What is a MOS Capacitor?
What is a MOS Capacitor?
MOS Capacitor Defined
MOS stands for Metal Oxide Semiconductor. An MOS capacitor comprises a semiconductor body or substrate, an insulator, and a metal gate. Typically, the gate is made from heavily doped n+ poly-silicon that functions like metal. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) serves as the dielectric material between the capacitor plates, where the metal and semiconductor layers act as the two plates.
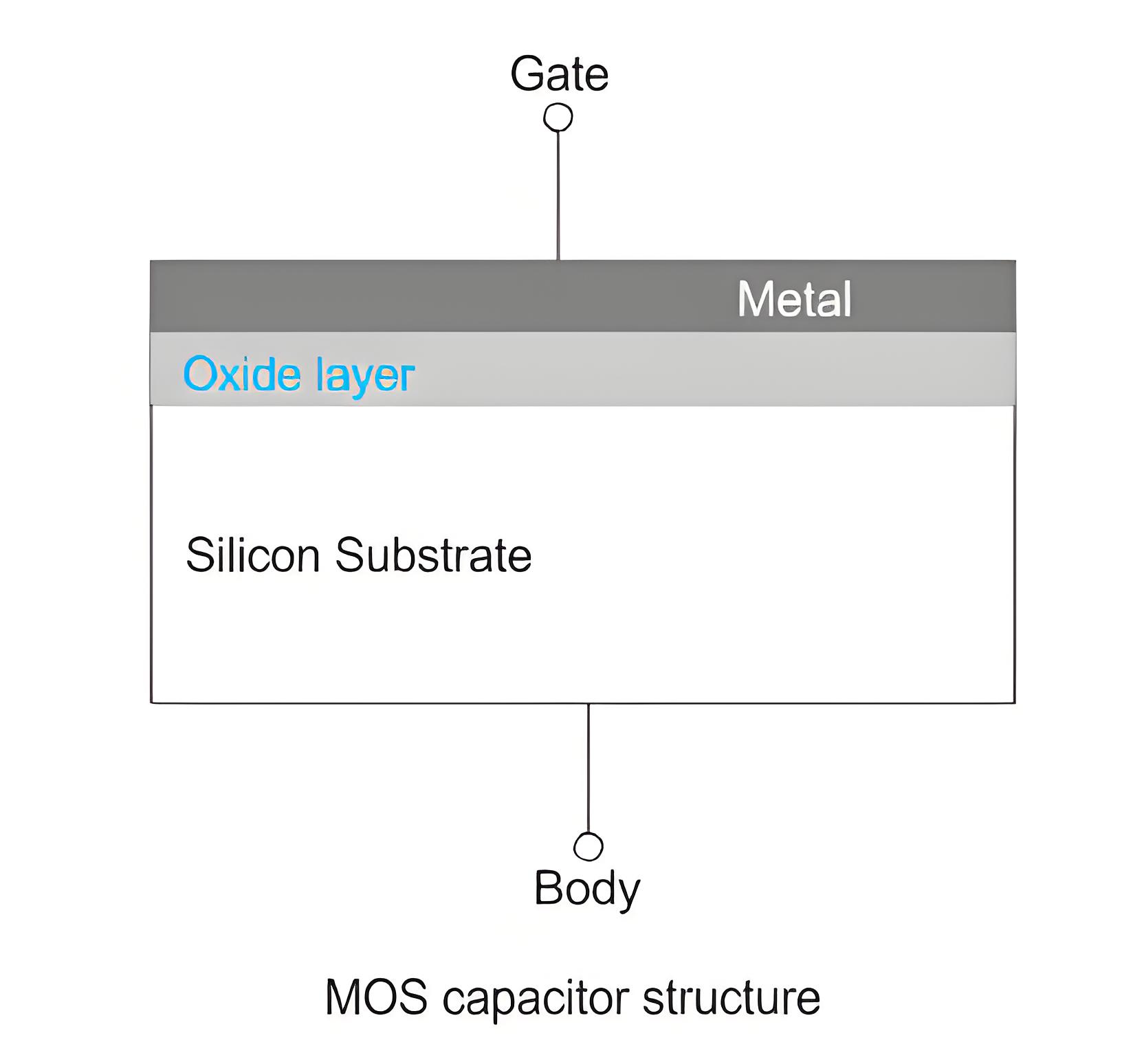
The capacitance of an MOS capacitor varies with the voltage applied to its gate terminal, with the body typically grounded during this application.
