What is a TRIAC?
What is a TRIAC?
TRIAC Definition
A TRIAC is defined as a three-terminal AC switch that can conduct current in both directions, suitable for AC systems.
A TRIAC is defined as a three-terminal AC switch that can conduct in both directions, unlike other silicon controlled rectifiers. It can conduct whether the applied gate signal is positive or negative, making it ideal for AC systems.
This is a three terminal, four layer, bi-directional semiconductor device that controls AC power. The triac of maximum rating of 16 kw is available in the market.
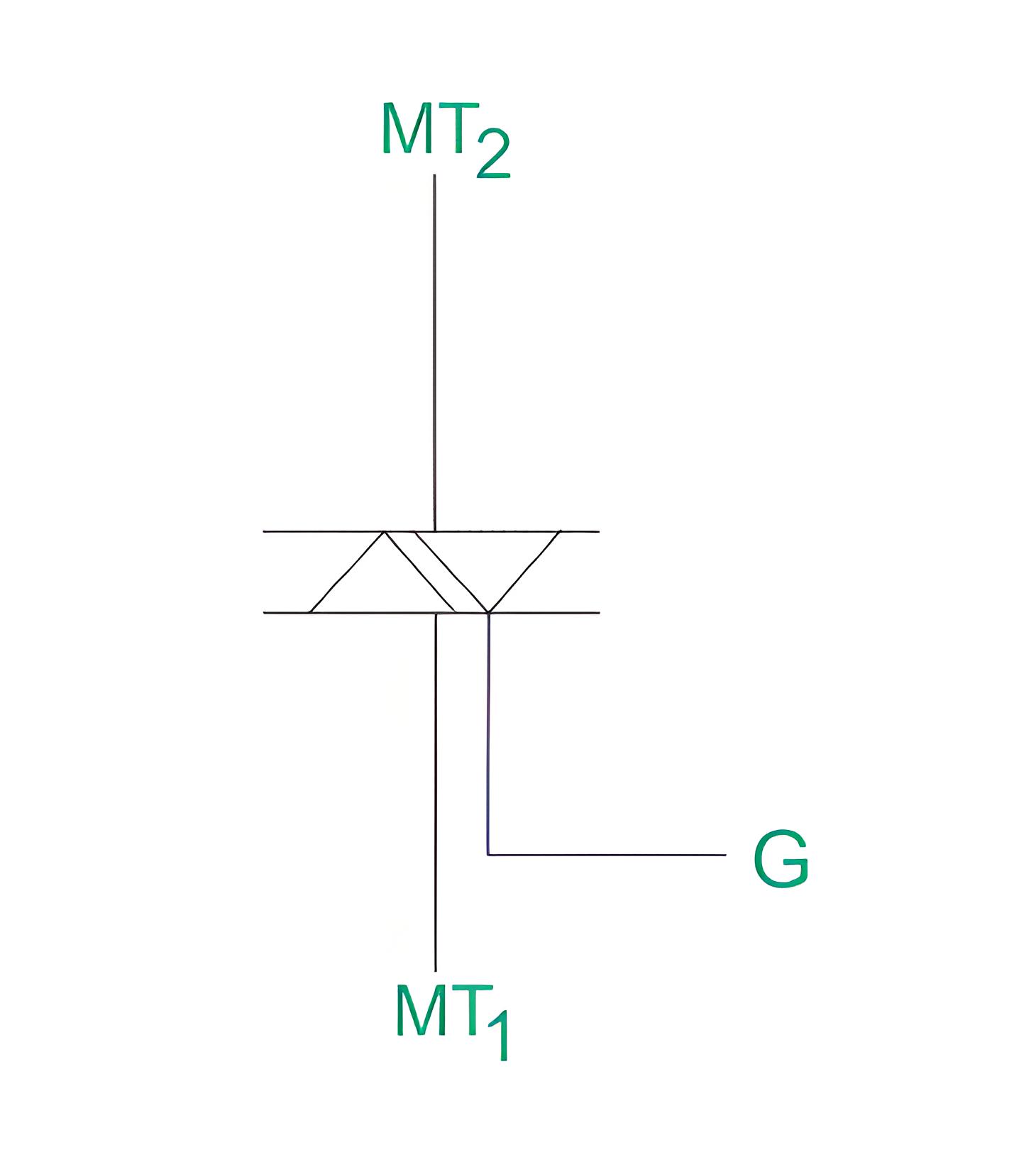
Figure shows the symbol of triac, which has two main terminals MT1 and MT2 connected in inverse parallel and a gate terminal.
