Resistance of a Diode
Diode Resistance
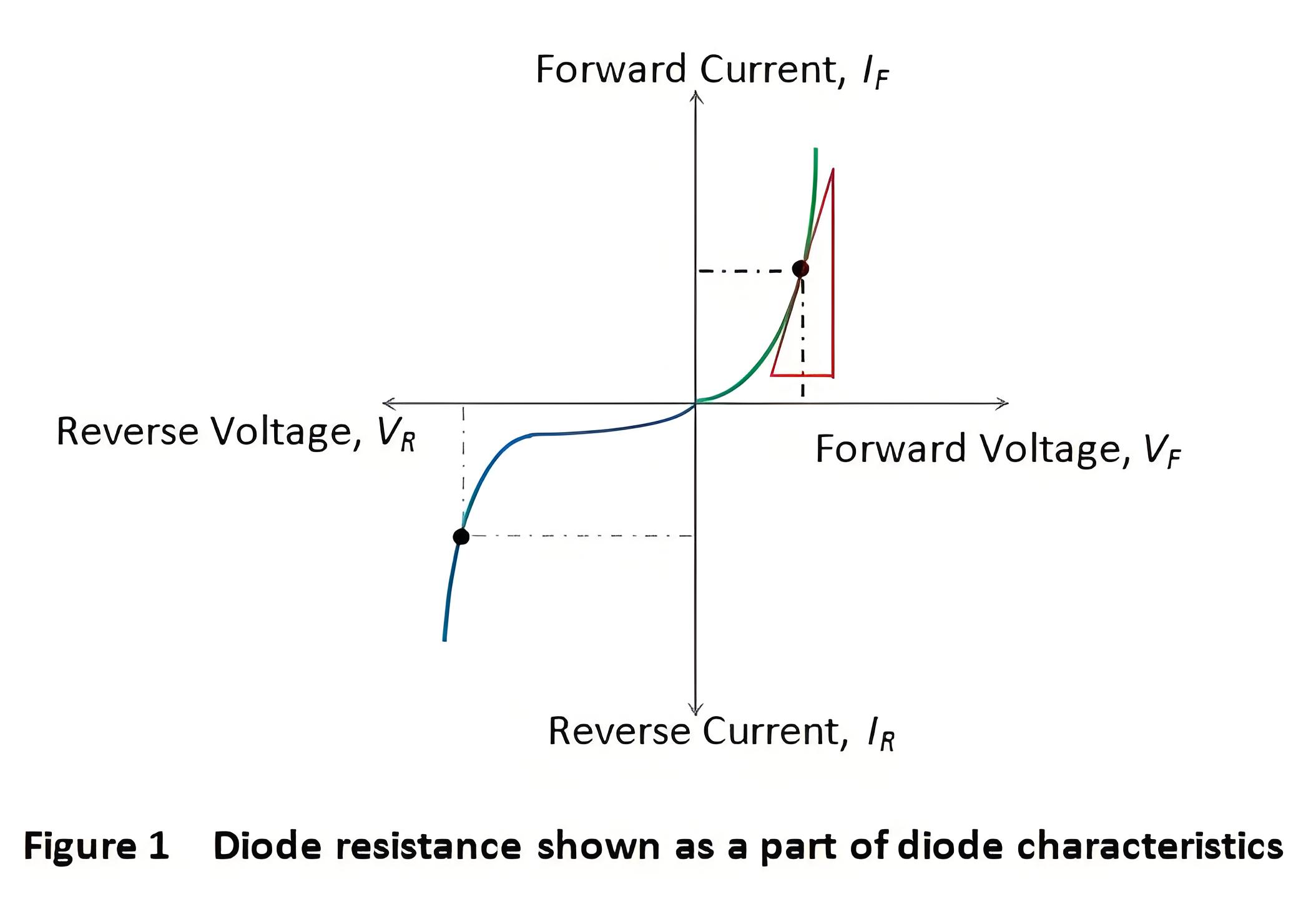
Resistance opposes the flow of current through a device. Diode resistance is the effective opposition a diode offers to current flow. Ideally, a diode offers zero resistance when forward biased and infinite resistance when reverse biased. However, no device is perfect. Practically, every diode has small resistance when forward biased and significant resistance when reverse biased. We can characterize a diode by its forward and reverse resistances.
