PN Junction Bias
PN Junction Diode Definition
A PN junction diode is defined as a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction in forward bias and blocks current in reverse bias.
Forward Bias
In forward bias, the p-type region is connected to the positive terminal and the n-type to the negative terminal, reducing the depletion layer and allowing current flow.
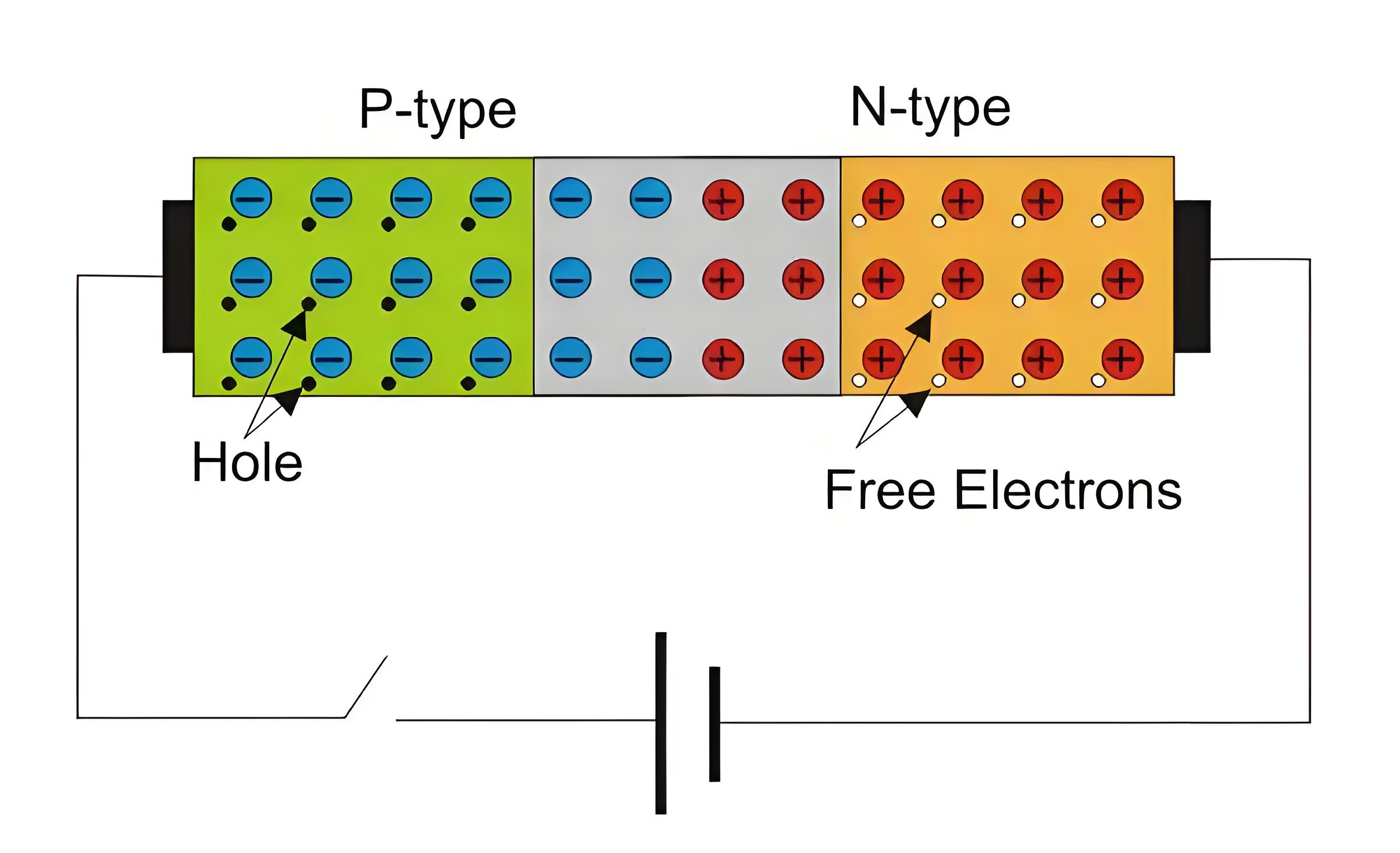
Reverse Bias
In reverse bias, the p-type region is connected to the negative terminal and the n-type to the positive terminal, increasing the depletion layer and preventing current flow.