Construction of Triac
Two SCRs are connected in inverse parallel with a common gate terminal. The gate is connected to both the N and P regions, allowing a gate signal regardless of polarity. Unlike other devices, it doesn’t have an anode and cathode, working bilaterally with three terminals: main terminal 1 (MT1), main terminal 2 (MT2), and gate terminal (G).
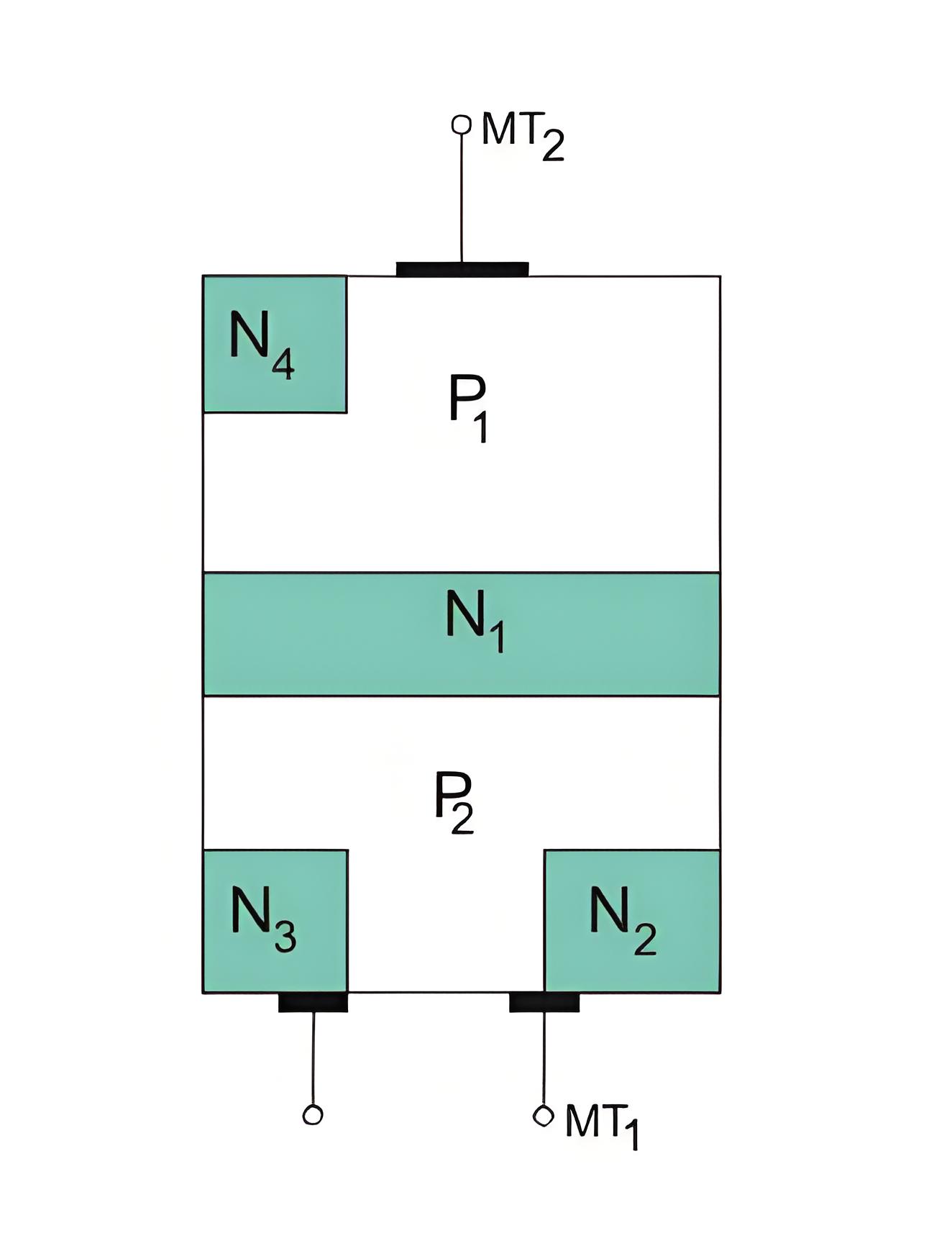
Figure shows the construction of a triac. There are two main terminals namely MT1 and MT2 and the remaining terminal is gate terminal.