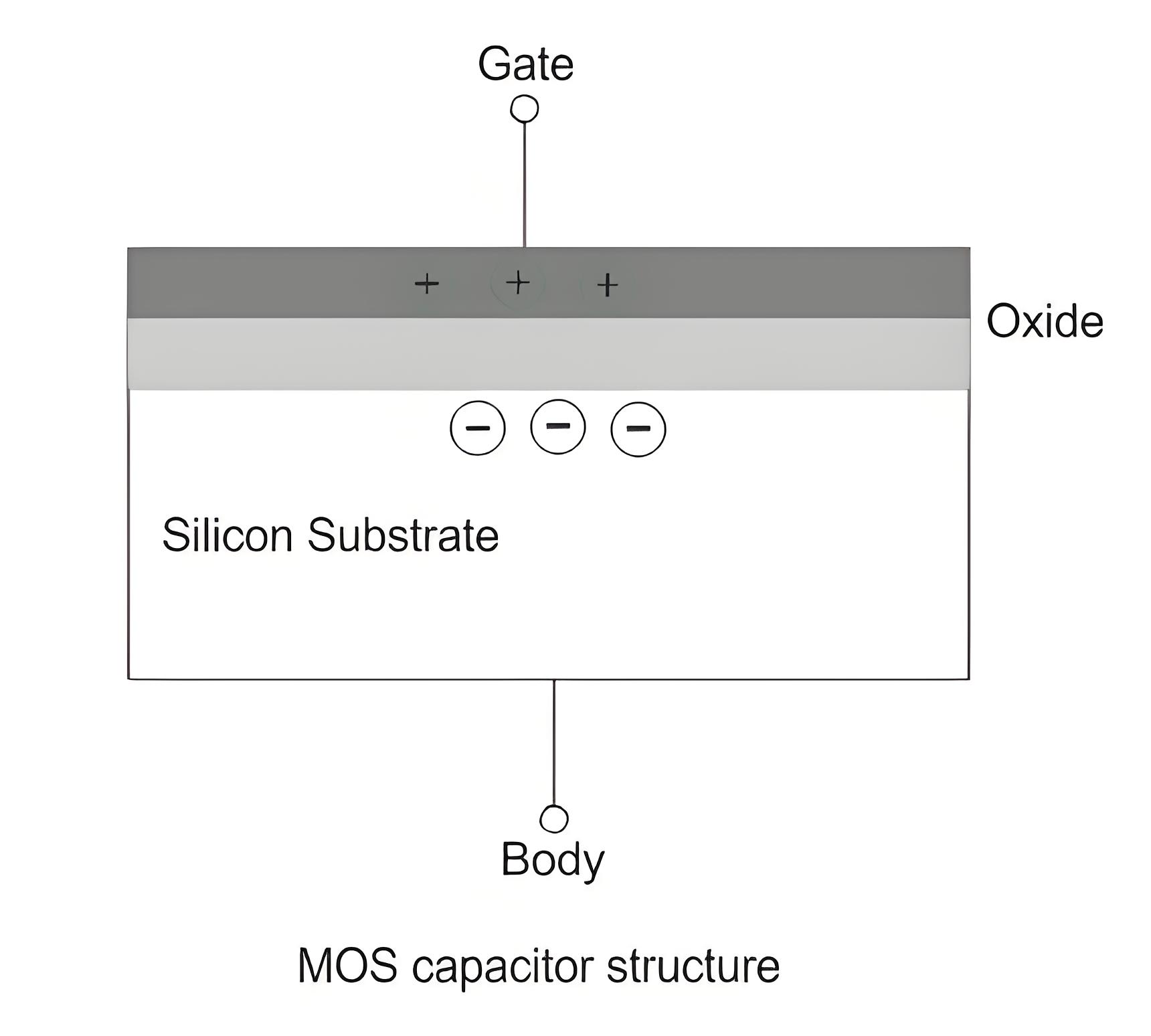
The flat band voltage is an important term related to the MOS capacitor. It is defined as the voltage at which there is no charge on the capacitor plates and hence there is no static electric field across the oxide. An applied positive gate voltage larger than the flat band voltage (Vgb > Vfb) then positive charge is induced on the metal (poly silicon) gate and negative charge in the a title=”Theory of Semiconductor” href=”/theory-of-semiconductor/”>semiconductor. The only negative charged electrons are available as negative charges and they accumulate at the surface. This is known as surface accumulation.
