Current Density in Metal and Semiconductor
Current Density Definition
Current density is defined as the electric current per unit area of a conductor’s cross-section, denoted by J.
Formula for Current Density
The current density in a metal is calculated using J = I/A, where I is the current and A is the cross-sectional area.
Semiconductor Current Flow
In semiconductors, current density is due to both electrons and holes, which move in opposite directions but contribute to the same direction of current.
Current Density in Metal
Imagine a conductor with a cross-section of 2.5 square mm. If an electric potential causes a current of 3 A, the current density is 1.2 A/mm² (3/2.5). This assumes the current is uniformly distributed. Thus, current density is defined as the electric current per unit cross-sectional area of the conductor.
Current density, denoted by J, is given by J = I/A, where ‘I’ is the current and ‘A’ is the cross-sectional area. If N electrons pass through a cross-section in time T, then the charge transferred is Ne, where e is the charge of an electron in coulombs.
Now the amount of charge passing the cross-section per unit time is
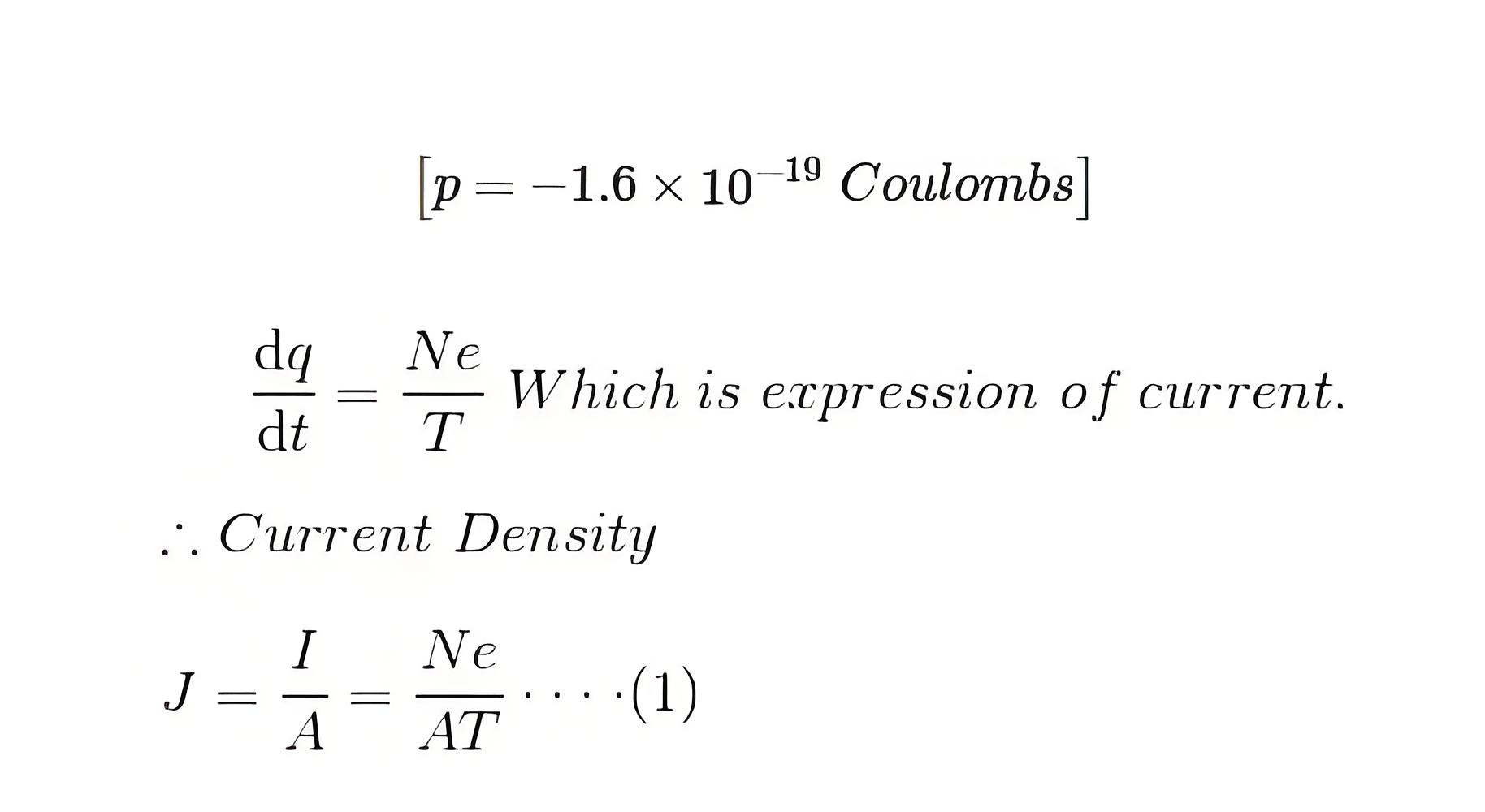
Again if N number of electrons lie in the L length of the conductor, then the electron concentration is
Now, from equation (1) we can write,
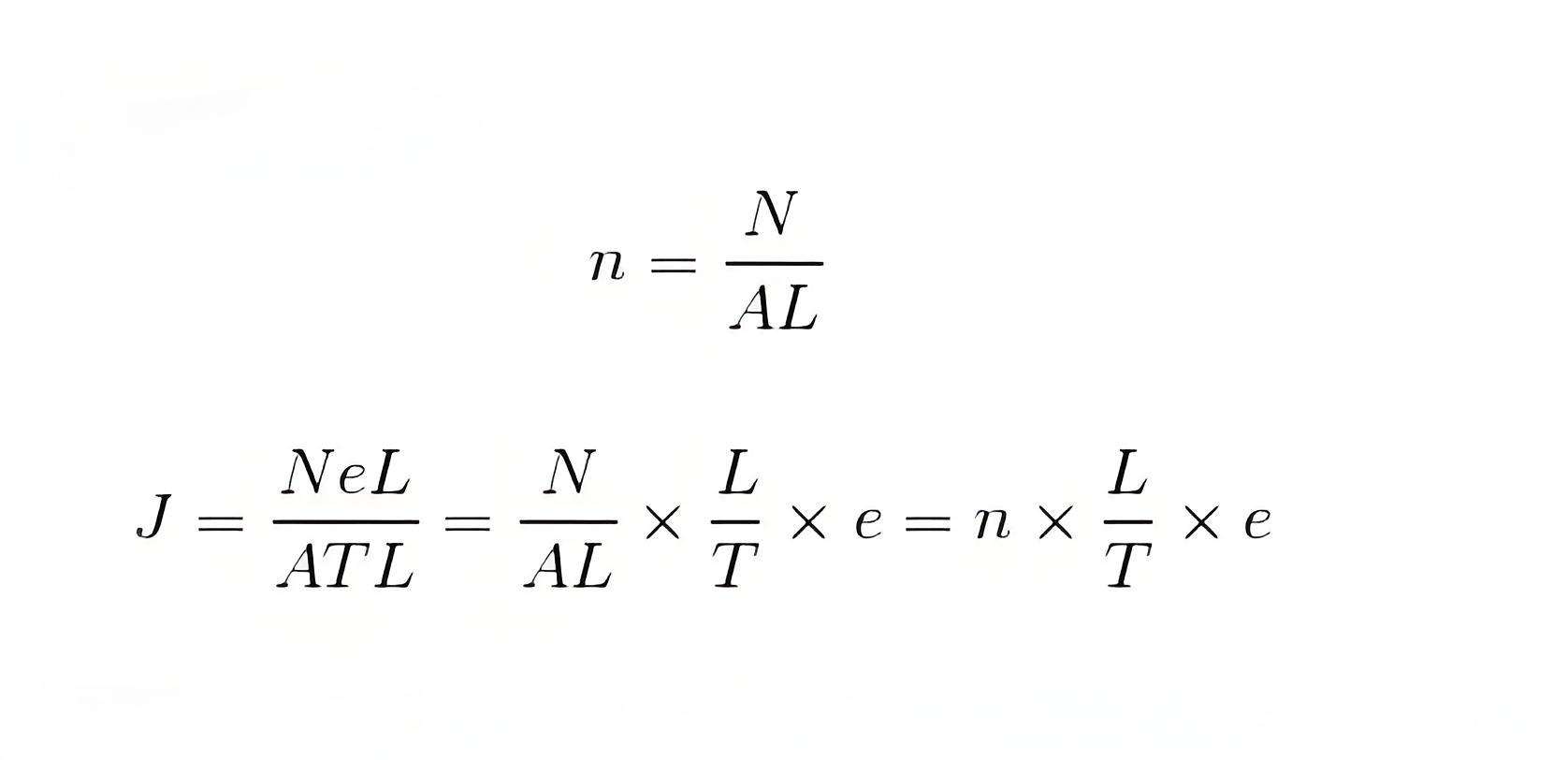
Since, N number of electrons lie in the length L and they all pass the cross-section in time T, the drift velocity of the electrons will be,
