What is a Thermocouple?
What is a Thermocouple?
Thermocouple Definition
A thermocouple is a device that converts temperature differences into an electric voltage, based on the principle of the thermoelectric effect. It is a type of sensor that can measure temperature at a specific point or location. Thermocouples are widely used in industrial, domestic, commercial, and scientific applications due to their simplicity, durability, low cost, and wide temperature range.
Thermoelectric Effect
The thermoelectric effect is the phenomenon of generating an electric voltage due to a temperature difference between two different metals or metal alloys. This effect was discovered by German physicist Thomas Seebeck in 1821, who observed that a magnetic field was created around a closed loop of two dissimilar metals when one junction was heated, and the other was cooled.
The thermoelectric effect can be explained by the movement of free electrons in the metals. When one junction is heated, the electrons gain kinetic energy and move faster toward the colder junction. This creates a potential difference between the two junctions, which can be measured by a voltmeter or an ammeter. The magnitude of the voltage depends on the type of metals used and the temperature difference between the junctions.
Thermocouple Work
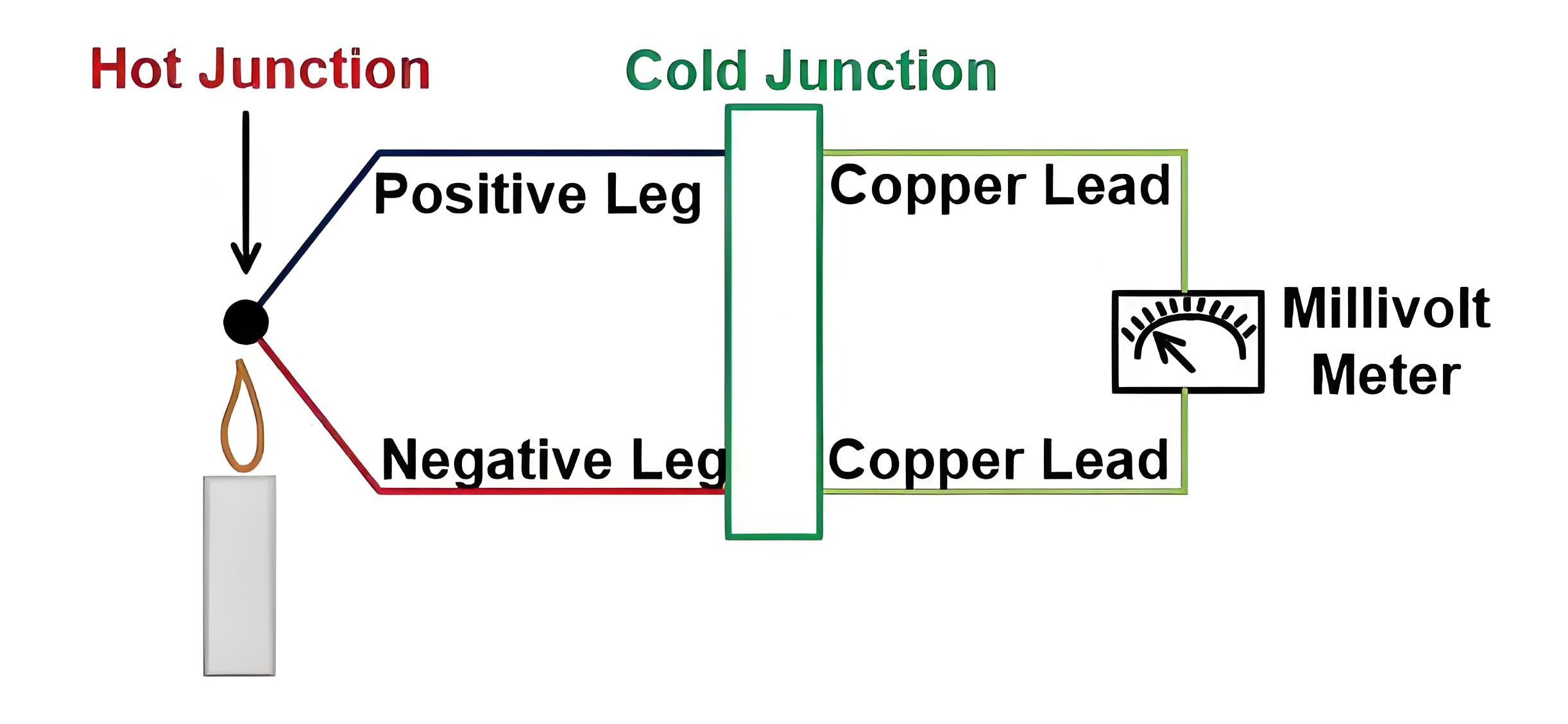
A thermocouple consists of two wires made of different metals or metal alloys, joined together at both ends to form two junctions. One junction called the hot or measuring junction, is placed at the location where the temperature is to be measured. The other junction called the cold or reference junction, is kept at a constant and known temperature, usually at room temperature or in an ice bath.
When there is a temperature difference between the two junctions, an electric voltage is generated across the thermocouple circuit due to the thermoelectric effect. This voltage can be measured by a voltmeter or an ammeter connected to the circuit. By using a calibration table or a formula that relates the voltage to the temperature for a given type of thermocouple, the temperature of the hot junction can be calculated.
