What is Semiconductor Physics?
What is Semiconductor Physics?
Semiconductor Physics Definition
Semiconductor physics is defined as the study of materials with electrical conductivity between conductors and insulators, primarily involving elements like silicon and germanium.
Properties of Semiconductors
Semiconductors have moderate resistivity and a negative temperature coefficient of resistance, meaning their resistance decreases with increasing temperature.
Covalent Bonding
The valence electrons in semiconductor atoms take a vital role in bonding between atoms in the semiconductor crystal. Bonding between atoms occurs because each atom has a tendency to feel its outer most cell with eight electrons.
Each semiconductor atom has four valence electrons and can share four electrons from neighboring atoms to complete eight electrons in its outermost shell. This sharing of electrons creates covalent bonds.
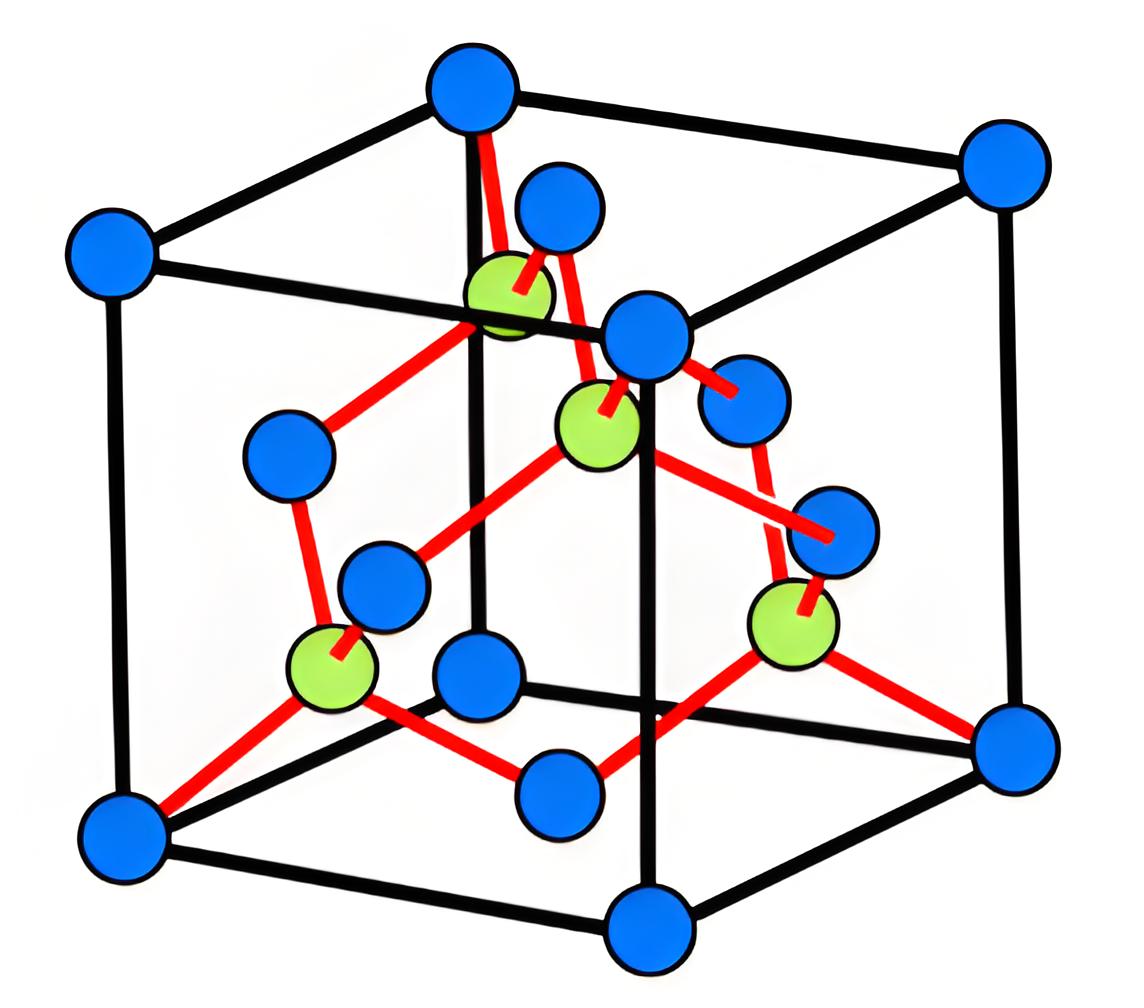
Each semiconductor atom creates four covalent bonds with four neighbouring atoms in the crystal. That means, one covalent bond is created with each of four neighbouring semiconductor atom. The figure below shows the covalent bonds formed in a germanium crystal.
