Types and Components of Laser
LASER
The acronym LASER stands for Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. A laser is a device that produces a unique type of light not found naturally. This light is generated through optical amplification, which relies on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. It is different from conventional light in three ways. First, the lights from LASER contains only one color or wavelength that is why it is called ‘monochromatic’. Secondly, all the wavelengths are in phase- because of this, it is known as coherent. And thirdly, laser light beams are very narrow and can be concentrated on one tiny spot- this property makes it be known as ‘collimated’. These are also the characteristics of LASER.
For its operation, population inversion is much needed. When a group of atoms or molecules exist with more no electrons in an excited state than in lower energy states, population inversion takes place. Now, when an electron is in an excited state, it may decay to an empty lower energy state. If an electron decays without external influence, emitting a photon, that is known as spontaneous emission.
Stimulated emission occurs when a photon stimulates an electron, causing it to emit a second photon and return to a lower energy level. This process results in the production of two coherent photons. Now, if a significant population inversion exists, then stimulated emission can produce significant amplification of light. Photons which are produced in stimulated emission produce coherent light as they have definite phase relationship.
The principle of laser was first discovered by Einstein in 1917 but it was not until 1958 that laser was successfully developed.
Lasers have a wide range of applications. They are integral to consumer devices like CD and DVD players, and printers. In medicine, they are used for surgeries and skin treatments, while in industry, they assist in cutting and welding materials. They are used in military and law enforcement devices for marking targets and measuring range. Lasers also have many important applications in scientific research.
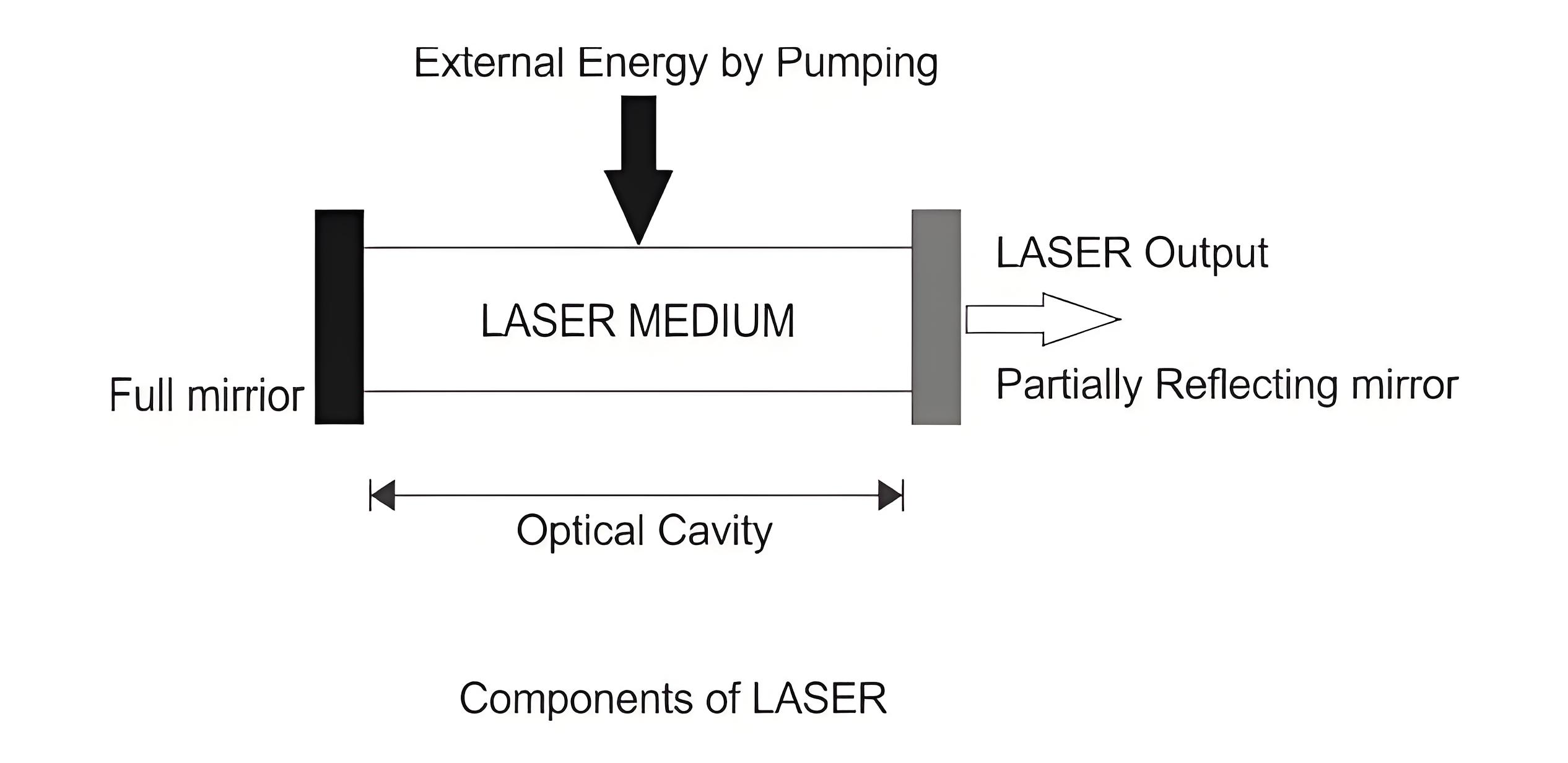
Components of LASER
Lasing material or active medium.
External energy source.
Optical resonator.
Types of LASER
Solid State LASER
Gas LASER
Dye or Liquid LASER
Excimer LASER
Chemical LASER
Semiconductor LASER
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