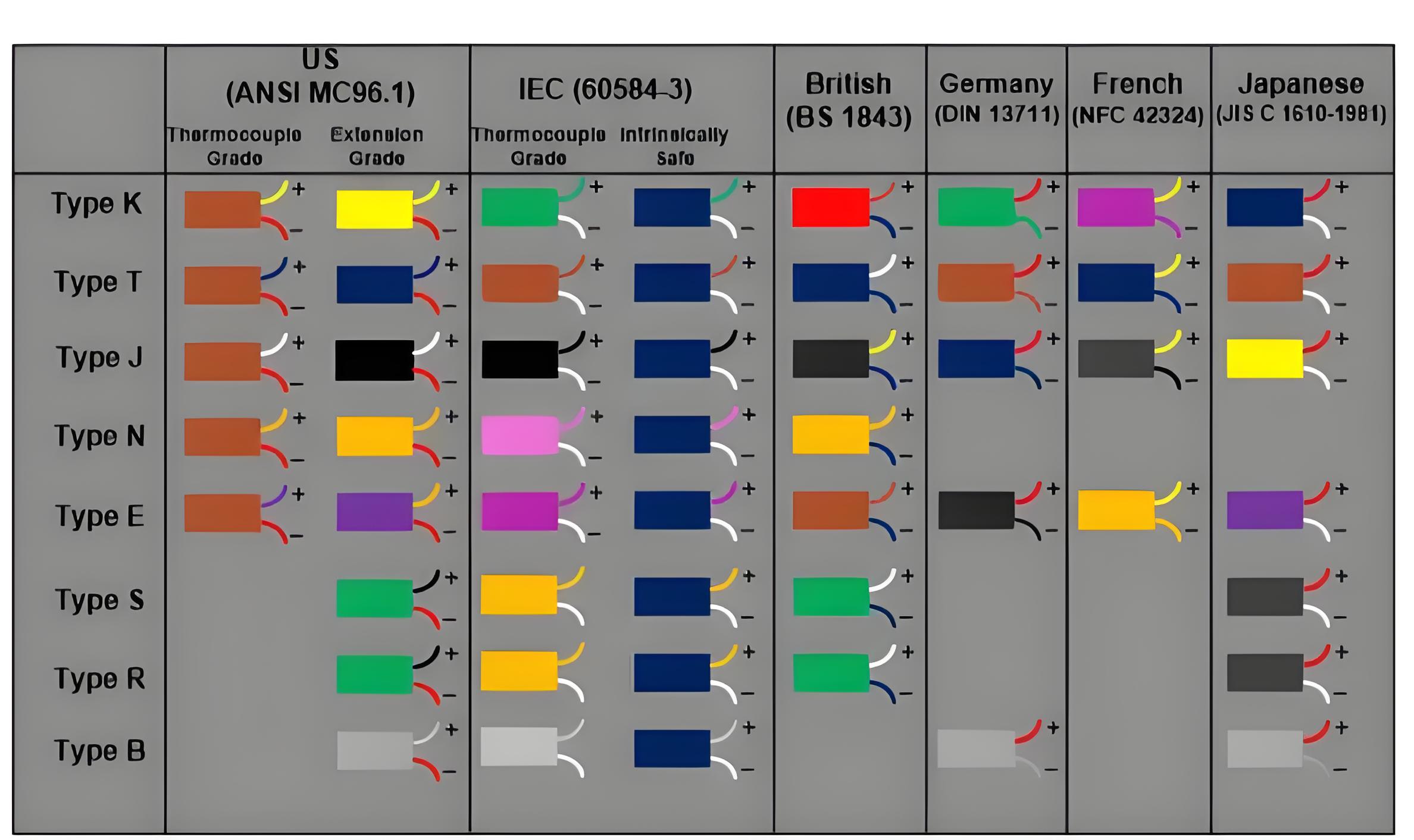
Types of Thermocouples
Various types, such as K, J, T, and E, differ by metal combinations, temperature ranges, and specific applications.
Advantages
They can measure a wide range of temperatures, from cryogenic to very high temperatures.
They are simple, robust, and reliable devices that can withstand harsh environments and vibrations.
They are inexpensive and easy to install and replace.
They have a fast response time and can measure dynamic temperature changes.
They do not require external power or amplification for their operation.
Disadvantages
They have low accuracy and stability compared to other sensors.
They are susceptible to errors due to corrosion, oxidation, contamination, or aging of the wires.
They require a reference junction at a known temperature for accurate measurement.
They have a non-linear output that requires complex calibration or compensation.
They may generate unwanted thermoelectric voltages due to parasitic junctions in the circuit.
Selection Criteria
Choose based on temperature range, accuracy, environment compatibility, size, electrical characteristics, and cost.
Common Applications
Steel and iron industries
Gas appliances
Thermopile radiation sensors
Manufacturing
Power production
Process plants
Thermocouples as vacuum gauge
Conclusion
Thermocouples are widely used temperature sensors that consist of two different types of metals joined together at one end. When the junction of the two metals is heated or cooled, a voltage is created that can be correlated back to the temperature.
Thermocouples have many advantages and disadvantages compared to other temperature sensors. They can measure a wide range of temperatures, from cryogenic to very high temperatures. They are simple, robust, and reliable devices that can withstand harsh environments and vibrations. They are inexpensive and easy to install and replace. They have a fast response time and can measure dynamic temperature changes. However, they have low accuracy and stability compared to other sensors. They are susceptible to errors due to corrosion, oxidation, contamination, or aging of the wires. They require a reference junction at a known temperature for accurate measurement. They have a non-linear output that requires complex calibration or compensation.
To select the right thermocouple, consider the temperature range and accuracy needed, the chemical compatibility and durability of the wires, the size and shape of the probe, the electrical characteristics and noise immunity, and the availability and cost of the type and accessories.
Thermocouples are used in a wide range of applications across various industries and domains. Some of the common applications of thermocouples are steel and iron industries, gas appliances, thermopile radiation sensors, manufacturing, power production, process plants, and thermocouple as vacuum gauges.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.