Forward Resistance
Even with forward biasing, a diode won’t conduct until it reaches a minimum threshold voltage. Once the applied voltage exceeds this threshold, the diode starts to conduct. The resistance offered by the diode in this condition is called forward resistance. In other words, forward resistance is the resistance a diode shows when it is forward biased.
Forward resistance is classified into two types viz., static or dynamic depending on whether the current flowing through the device is DC (Direct Current) or AC (Alternating Current), respectively.
Static or DC Resistance
It is the resistance offered by the diode to the flow of DC through it when we apply a DC voltage to it. Mathematically the static resistance is expressed as the ratio of DC voltage applied across the diode terminals to the DC flowing through it (shown by the black dotted line in Figure 1) i.e.
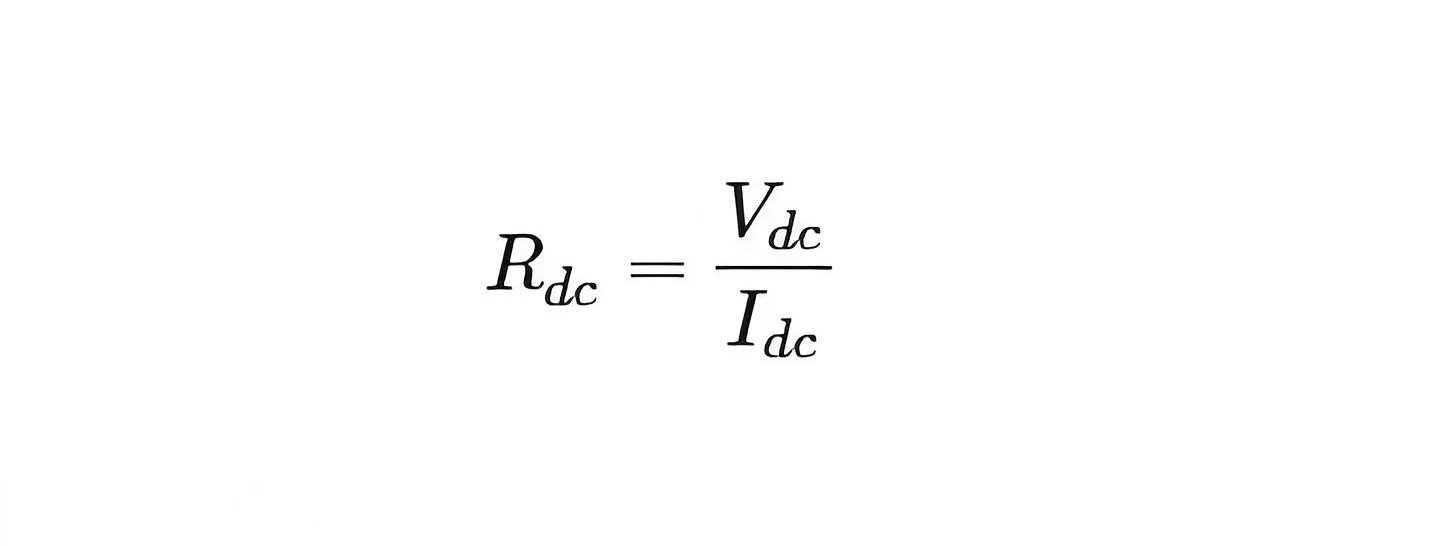
Dynamic or AC Resistance
Dynamic resistance is the resistance a diode offers to AC current when connected to a circuit with an AC voltage source. It is calculated as the ratio of the change in voltage across the diode to the change in current through it.
