What are Energy Bands of Silicon ?
What are Energy Bands of Silicon ?
Silicon Definition
Silicon is defined as a semiconductor with properties between those of a conductor and an insulator, crucial for electronics.
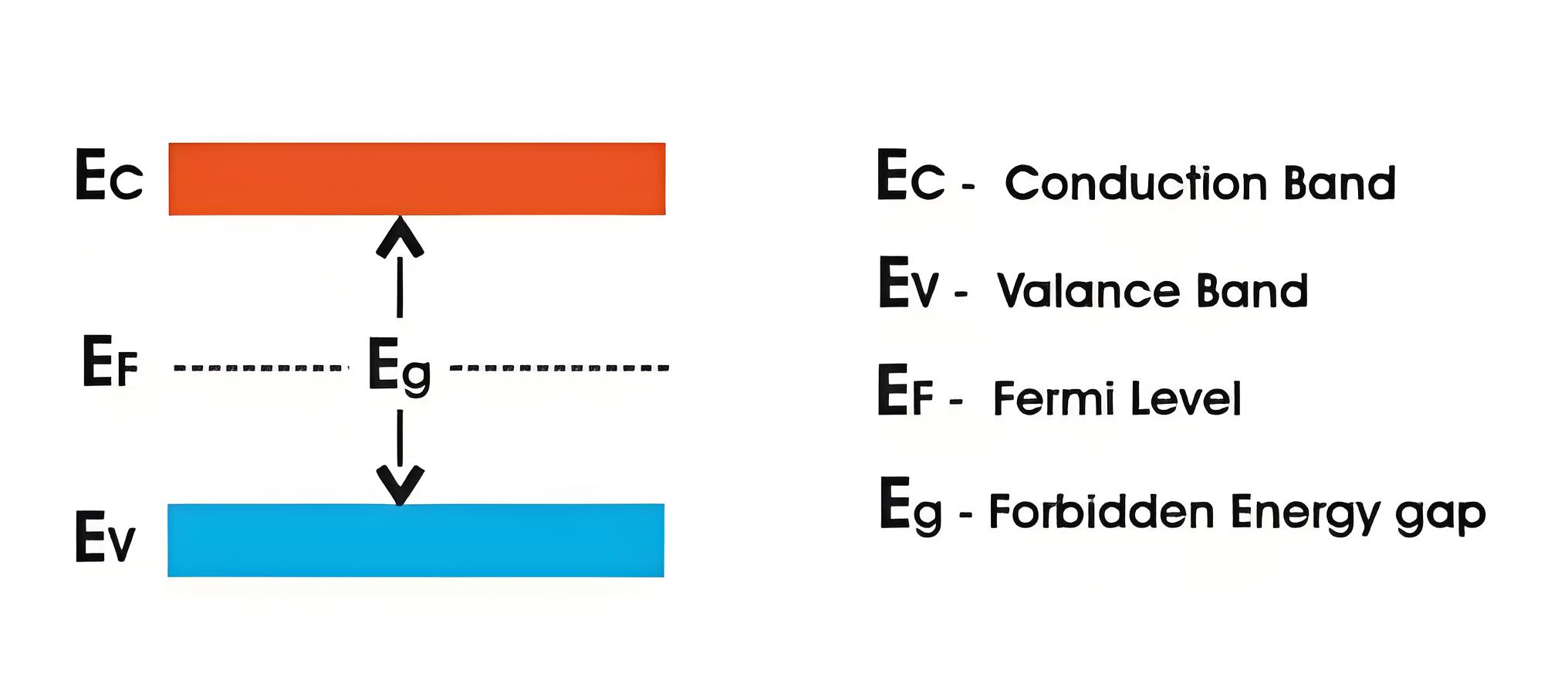
Silicon is defined as a semiconductor with fewer free electrons than a conductor but more than an insulator. This unique characteristic makes silicon widely used in electronics. Silicon has two types of energy bands: the conduction band and the valence band. The valence band is formed by energy levels with valence electrons. At absolute 0oK temperature, the valence band is filled with electrons, and no current flows.
The conduction band is the higher energy level band where free electrons, which can move throughout the solid, are found. These free electrons are responsible for current flow. The energy gap between the conduction band and the valence band is called the forbidden energy gap. This gap determines if a material is a metal, insulator, or semiconductor.
