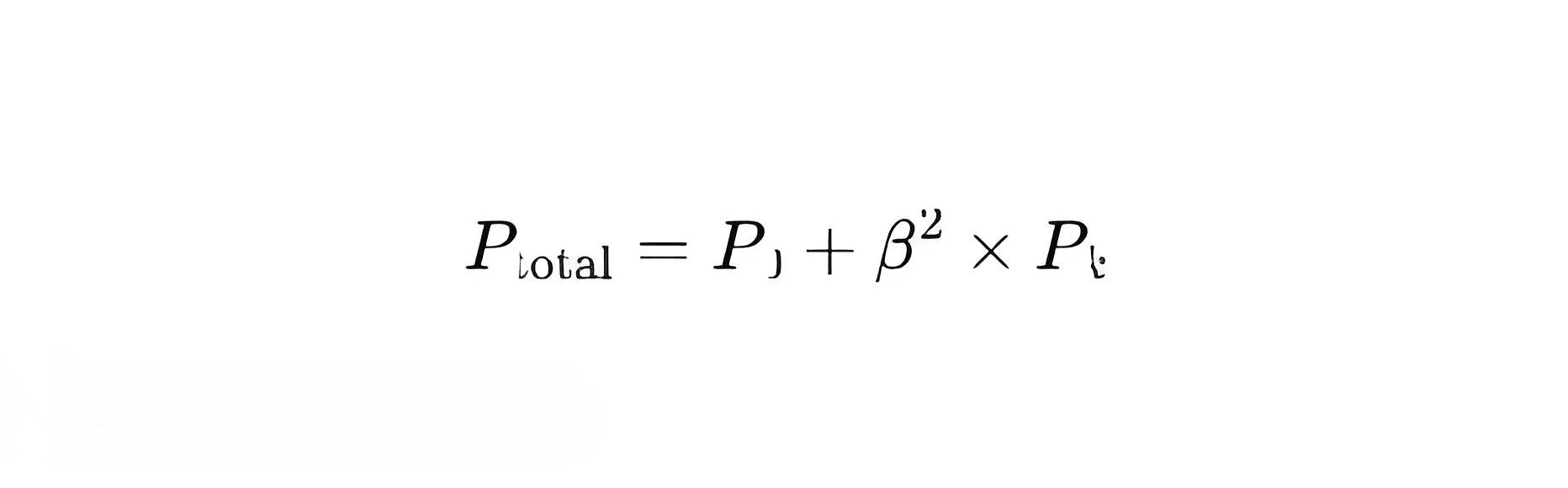
β: Load ratio (actual load / rated load).
Efficiency Classes (e.g., IE4, IE5) require total losses reduced by 10%~30%, achieved via:
- High-permeability silicon steel (reduces no-load losses).
- Optimized winding design (minimizes eddy current losses).
Practical Application Example
Case: 35kV Oil-Immersed Transformer (IEC 60076-7)
Rated Parameters:
- Capacity: 10 MVA
- Guaranteed no-load loss: 5 kW
- Guaranteed load loss: 50 kW (at 75°C).
Test Data:
No-load loss: 5.2 kW (within +15% tolerance → 5.75 kW limit).
Load loss (tested at 30°C):
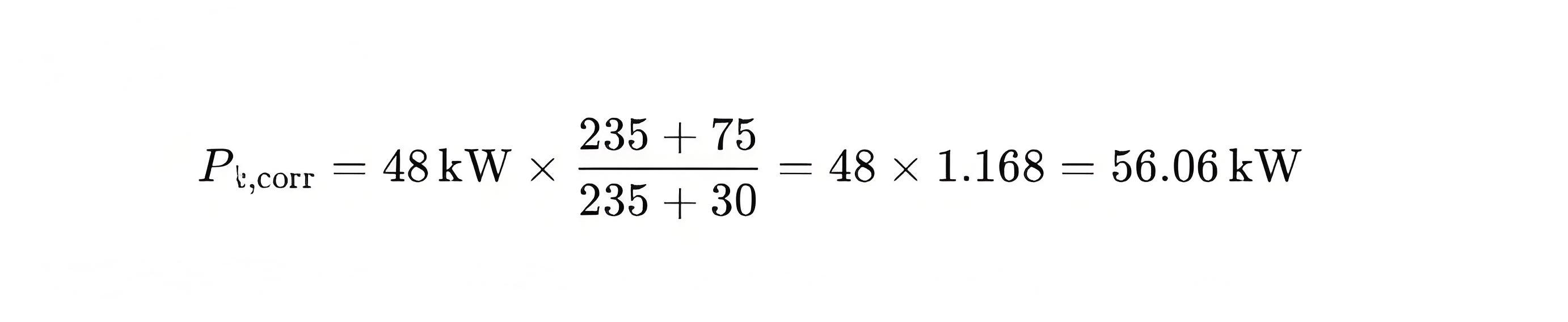
Conclusion: Load loss exceeds tolerance? Verify against 50 × 1.15 = 57.5 kW.
VI. Common Issues and Considerations
Ambient Temperature:
Tests must be conducted between -25°C to +40°C; corrections required outside this range.
Harmonic Losses:
Evaluate additional harmonic losses under non-sinusoidal loads per IEC 60076-18.
Digital Testing:
Use IEC 61869-calibrated sensors for accuracy.