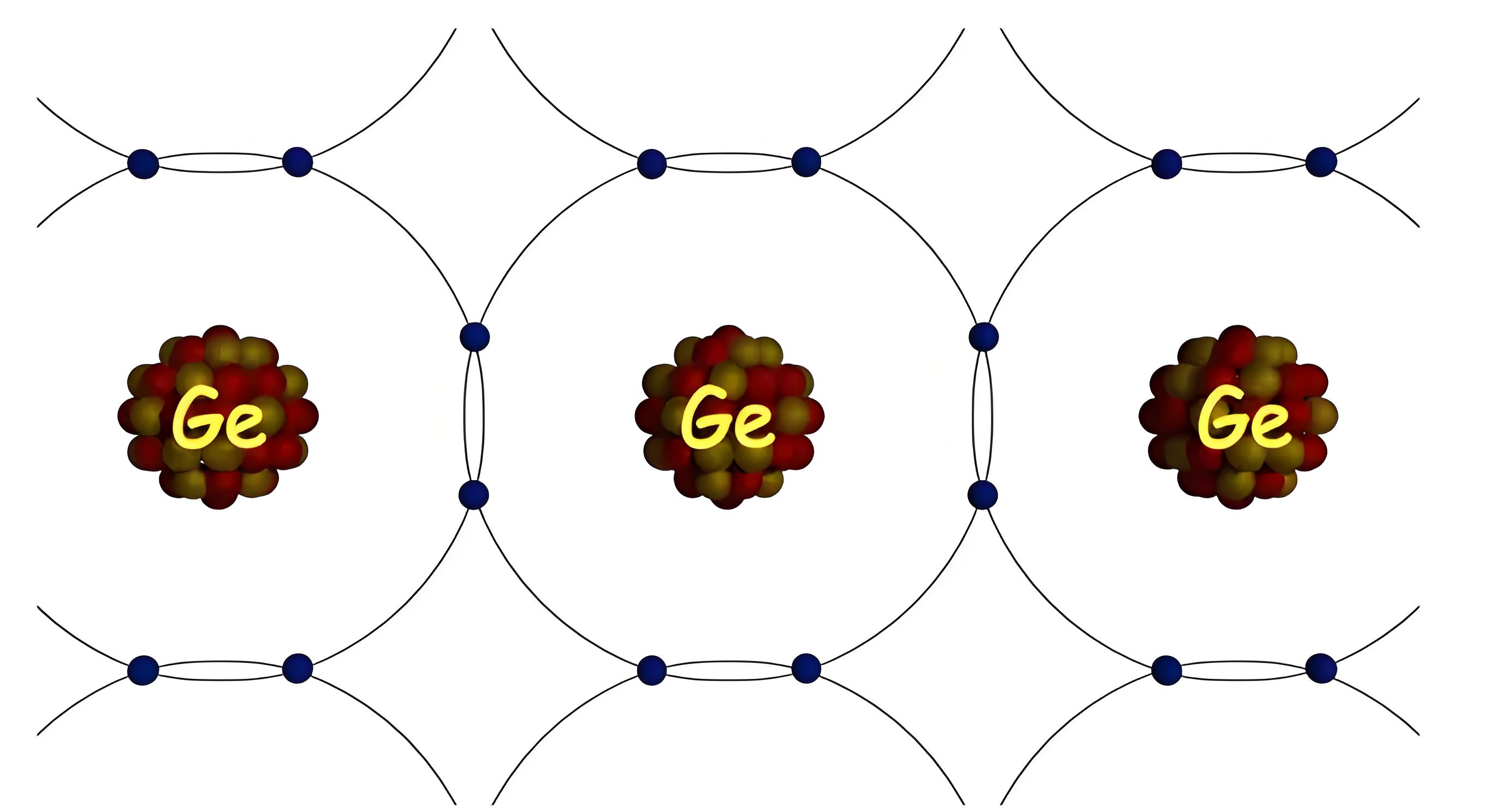
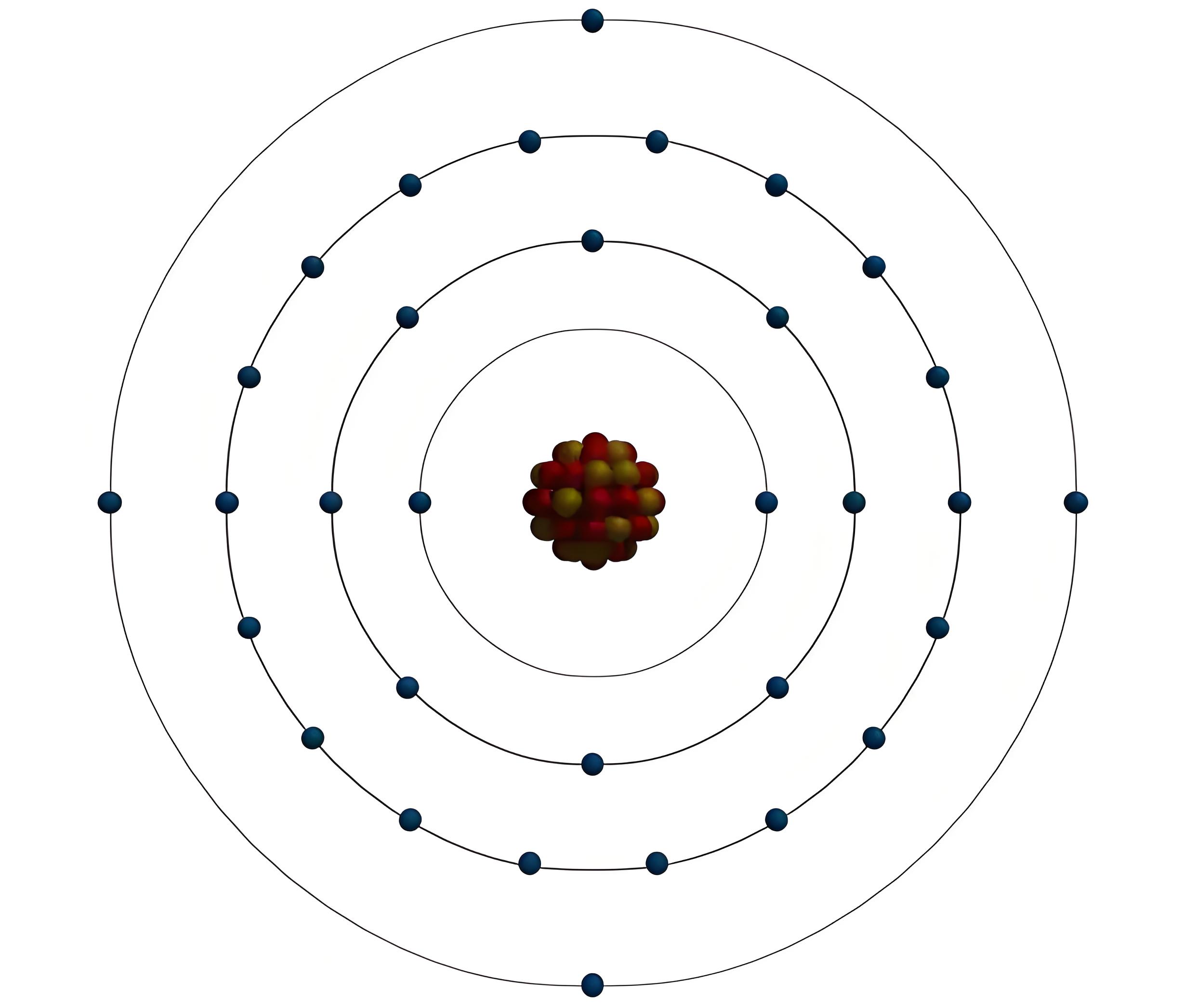
In germanium crystal, each atom has eight electrons in its last orbit. But in an isolated single germanium atom, there are 32 electrons. The first orbit consists of 2 electrons. The second orbit consists of 8 electrons. The third orbit consists of 18 electrons and rests 4 electrons are in fourth or outer most orbit.
But in a germanium crystal, each atom shares 4 valence electrons from four neighbouring atoms to fill its outermost orbit with eight electrons. In this way, each of them in the crystal will have eight electrons in its outermost orbit.
Forming covalent bonds associates each valence electron with an atom, leaving no free electrons in an ideal semiconductor crystal. The atoms are orderly arranged due to these bonds, creating the crystal structure of a semiconductor.
Energy Band Theory
Semiconductors have a small energy gap between the valence and conduction bands, allowing electrons to move and conduct electricity when energy is applied.
Types of Semiconductors
Intrinsic Semiconductor
Extrinsic Semiconductor
N-type and P-type Semiconductor
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