Operation of Triac
The TRIAC can be activated by applying a gate voltage higher than the break over voltage. Alternatively, it can be turned on by a 35-microsecond gate pulse. When the voltage is below the break over voltage, gate triggering is used.There are four different modes of operations, they are-
When MT2 and Gate being Positive with Respect to MT1 When this happens, current flows through the path P1-N1-P2-N2. Here, P1-N1 and P2-N2 are forward biased but N1-P2 is reverse biased. The triac is said to be operated in positively biased region. Positive gate with respect to MT1 forward biases P2-N2 and breakdown occurs.
When MT2 is Positive but Gate is Negative with Respect to MT1 The current flows through the path P1-N1-P2-N2. But P2-N3 is forward biased and current carriers injected into P2 on the triac.
When MT2 and Gate are Negative with Respect to MT1 Current flows through the path P2-N1-P1-N4. Two junctions P2-N1 and P1-N4 are forward biased but the junction N1-P1 is reverse biased. The triac is said to be in the negatively biased region.
When MT2 is Negative but Gate is Positive with Respect to MT1 P2-N2 is forward biased at that condition. Current carriers are injected so the triac turns on. This mode of operation has a disadvantage that it should not be used for high (di/dt) circuits. Sensitivity of triggering in mode 2 and 3 is high and if marginal triggering capability is required, negative gate pulses should be used. Triggering in mode 1 is more sensitive than mode 2 and mode 3.
Characteristics of a Triac
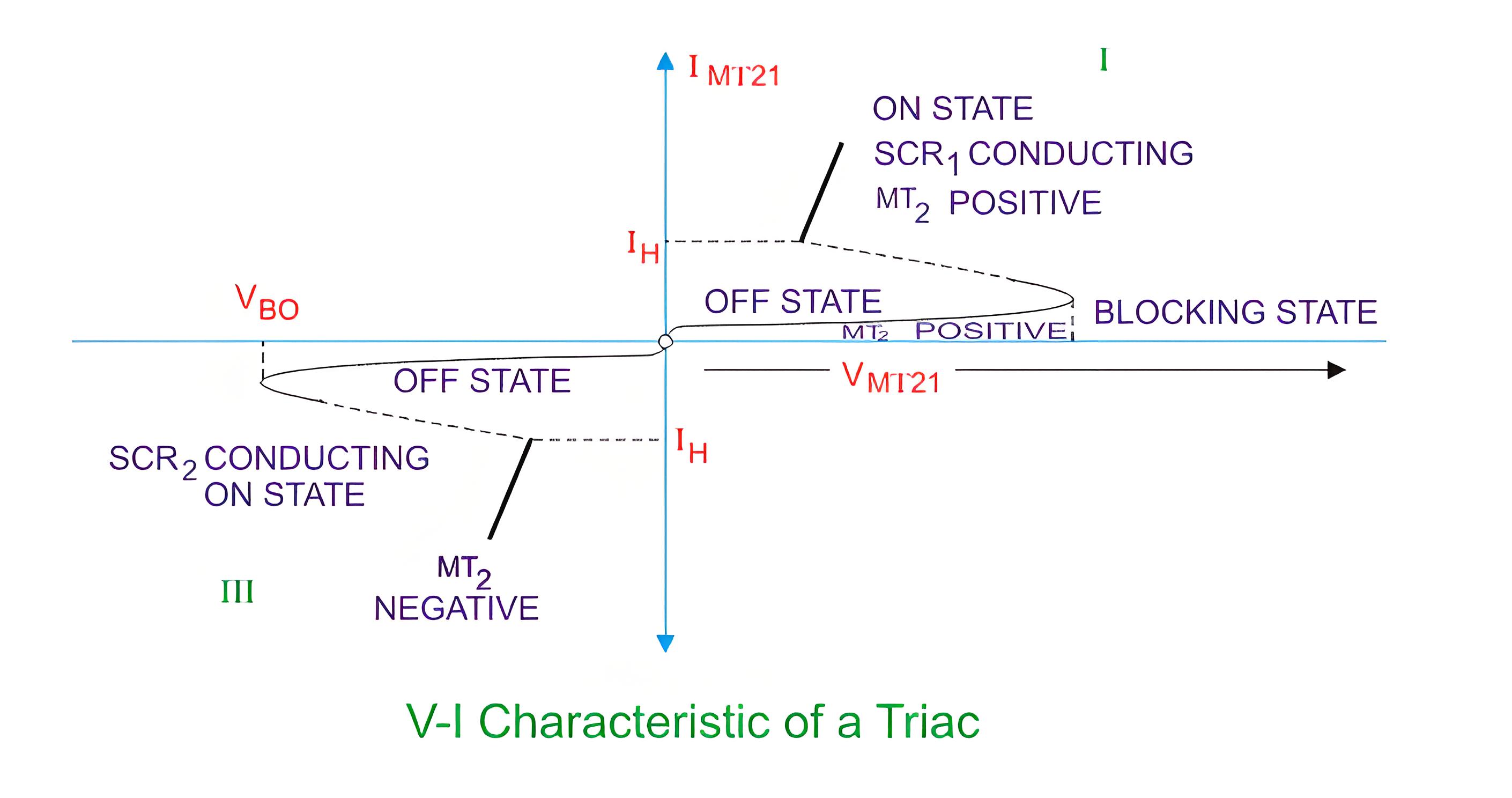
The triac characteristics is similar to SCR but it is applicable to both positive and negative triac voltages. The operation can be summarized as follows-