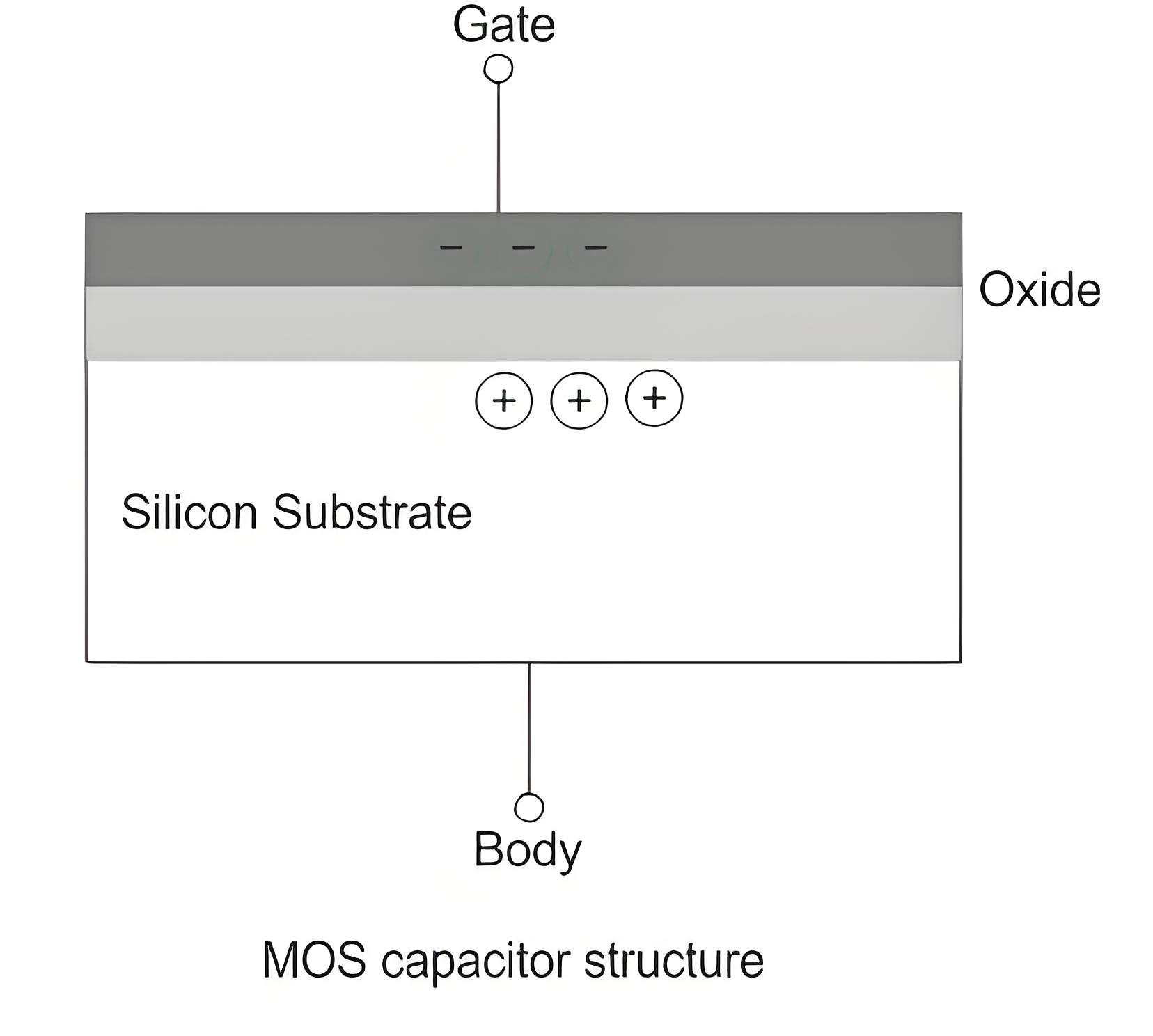
If the applied gate voltage is lower than the flat band voltage (Vgb < Vfb) then a negative charge is induced at the interface between the poly-silicon gate and the oxide and positive charge in the semiconductor.
This is only possible by pushing the negatively charged electrons away from the surface exposing the fixed positive charges from donors. This is known as surface depletion.
While the MOS capacitor is not extensively used alone, it is integral to MOS transistors, which are the most widely used semiconductor devices.