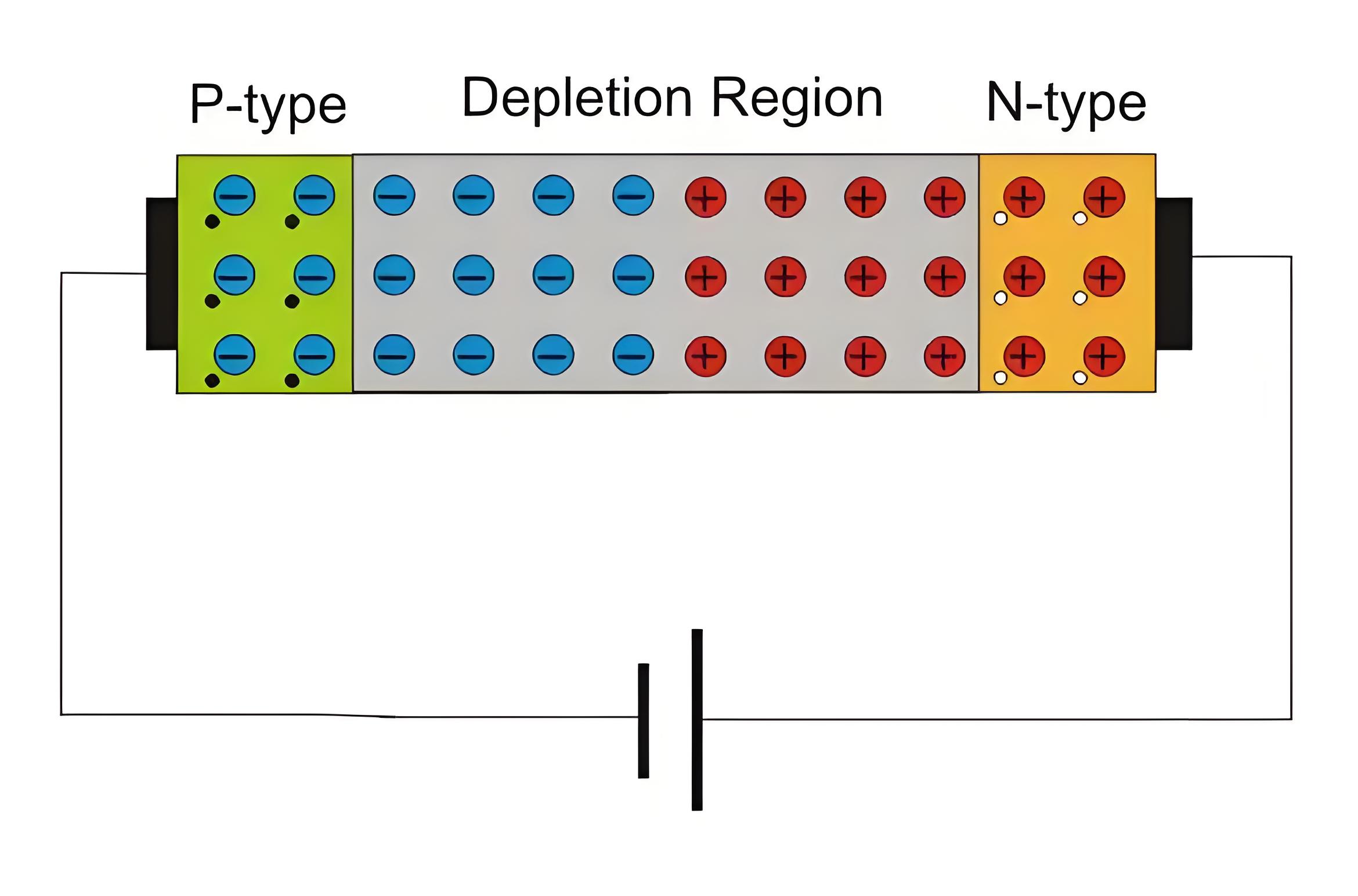
Current Behavior
In forward bias, current flows easily once the depletion layer is reduced. In reverse bias, only a minimal current flows due to minority carriers.
Breakdown Conditions
High reverse voltage can cause breakdowns (Zener or Avalanche), leading to a sharp increase in current, which is crucial in understanding diode operation limits.