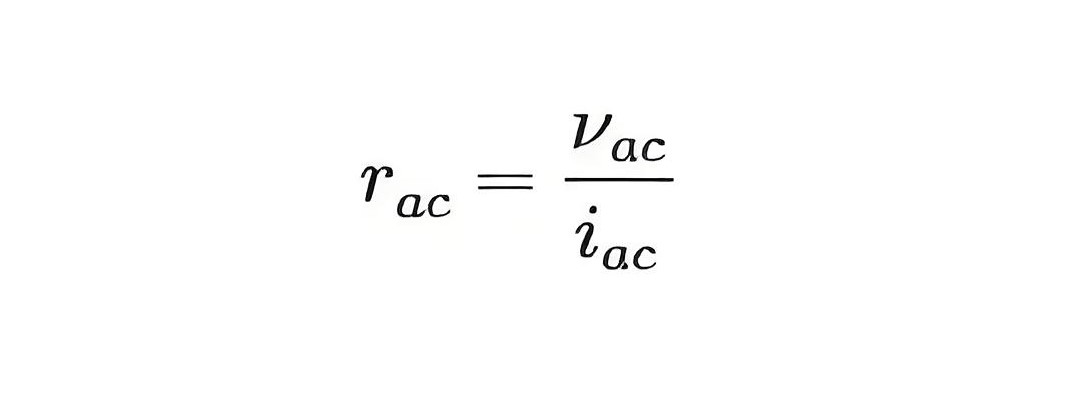
Reverse Resistance
When we connect the diode in reverse biased condition, there will be a small current flowing through it which is called the reverse leakage current. We can attribute the cause behind this to the fact that when the diode functions in its reverse mode, it will not be completely free of charge carriers. That is, even in this state, one can experience the flow of minority carriers through the device.
Due to this current flow, the diode exhibits reverse resistance characteristic which is shown by the purple dotted line in Figure 1. The mathematical expression for the same is similar to that for the forward resistance and is given by
Where, Vr and Ir are the reverse voltage and the reverse current respectively.
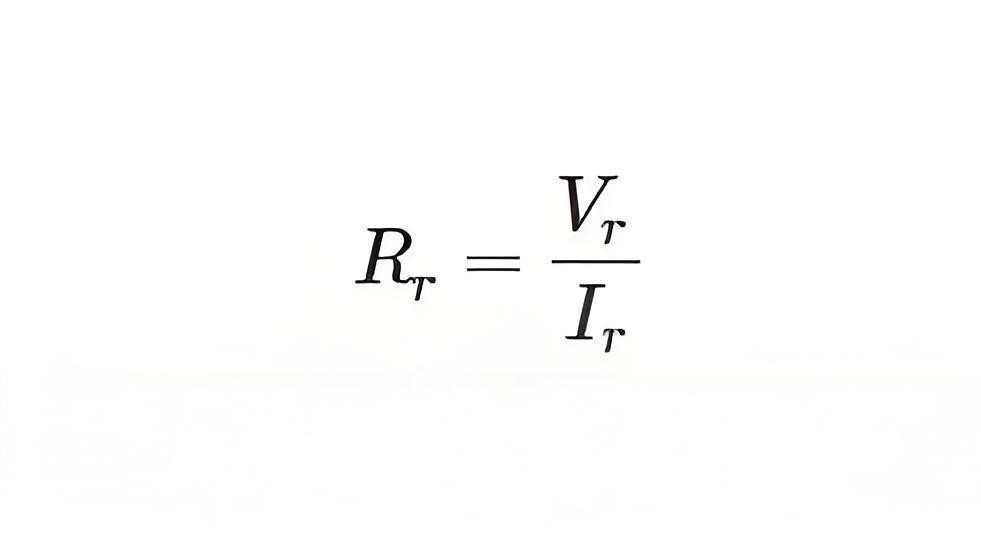
After knowing the basic facts about the diode resistance, it is important to note the fact that“Generally the diodes have a high ratio of reverse to forward resistance, which makes them essentially unidirectional in function”.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