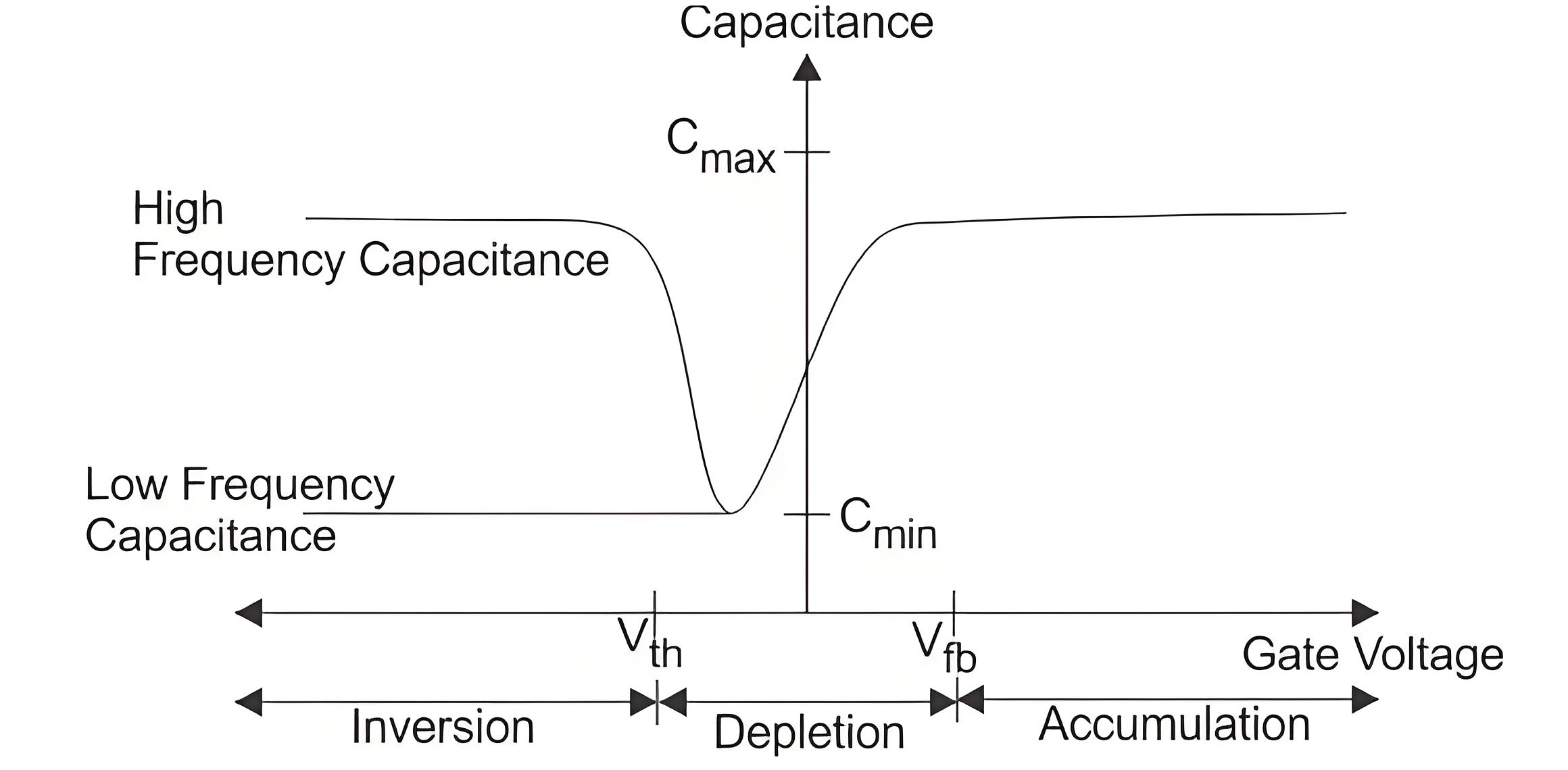
The typical capacitance-voltage characteristics of a MOS capacitor with n-type body is given below,
Capacitance vs. Gate Voltage (CV) diagram of a MOS Capacitor. The flatband voltage (Vc-v curve of mos capacitorfb) separates the Accumulation region from the Depletion region. The threshold voltage (Vth) separates the depletion region from the inversion region.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