Hence, equation (2) can also be rewritten as
Now if applied electric field to the conductor is E, then drift velocity of the electrons increases proportionally,
Where, μ is defined as the mobility of electrons
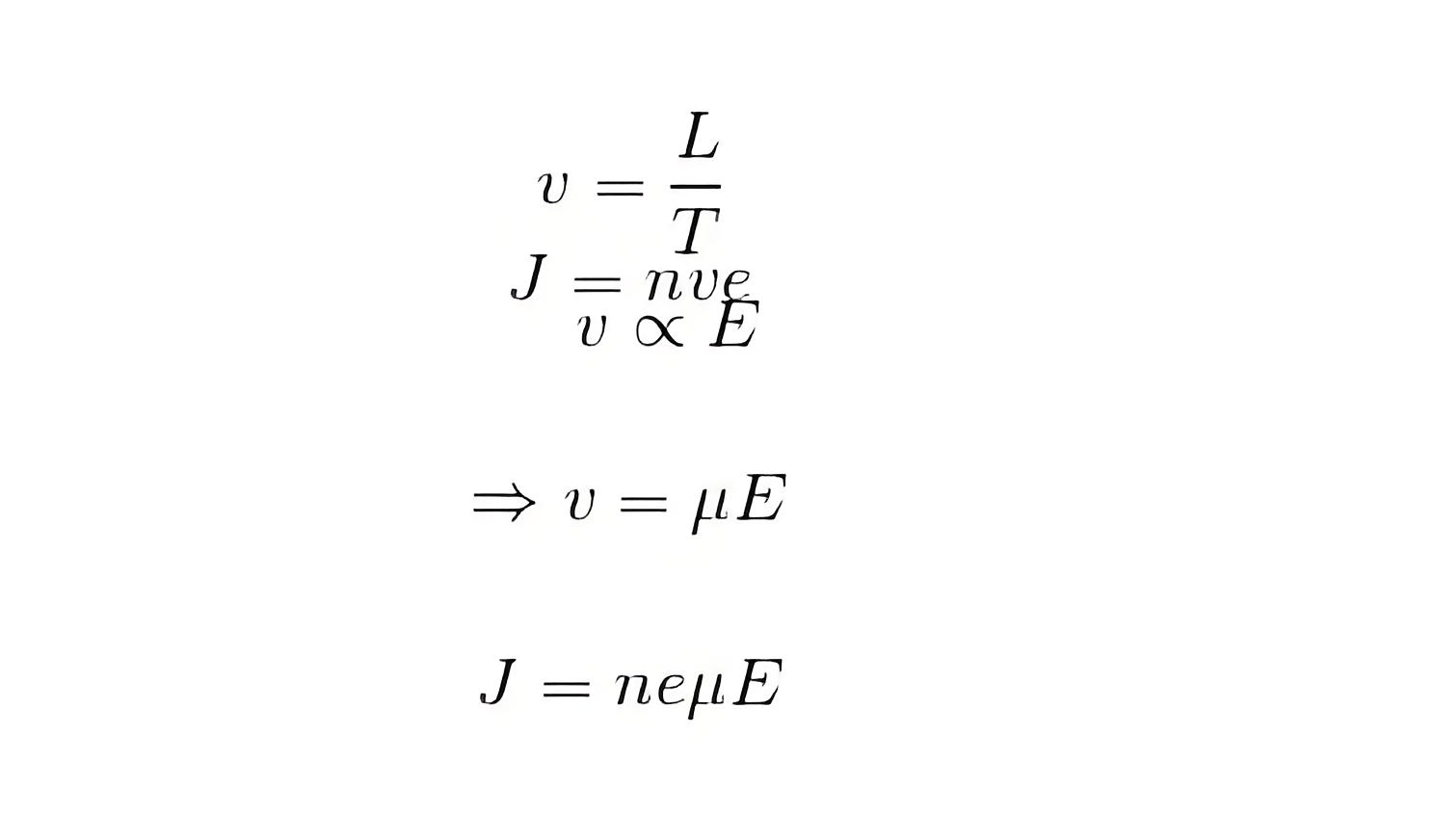
Current Density in Semiconductor
The total current density in a semiconductor is the sum of the current densities due to electrons and holes, each having different mobilities.
Relation to Conductivity
Current density (J) is related to conductivity (σ) through the formula J = σE, where E is the electric field intensity.
The Electricity Encyclopedia is dedicated to accelerating the dissemination and application of electricity knowledge and adding impetus to the development and innovation of the electricity industry.