V-I Characteristics of A PN Junction
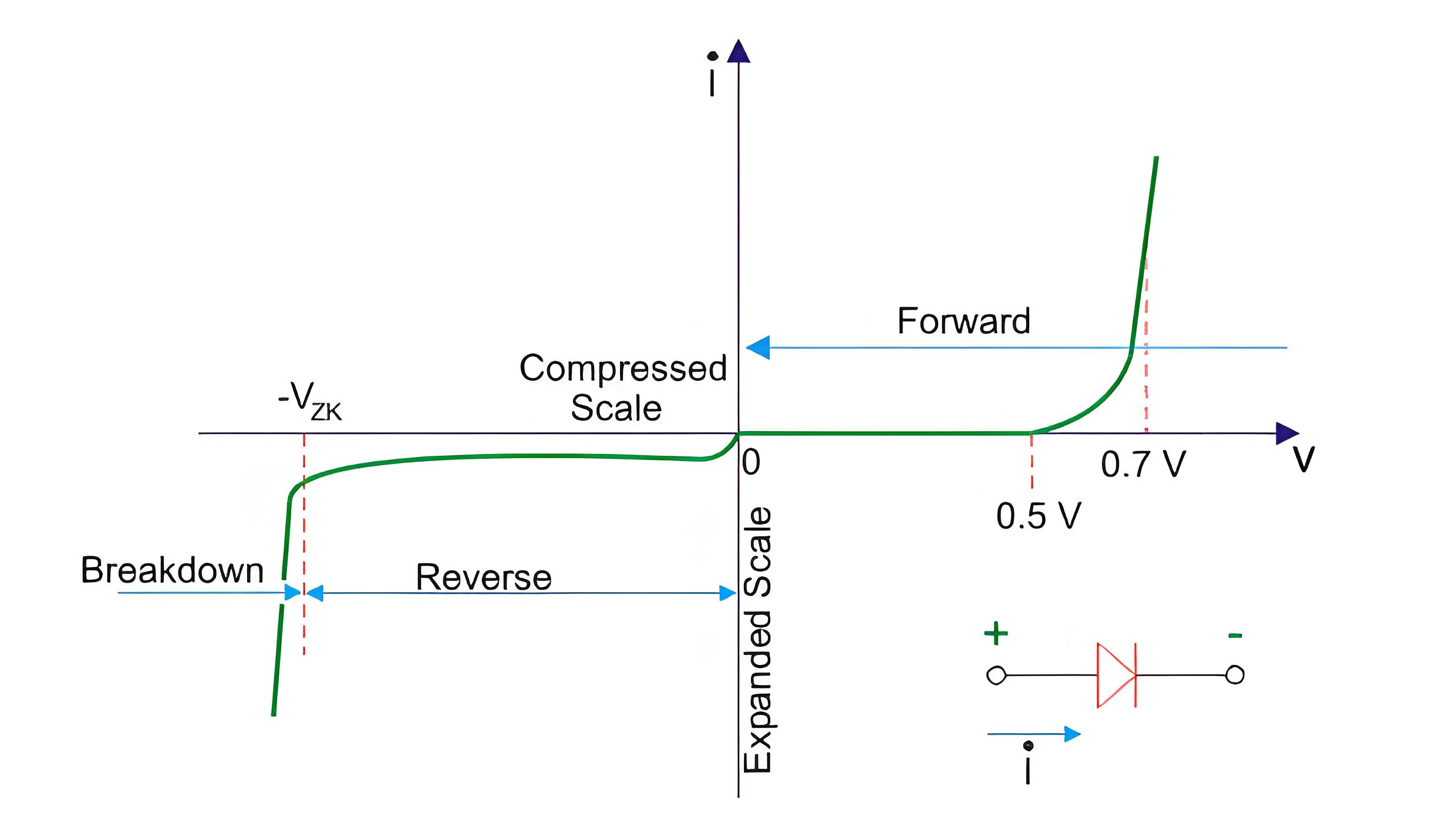
In the forward bias, the operational region is in the first quadrant. The threshold voltage for Germanium is 0.3 V and for Silicon is 0.7 V. Beyond this threshold voltage, the graph goes upward in a non-linear manner. This graph is for the dynamic Resistance of the junction in the forward bias.
In the reverse bias the voltage increases in the reverse direction across the p-n junction, but no current due to the majority carriers, only a minimal leakage current flows. But at a certain reverse voltage p-n junction breaks in conduction.
