What is Slew Rate?
What is Slew Rate?
Slew Rate Definition
In electronics, the slew rate is defined as the maximum rate of output voltage change per unit time. It is denoted by the letter S. The slew rate helps us to identify the amplitude and maximum input frequency suitable to an operational amplifier (OP amp) such that the output is not significantly distorted.
To achieve the best performance, the slew rate should be maximized, allowing for the greatest undistorted output voltage swing.
The slew rate is crucial for ensuring that an OP amp reliably delivers an output that matches the input. It varies with voltage gain and is typically specified at unity (+1) gain condition.
A typically general-purpose device may have a slew rate of 10 . This means that when a large step input signal is applied to the input, the electronic device can provide an output of 10 volts in 1 microsecond. V/mu S
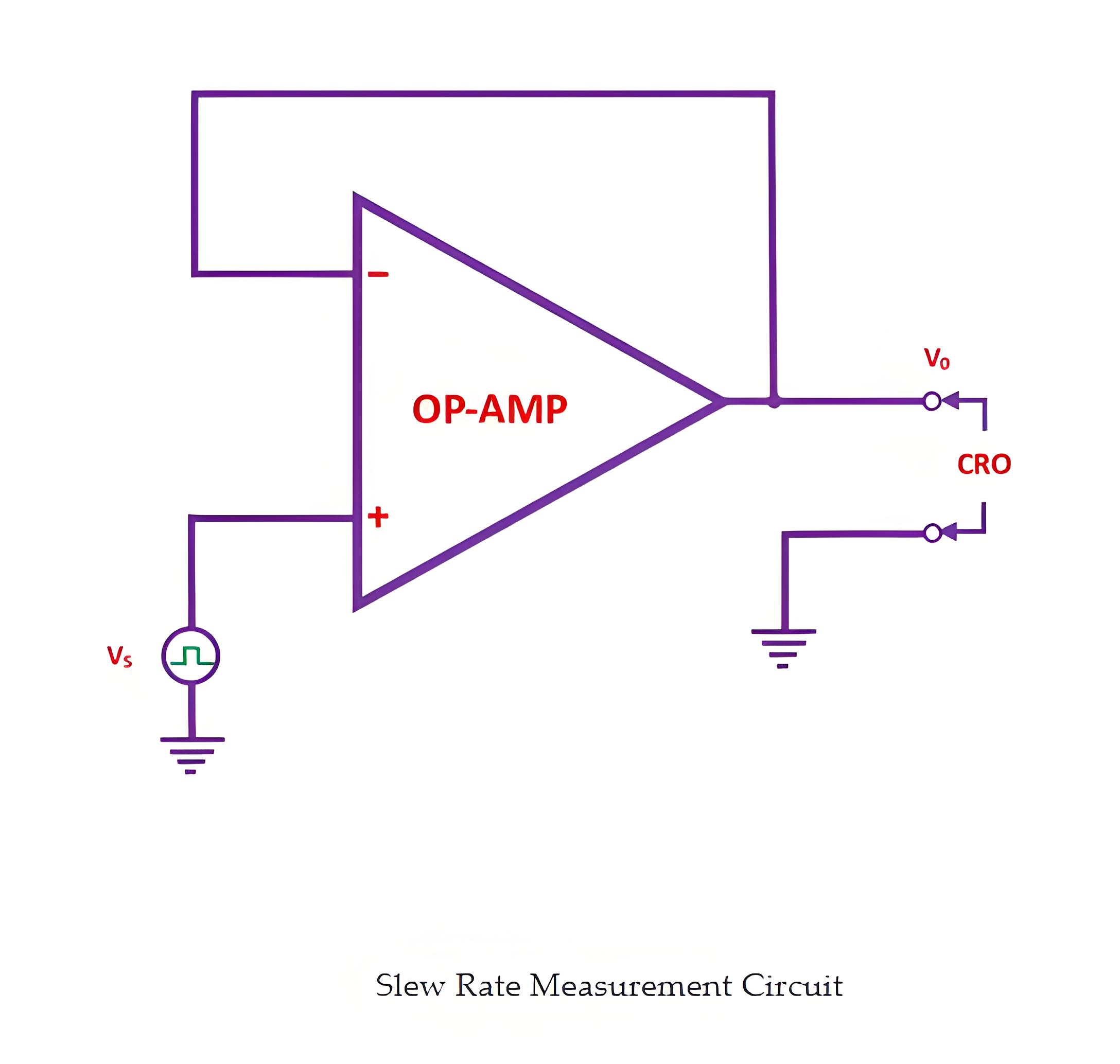
Measuring Slew Rate
To measure slew rate, apply a step signal to the amplifier, then observe the rate of voltage change from 10% to 90% of its maximum amplitude using an oscilloscope.
