What is Diode Test ?
What is Diode Test ?
Diode Definition
A diode is defined as a semiconductor device that allows electric current to flow in one direction only.
Diode Test Mode
This mode on digital multimeters applies a small voltage to a diode and measures the voltage drop, indicating the diode’s condition.
To test a diode with diode test mode
Turn off the power source of the circuit that contains the diode. If possible, remove the diode from the circuit for more accurate results.
Set the multimeter to diode test mode by rotating the dial or pressing the button.
Connect the positive (red) lead of the multimeter to the anode of the diode, and the negative (black) lead to the cathode. The diode is now forward-biased.
Read the voltage drop on the multimeter display. A good silicon diode should have a voltage drop between 0.5 V and 0.8 V. A good germanium diode should have a voltage drop between 0.2 V and 0.3 V.
Reverse the leads of the multimeter, so that the positive lead is on the cathode and the negative lead is on the anode. The diode is now reverse-biased.
Read the voltage drop on the multimeter display again. A good diode should show OL (overload), which means infinite resistance or no current flow.
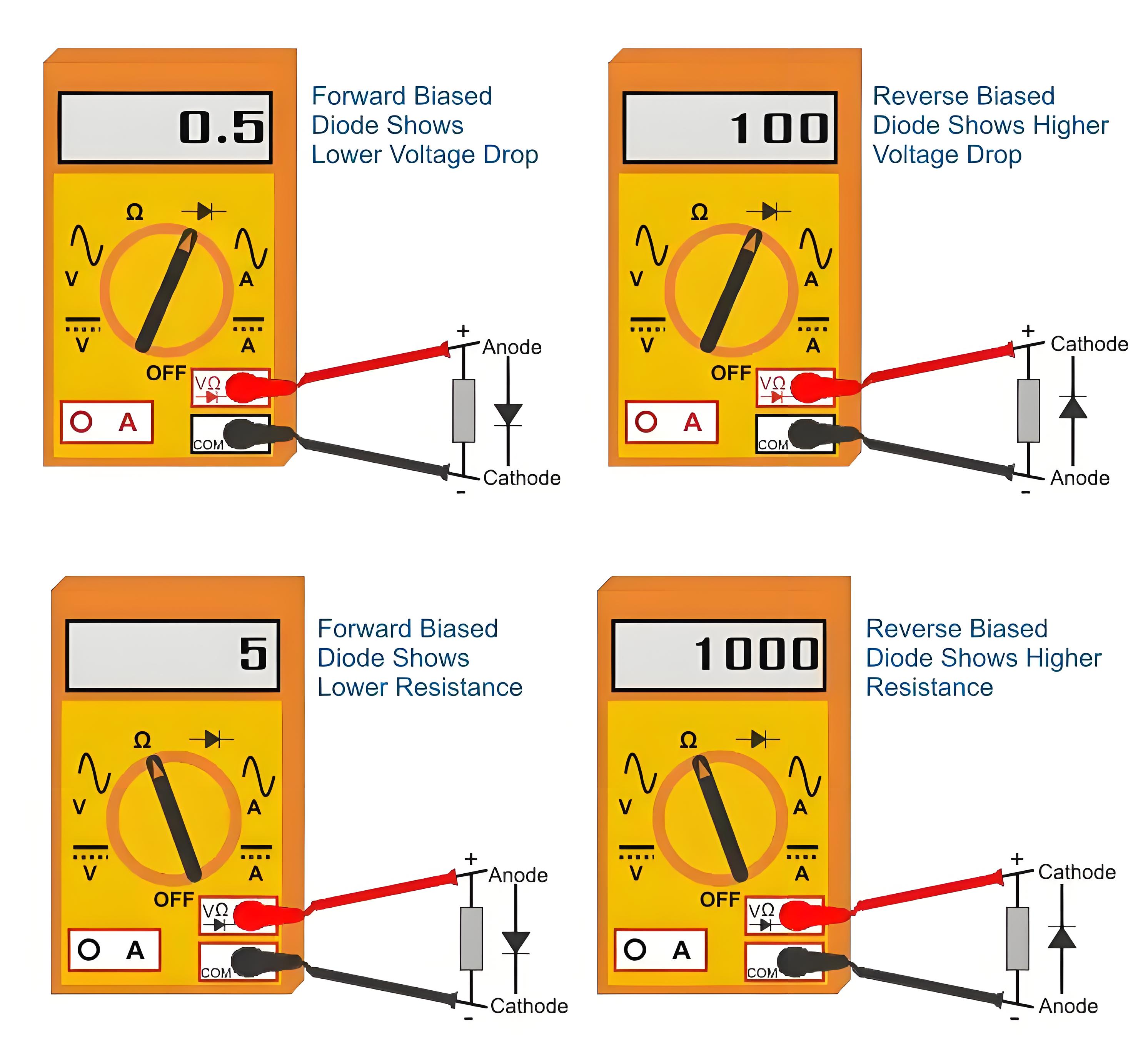
If the readings are different from what is expected, then the diode may be faulty or damaged. A low voltage drop in both directions means the diode is shorted (low resistance). A high voltage drop or OL in both directions means the diode is open (high resistance).
Test a Diode with an Analog Multimeter
Turn off the power source of the circuit that contains the diode. If possible, remove the diode from the circuit for more accurate results.
Set the selector switch of the analog multimeter to its resistance mode. Choose a low range (such as 1 kΩ) for better sensitivity.
Connect the negative (black) lead of the multimeter to the anode of the diode, and the positive (red) lead to the cathode. The diode is now forward-biased.
Read the needle position on the scale of the multimeter. A good diode should have a low resistance value, which means a high needle deflection towards the right side of the scale.
Reverse the leads of the multimeter, so that the negative lead is on the cathode and the positive lead is on the anode. The diode is now reverse-biased.
Read the needle position on the scale of the multimeter again. A good diode should have a high resistance value, which means a low needle deflection towards the left side of the scale.
If the readings are different from what is expected, then the diode may be faulty or damaged. A high needle deflection in both directions means the diode is shorted (low resistance). A low needle deflection in both directions means the diode is open (high resistance).
Conclusion
Testing a diode is a simple and useful way to check its functionality and quality. It can be done with either an analog or a digital multimeter, using different modes and methods. The main principle is to measure the resistance or voltage drop across the diode when it is forward-biased and reverse-biased, and compare it with the expected values for a good diode. A good diode should have low resistance in forward bias and high resistance in reverse bias. A faulty or damaged diode may have low or high resistance in both directions or no resistance at all.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













