Energy Loss in Transformers
Definition of Transformer Losses
Losses in a transformer include electrical losses such as core losses and copper losses, which are the difference between input and output power.
Copper Loss in Transformer
Copper loss is the I²R loss occurring in the primary and secondary windings of the transformer, depending on the load.
Core Losses in Transformer
Core losses, also known as iron losses, are fixed and do not vary with the load, depending on the core material and design.
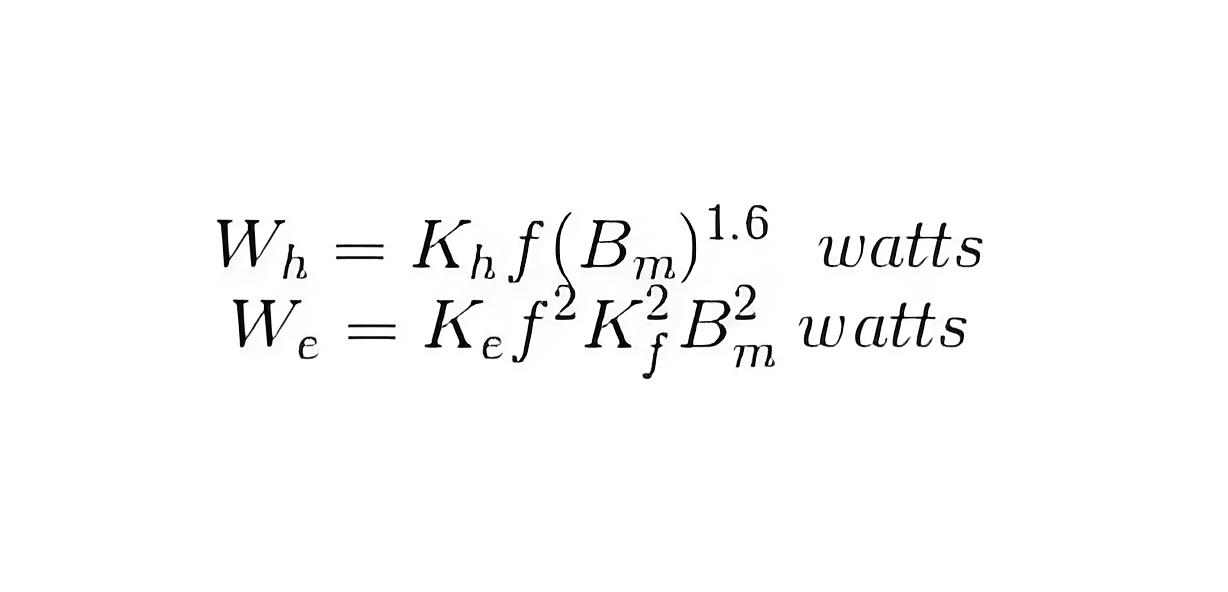
Kh = Hysteresis constant.
Ke = Eddy current constant.
Kf = form constant.
Hysteresis Loss in Transformer
Hysteresis loss occurs due to the energy required to realign the magnetic domains in the transformer’s core material.
Eddy Current Loss in Transformer
Eddy current loss happens when alternating magnetic flux induces circulating currents in the transformer’s conductive parts, dissipating energy as heat.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.