What is Diode Current Equation?
What is Diode Current Equation?
Diode Current Equation Definition
The diode current equation expresses the relationship between the current flowing through the diode as a function of the voltage applied across it. Mathematically the diode current equation can be expressed as:
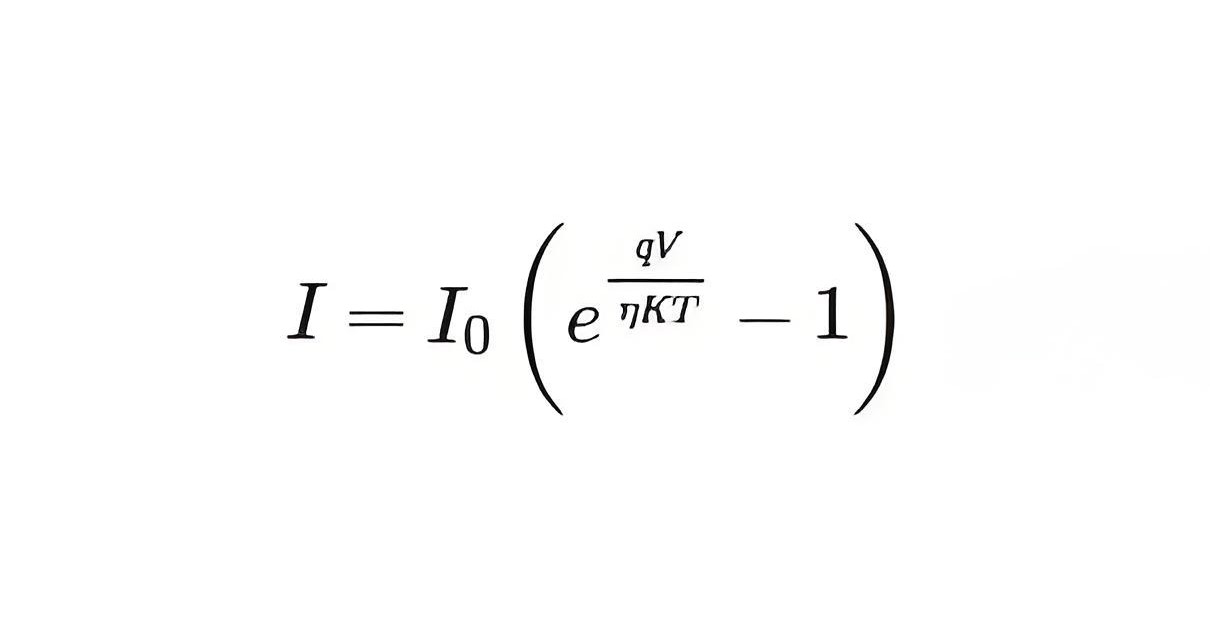
I is the current flowing through the diode
I0 is the dark saturation current,
q is the charge on the electron,
V is the voltage applied across the diode,
η is the (exponential) ideality factor.
is the Boltzmann constant
T is the absolute temperature in Kelvin.
Key Components
The equation includes the dark saturation current and the ideality factor, which are critical for understanding diode behavior.
Forward vs. Reverse Bias
In forward bias, the diode conducts a large current, while in reverse bias, current flow is minimal due to the negligible exponential term.
Temperature Impact
At standard room temperature, the diode’s behavior is influenced by the thermal voltage, which is around 25.87 mV.
Understanding how to derive and apply this equation is essential for effectively using diodes in electronic circuits.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