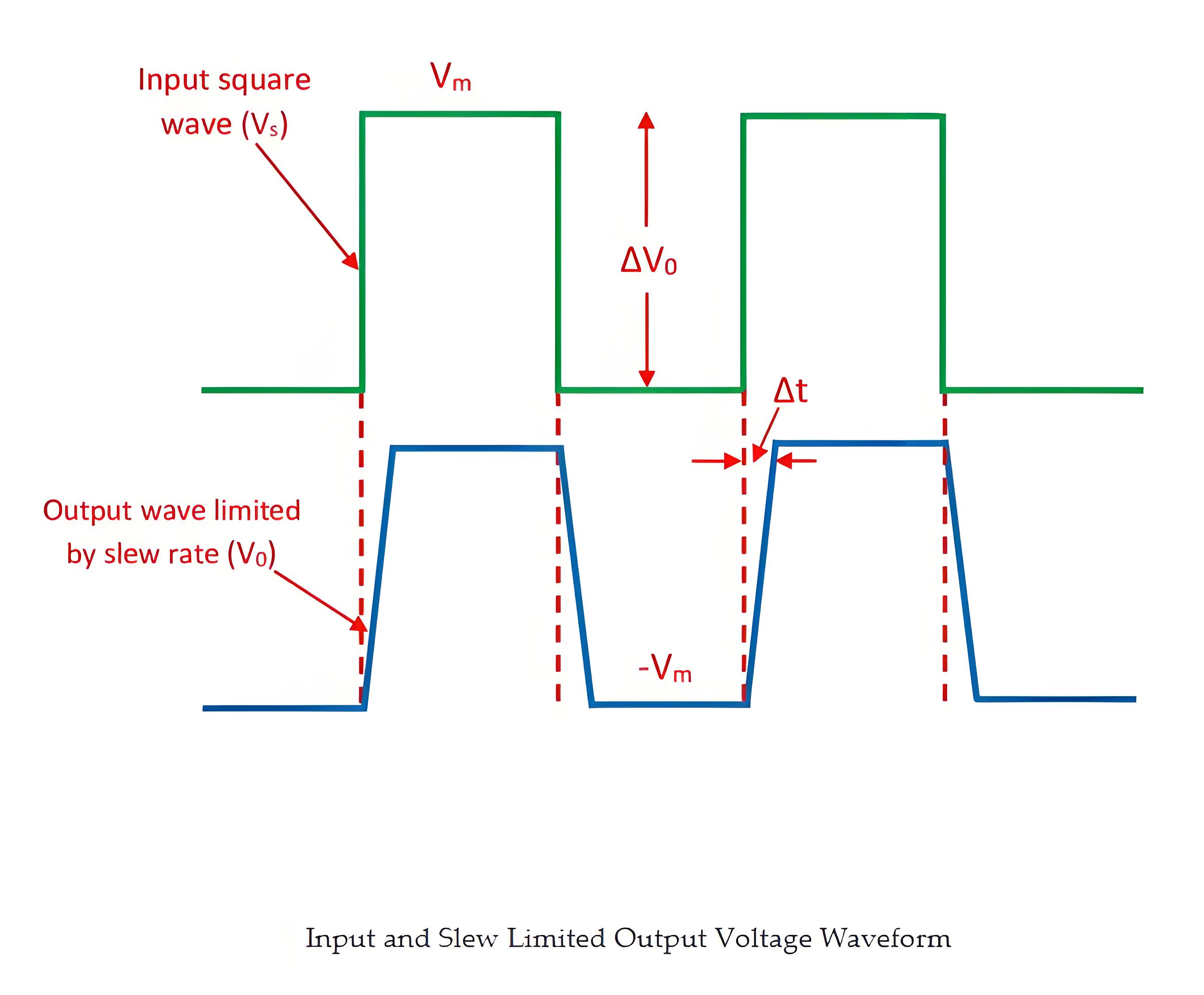
Slew Rate Formula
The formula for calculating slew rate is by dividing the change in output voltage by the change in time, illustrating how quickly the output voltage can change.