The size of the forbidden energy gap determines if a solid is a metal, insulator, or semiconductor. Metals have no gap, insulators have a large gap, and semiconductors have a moderate gap. Silicon has a forbidden gap of 1.2 eV at 300 K.
In a silicon crystal, covalent bonds hold the atoms together, making silicon electrically neutral. When an electron breaks away from its covalent bond, it leaves a hole. As temperature increases, more electrons jump into the conduction band, creating more holes in the valence band.
Energy Band Diagram of Silicon
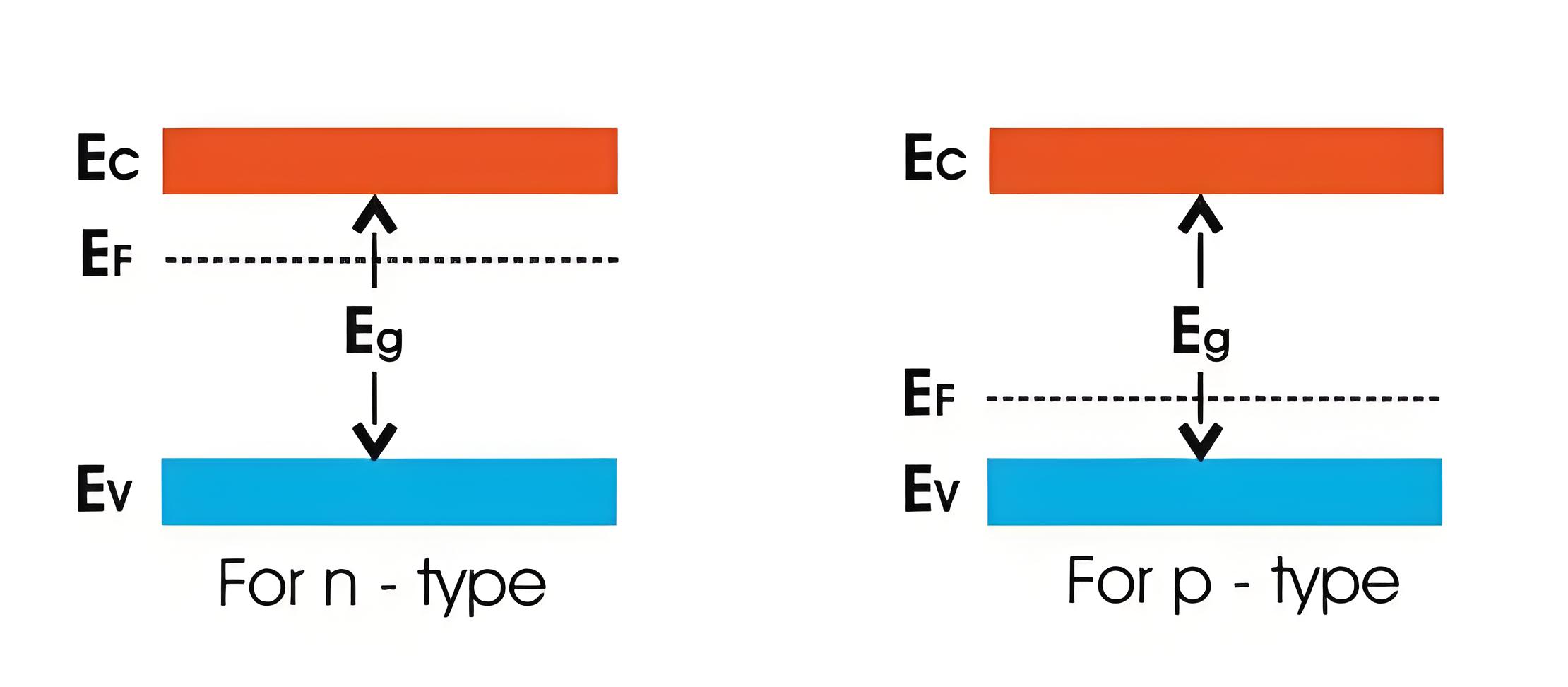
The energy band diagram of silicon shows the energy levels of electrons. In intrinsic silicon, the Fermi level is in the middle of the energy gap. Doping intrinsic silicon with donor atoms makes it n-type, moving the Fermi level closer to the conduction band. Doping with acceptor atoms makes it p-type, moving the Fermi level closer to the valence band.
Energy Bands Diagram of Intrinsic Silicon
Energy Bands Diagram of Extrinsic Silicon
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