It is only due to the minority carriers. This amount of voltage is sufficient for these minority carriers to break the depletion region. In this situation, a sharp current will flow through this junction. This breakdown of voltage is of two types.
Avalanche Breakdown: it is not a sharp graph, rather inclined linear graph, i.e. after the break down a small increase in reverse voltage causes more sharp current gradually.
Zener Breakdown: This breakdown is sharp and no need to increase reverse bias voltage to get more current, because current flows sharply.
Resistances of p-n Junction
Dynamic Resistance of p-n Junction
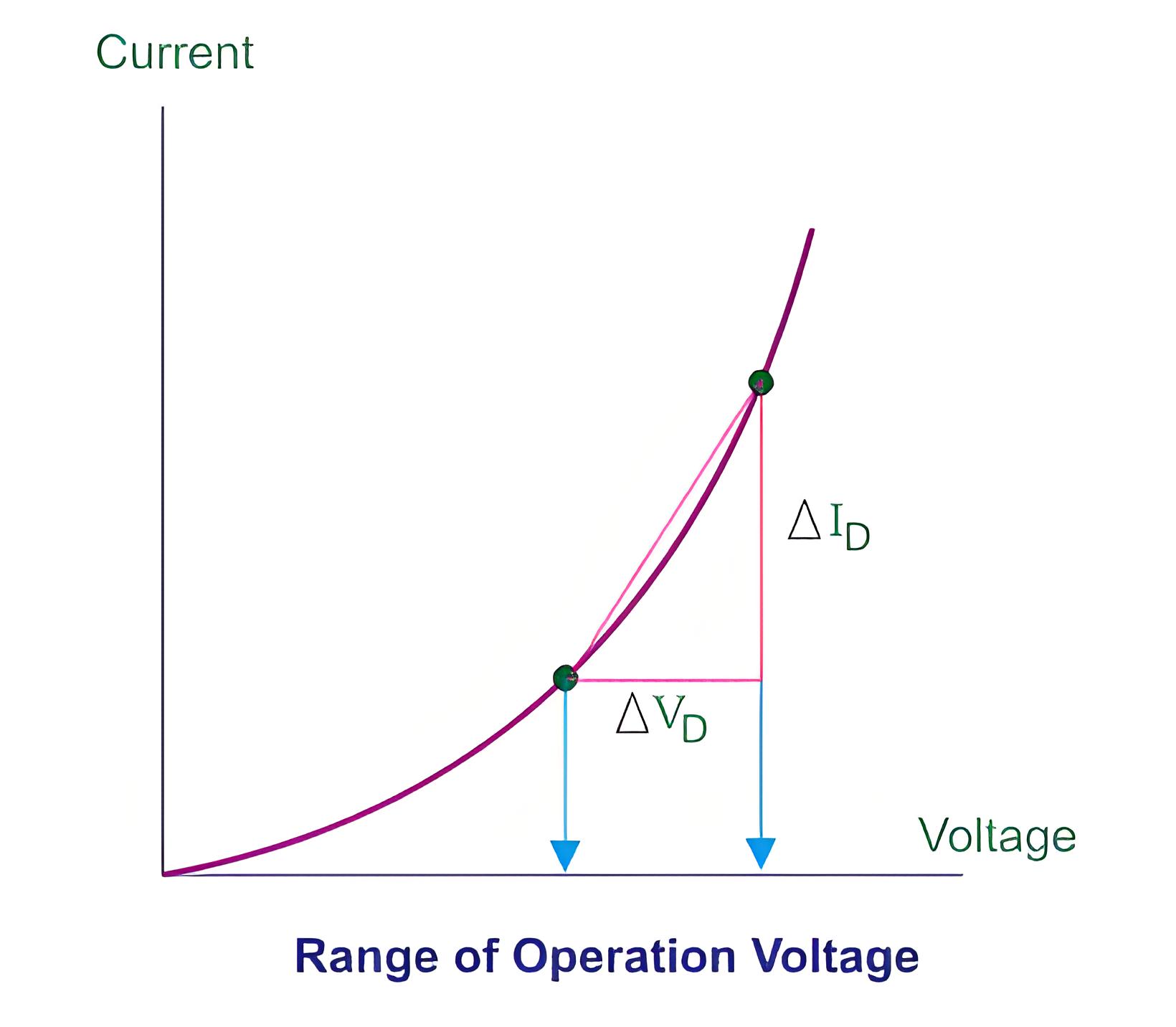
From V-I characteristics of a p-n junction, it is clear that graph is not linear. The forward biased p-n junction resistance is rd ohm; it is called AC resistance or dynamic resistance. It is equivalent to the slope of voltage-current of the PN junction.