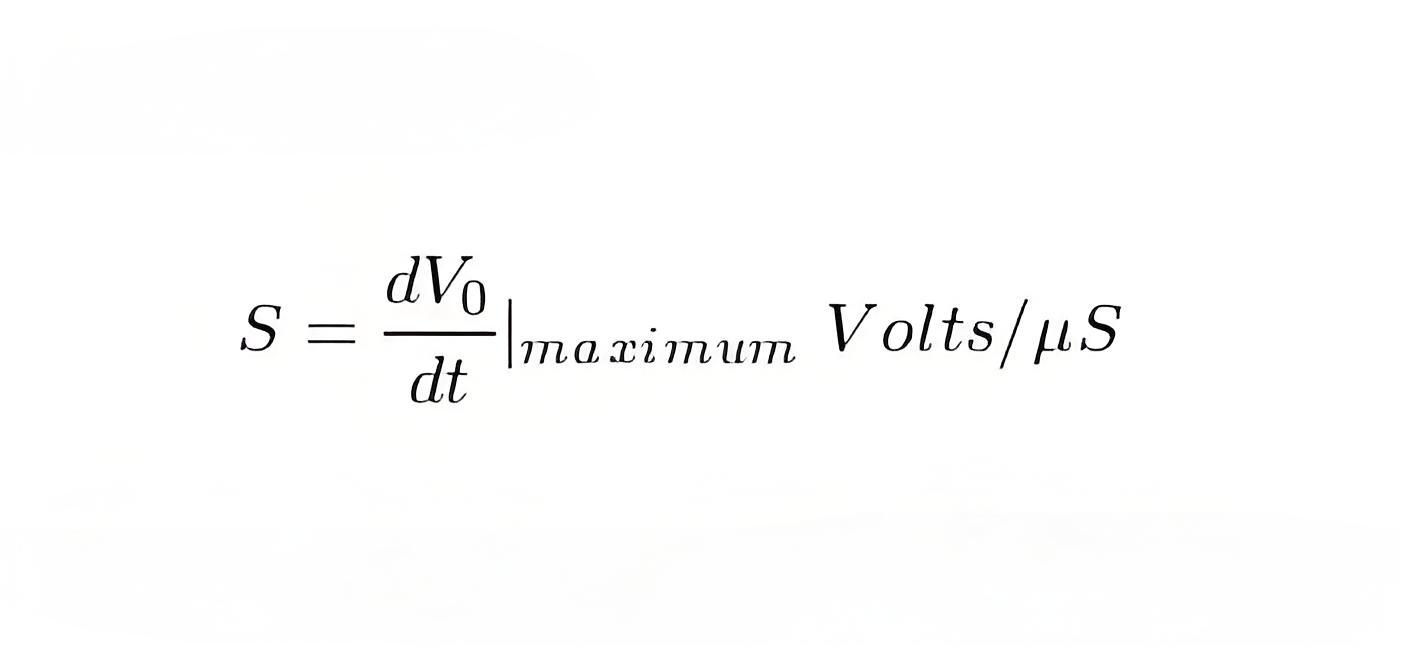
Impact on Frequency
To provide stability, frequency compesation is used in all op-amps to reduce the high-frequency response have a considerable effect on slew rate. A reduced frequency response limits the rate of change that occurs at the output of the amplifiers and hence it affects the slew rate of an op-amp.
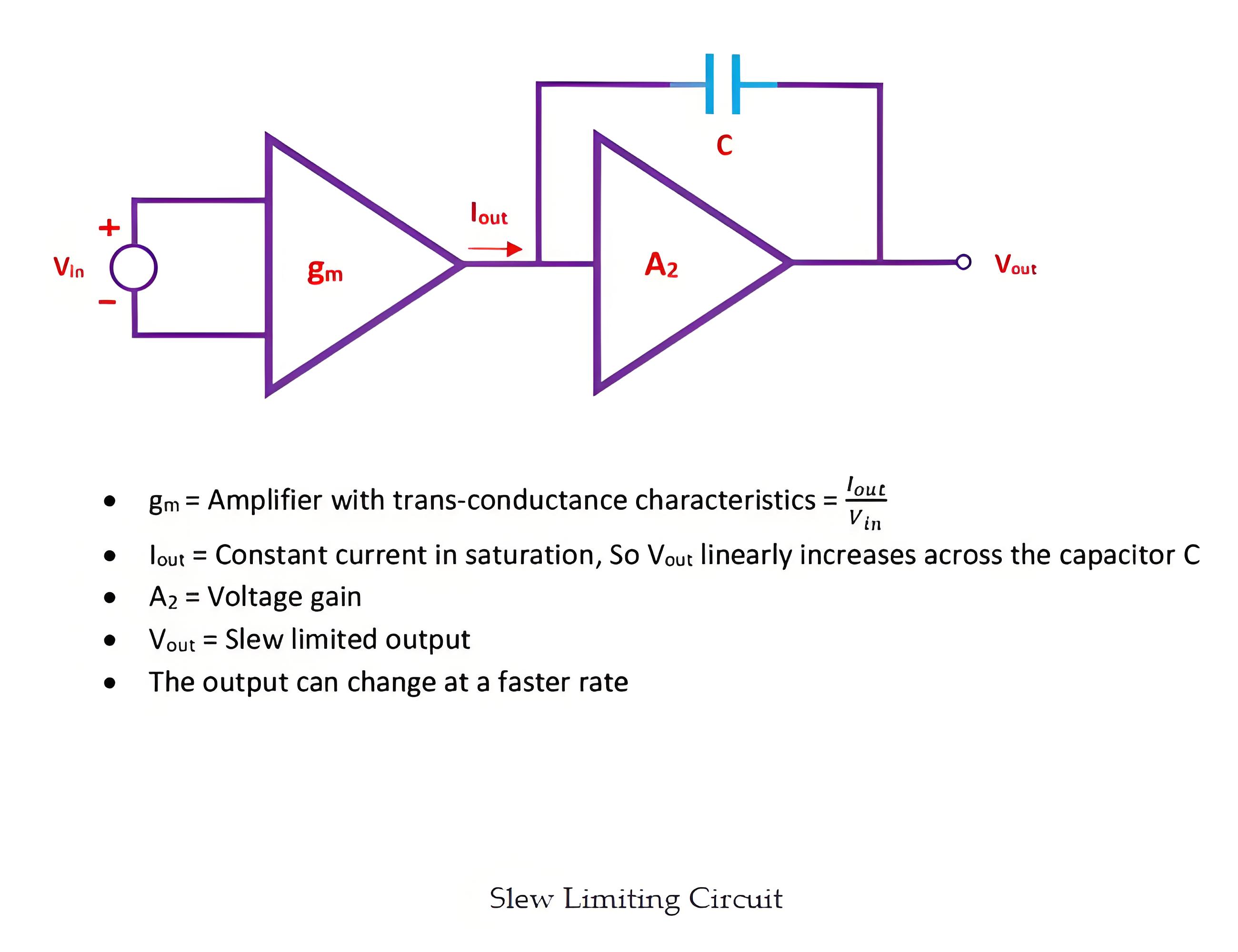
Now, the frequency compensation at the second stage of the op-amp is the low pass characteristic and it is similar to an integrator. Hence constant current input will produce a linearly increasing output. If the second stage has an effective input capacitance C and voltage gain A2, then the slew rate can be expressed as
