What is Gallium Arsenide Semiconductor?
What is Gallium Arsenide Semiconductor?
GaAs Semiconductor Definition
A GaAs semiconductor is defined as a compound of gallium and arsenic from the III-V group, used in various electronic and optoelectronic devices.
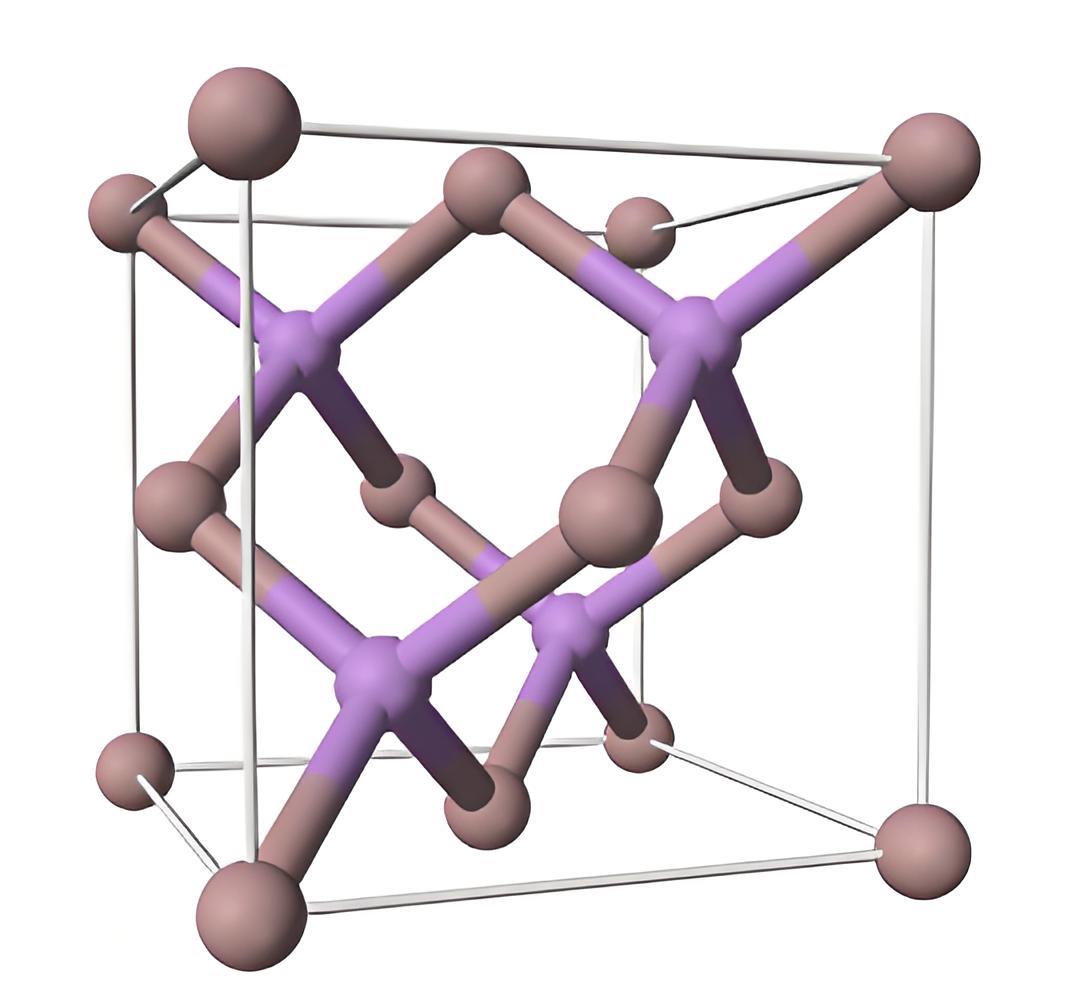
Direct Band Gap
GaAs has a direct band gap of 1.424 eV at 300 K, enabling it to emit light, essential for LEDs, laser diodes, and solar cells.