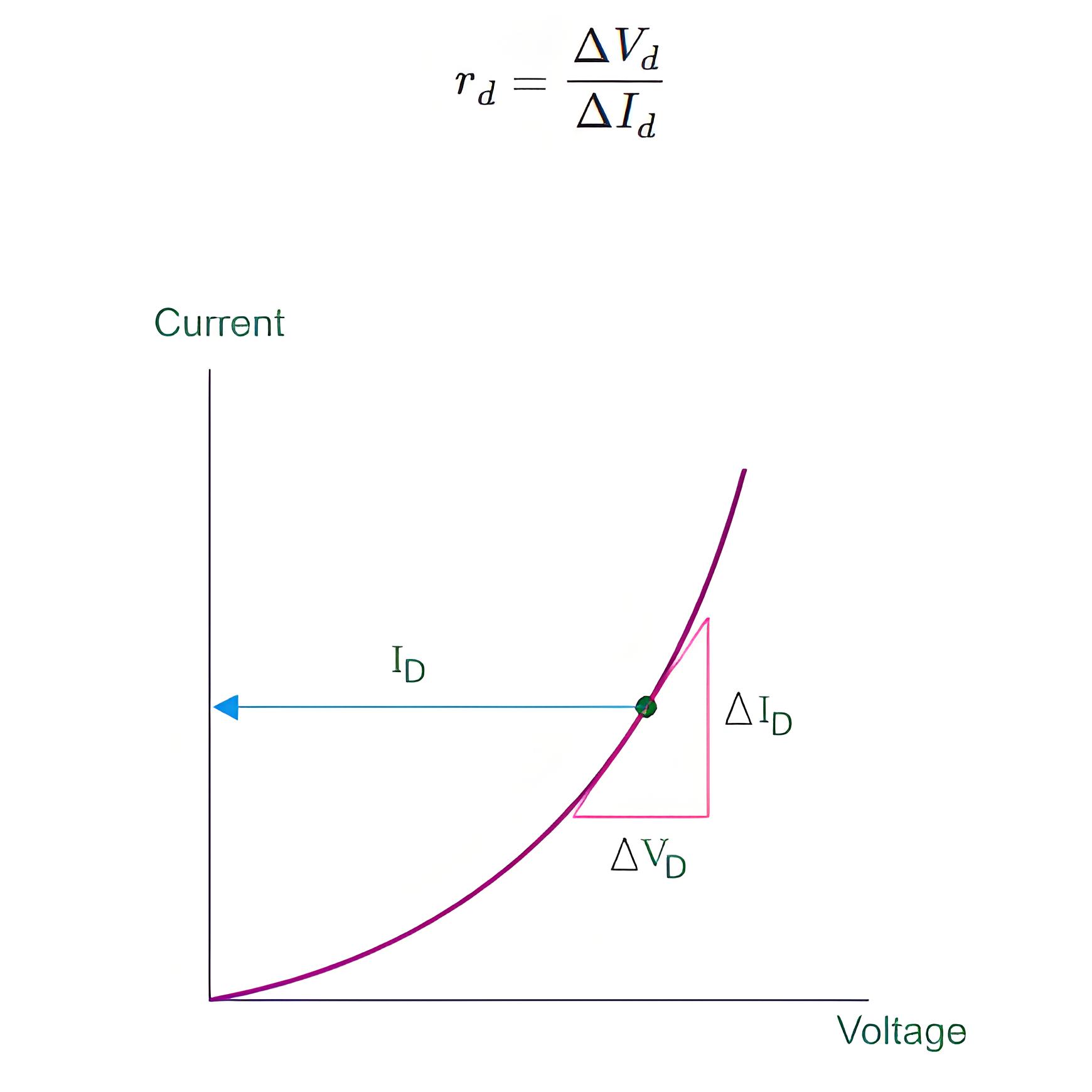
Average AC Resistance of p-n Junction
Average AC resistance is determined by the straight line drawn linking the intersection of the minimum and maximum values of the external input voltage.Some important terms related to p-n Junction
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