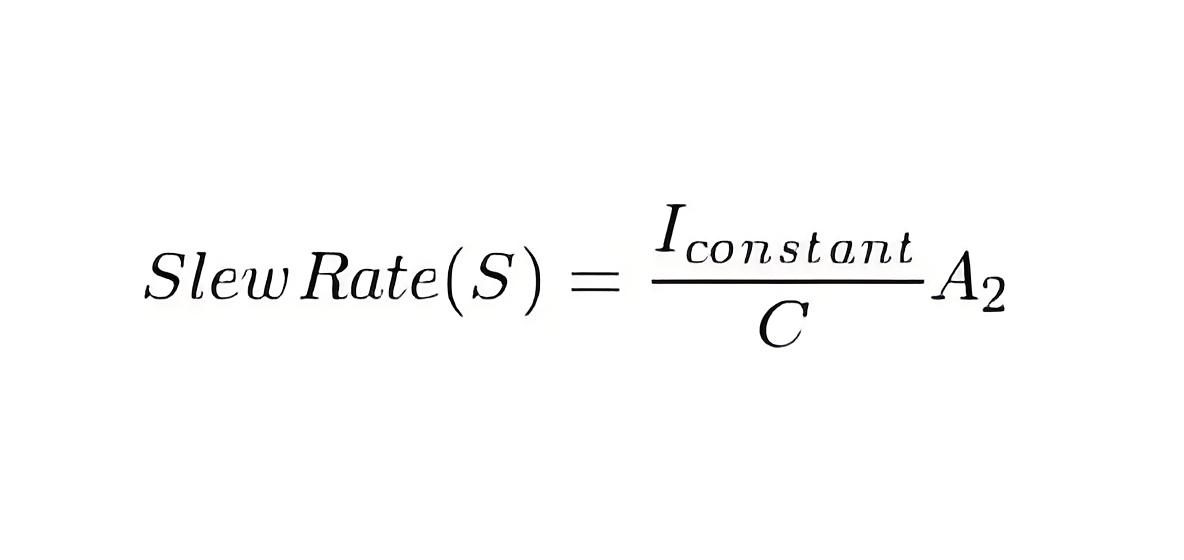
Where Iconstant is the constant current of the first stage in saturation.
Slew Rate Applications
In musical instruments, slew circuitry is used to provide a slide from one note to another i.e. portamento (also called glide or lag).
Slew circuitry is used where the control voltage is slowly transitioned to different values over a period of time.
In certain electronics applications where speed is required and the output needs to change over a period of time, software-generated slew functions or slew circuitry are used.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