Preparation of GaAs semiconductor
There are several methods for producing GaAs semiconductors, depending on the desired purity, quality, and application of the material.
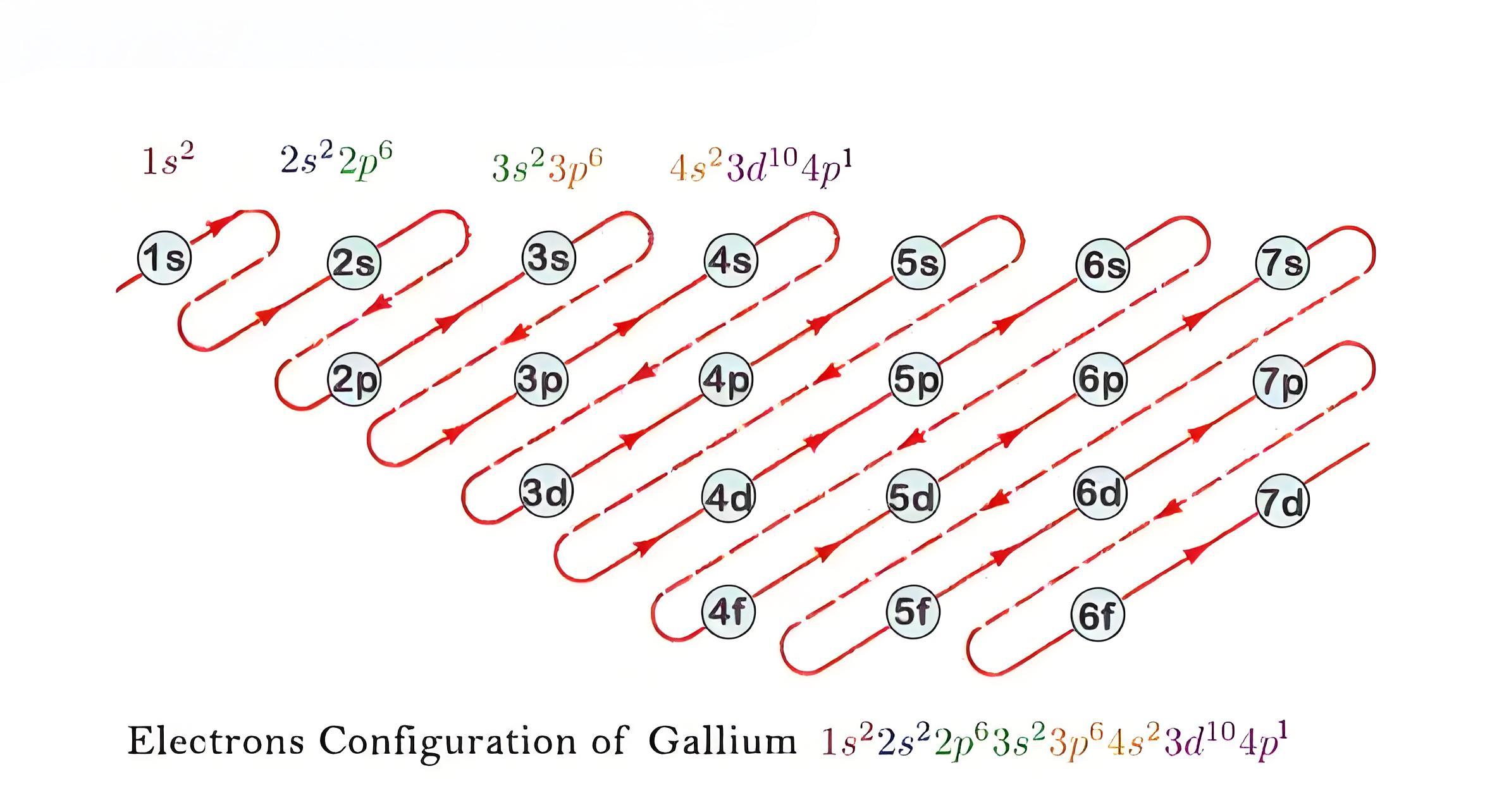
Some of the common methods are:
The vertical gradient freeze (VGF) process
The Bridgman-Stockbarger technique
The liquid encapsulated Czochralski (LEC) growth
The vapour phase epitaxy (VPE) process
The metalorganic chemical vapour deposition (MOCVD) process
The molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) process
Properties of a GaAs Semiconductor
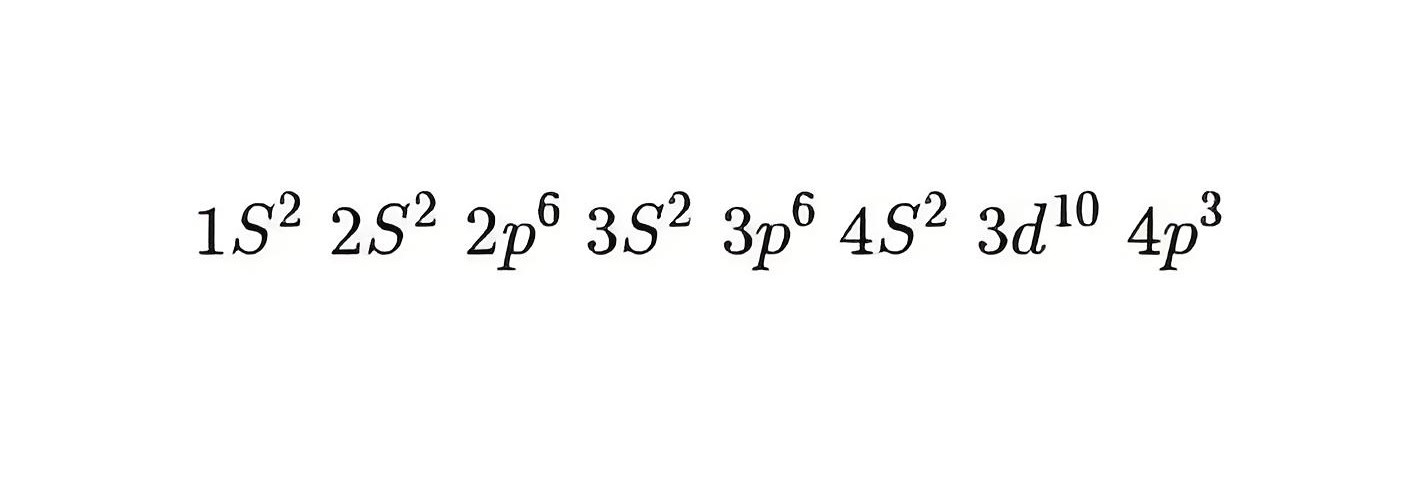
High electron mobility
Low reverse saturation current
Excellent temperature sensitivity
High breakdown voltage
Direct band gap
Advantages of GaAs Semiconductor
GaAs devices offer high speed, low noise, high efficiency, and excellent temperature stability, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Applications
Microwave frequency integrated circuits (MFICs)
Monolithic microwave integrated circuits (MMICs)
Infrared light-emitting diodes (LEDs)
Laser diodes
Solar cells
Optical windows
Conclusion
GaAs semiconductor is a compound of gallium and arsenic that has many desirable properties such as high electron mobility, low reverse saturation current, excellent temperature sensitivity, high breakdown voltage, and direct band gap. These properties enable GaAs to be used for various electronic and optoelectronic devices such as MFICs, MMICs, LEDs, laser diodes, solar cells, and optical windows. These devices have various applications and advantages in different fields, such as communication systems, radar systems, satellite systems, wireless systems, remote controls, optical sensors, optical storage systems, medical applications, space applications, and thermal imaging systems.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