First Quadrant Operation of Triac
Voltage at terminal MT2 is positive with respect to terminal MT1 and gate voltage is also positive with respect to first terminal.
Second Quadrant Operation of Triac
Voltage at terminal 2 is positive with respect to terminal 1 and gate voltage is negative with respect to terminal 1.
Third Quadrant Operation of Triac
Voltage of terminal 1 is positive with respect to terminal 2 and the gate voltage is negative.
Fourth Quadrant Operation of Triac
Voltage of terminal 2 is negative with respect to terminal 1 and gate voltage is positive.
When the TRIAC turns on, a heavy current flows through it, which can cause damage. To prevent this, a current limiting resistor should be used. Proper gate signals can control the firing angle of the device. Gate triggering circuits, such as a diac, can be used for this purpose, with gate pulses up to 35 microseconds.
Advantages of Triac
It can be triggered with positive or negative polarity of gate pulses.
It requires only a single heat sink of slightly larger size, whereas for SCR, two heat sinks should be required of smaller size.
It requires single fuse for protection.
A safe breakdown in either direction is possible but for SCR protection should be given with parallel diode.
Disadvantages of Triac
They are not much reliable compared to SCR.
It has (dv/dt) rating lower than SCR.
Lower ratings are available compared to SCR.
We need to be careful about the triggering circuit as it can be triggered in either direction.
Uses of Triac
They are used in control circuits.
It is used in High power lamp switching.
It is used in AC power control.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













